接口变量.(type) 是 Go 语言中类型断言的一种特殊形式,它只能在 switch 语句中使用。这种语法主要用于对接口变量的底层实际类型进行多分支检测,从而在一次操作中实现多种类型的匹配逻辑。它是处理接口类型多态场景的核心语法,能够让代码更加清晰和优雅。
语法
其基本语法结构如下:
switch v := 接口变量.(type) {
case 类型1:
// 在这里 v 的类型是 类型1
// 可以安全地调用 类型1 特有的方法或访问其字段
case 类型2:
// 在这里 v 的类型是 类型2
default:
// 如果以上所有类型都不匹配,则进入此分支
}
这个特性是 Go语言 在处理不确定类型时提供的一种强大且安全的机制。
用法示例
下面通过一个简单的动物世界例子来展示其基本用法:
package main
import "fmt"
// 定义接口
type Animal interface {
Speak() string
}
// 定义结构体
type Dog struct{}
func (d Dog) Speak() string { return "汪汪" }
type Cat struct{}
func (c Cat) Speak() string { return "喵喵" }
type Bird struct{}
func (b Bird) Speak() string { return "叽叽" }
func main() {
var animal Animal
// 示例1:Dog
animal = Dog{}
describe(animal)
// 示例2:Cat
animal = Cat{}
describe(animal)
// 示例3:Bird
animal = Bird{}
describe(animal)
// 示例4:nil
animal = nil
describe(animal)
}
func describe(a Animal) {
switch v := a.(type) {
case Dog:
fmt.Printf("这是一只狗: %s\n", v.Speak())
case Cat:
fmt.Printf("这是一只猫: %s\n", v.Speak())
case Bird:
fmt.Printf("这是一只鸟: %s\n", v.Speak())
case nil:
fmt.Println("动物是nil")
default:
fmt.Printf("未知动物类型: %T\n", v)
}
}
// 输出
// 这是一只狗: 汪汪
// 这是一只猫: 喵喵
// 这是一只鸟: 叽叽
// 动物是 nil
实用技巧
1. 同时判断多种类型
在一个 case 中,你可以用逗号分隔多种类型,它们会被同等处理。
func process(value interface{}) {
switch v := value.(type) {
case int, int32, int64:
// 所有整数类型进入此分支
fmt.Printf("整数: %v\n", v)
case string:
fmt.Printf("字符串: %s\n", v)
case bool:
fmt.Printf("布尔值: %v\n", v)
default:
fmt.Printf("其他类型: %T\n", v)
}
}
2. 获取底层类型信息与行为
switch type 不仅能判断具体类型,还能判断是否实现了某个接口,从而调用特定方法。
func getTypeInfo(db interface{}) {
switch v := db.(type) {
case interface{ DriverName() string }:
// 如果底层值有 DriverName 方法
fmt.Printf("驱动名称: %s\n", v.DriverName())
case fmt.Stringer:
// 如果实现了 String() 方法
fmt.Printf("字符串表示: %s\n", v.String())
default:
fmt.Printf("类型: %T, 值: %v\n", v, v)
}
}
这在处理如数据库连接等未知结构的 接口 时非常有用。
常见错误与避坑指南
1. 在 switch 外部使用 .type
这是最常见的语法错误。.type 是 switch 语句的专属语法糖,不能单独使用。
// 错误:编译报错,只能在 switch 中使用
// typeName := db.(type)
// 正确:使用普通的类型断言
if concreteDB, ok := db.(*sql.DB); ok {
// 处理 concreteDB
}
2. 忘记处理 nil 接口值
如果接口变量本身是 nil,那么 switch v := a.(type) 中的 v 也会是 nil,且不会匹配任何具体的类型 case(如 case *sql.DB)。一个好的实践是总是添加一个 case nil 来处理这种情况,防止后续逻辑出现意外。
func riskyCheck(db interface{}) {
switch v := db.(type) {
case nil:
fmt.Println("传入的接口为 nil")
case *sql.DB:
// 现在可以安全地假设 v 不是 nil 的 *sql.DB
// 但仍需注意 v 可能指向一个零值的 *sql.DB
if v != nil {
v.Query("SELECT 1")
}
}
}
与普通类型断言的比较
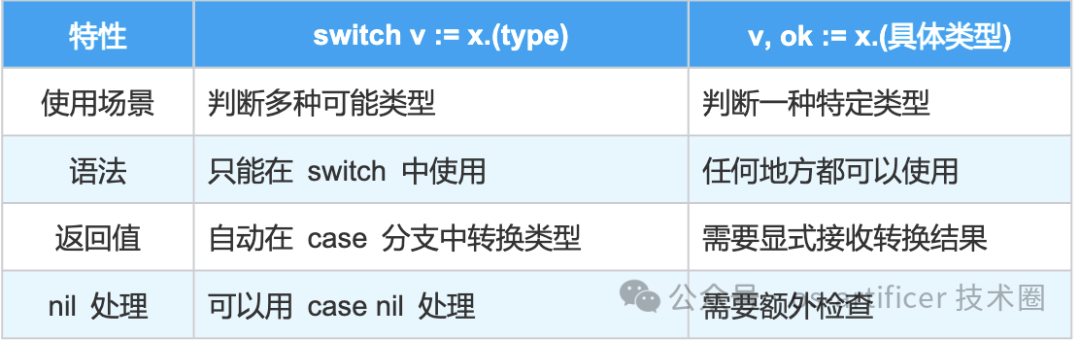
普通类型断言 value, ok := interfaceVar.(ConcreteType) 适合单次或少数几次的类型判断。而当需要判断的类型可能性很多时,一连串的 if-else 语句会让代码变得冗长且难以阅读。此时,switch type 结构提供了更清晰、更紧凑的语法,是更优的选择。
一个完整的实际应用示例:JSON 解析器
switch type 在解析未知结构的 JSON 数据时大放异彩。以下是一个递归打印 JSON 任意结构的示例:
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
)
func printValue(v interface{}) {
switch val := v.(type) {
case nil:
fmt.Println("nil")
case bool:
fmt.Printf("bool: %v\n", val)
case int:
fmt.Printf("int: %d\n", val)
case float64: // JSON 数字默认被解析为 float64
fmt.Printf("float64: %f\n", val)
case string:
fmt.Printf("string: %q\n", val)
case []interface{}:
fmt.Println("array:")
for i, item := range val {
fmt.Printf(" [%d]: ", i)
printValue(item)
}
case map[string]interface{}:
fmt.Println("object:")
for k, item := range val {
fmt.Printf(" %s: ", k)
printValue(item)
}
default:
fmt.Printf("unknown type: %T\n", val)
}
}
func main() {
jsonStr := `{
"name": "张三",
"age": 25,
"scores": [95.5, 88, 92],
"active": true,
"metadata": {"id": 1}
}`
var data interface{}
json.Unmarshal([]byte(jsonStr), &data)
printValue(data)
}
// 输出
// object:
// name: string: "张三"
// age: float64: 25.000000
// scores: array:
// [0]: float64: 95.500000
// [1]: float64: 88.000000
// [2]: float64: 92.000000
// active: bool: true
// metadata: object:
// id: float64: 1.000000
这个例子完美展示了如何利用 switch type 优雅地处理动态的、嵌套的数据结构,这是构建通用 JSON 工具或配置解析器的常见模式。
总结
- 语法限制:
variable.(type) 只能用在 switch 语句中,这是 Go 语法的明确规定。
- 类型安全:在每个
case 分支中,变量会自动且安全地转换为对应类型,无需再次断言。
- 可读性高:相比多个
if-else 的普通类型断言,switch type 结构在多类型判断时逻辑更清晰,代码更整洁。
- nil 处理:务必记得添加
case nil 分支来处理接口值为 nil 的情况,提高代码健壮性。
- 兜底处理:使用
default 分支来处理未预见到的类型,防止逻辑遗漏。
switch type 断言是 Go 语言中处理接口类型多态判断的最优雅和高效的方式之一。它特别适合处理需要根据多种可能的底层类型执行不同逻辑的场景,在协议解析、数据处理、插件系统等开发中应用广泛,是每一位 Go 开发者都应该熟练掌握的核心技巧。