今天我们来深入探讨MyBatis框架中最核心的模块之一——SQL解析模块。这个模块虽然在日常使用中不太显眼,但它却是连接我们编写的SQL语句和最终数据库执行的关键桥梁。
一、MyBatis整体架构与SQL解析模块
在深入SQL解析模块之前,我们先来看看MyBatis的整体架构。
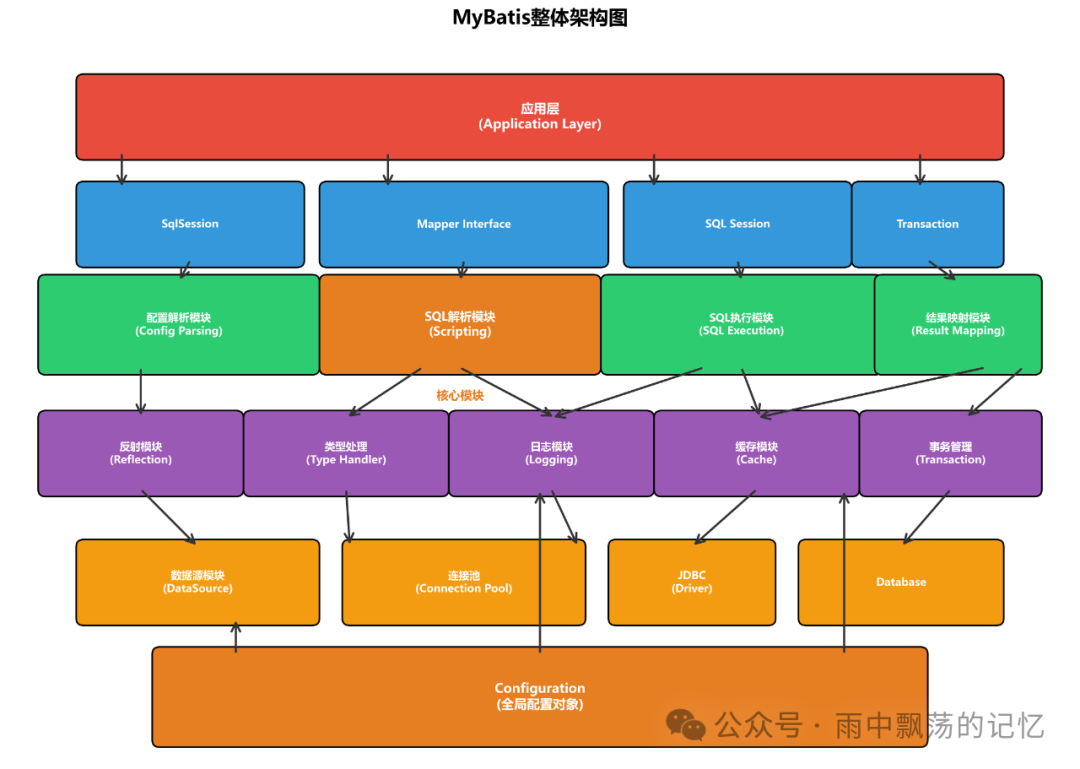
从架构图可以看出,MyBatis采用了清晰的分层设计,而SQL解析模块(Scripting模块)位于核心处理层,承担着至关重要的职责。
SQL解析模块的核心职责
SQL解析模块主要承担以下四大职责:
- SQL语句解析 — 将XML或注解中的SQL语句解析为SqlSource对象
- 动态SQL处理 — 处理if、choose、foreach等动态SQL标签
- 参数绑定 — 将Java对象参数绑定到SQL语句中的占位符
- SQL生成 — 根据运行时参数动态生成最终的可执行SQL
模块核心组件
SQL解析模块由以下核心类组成:
- LanguageDriver — 语言驱动接口,定义SQL解析的顶层接口
- XMLLanguageDriver — XML语言驱动,处理XML配置中的SQL
- XMLScriptBuilder — XML脚本构建器,解析动态SQL标签
- SqlSource — SQL源接口,表示SQL的抽象表示
- DynamicSqlSource — 动态SQL源,包含动态SQL标签
- RawSqlSource — 静态SQL源,不包含动态SQL标签
- BoundSql — 绑定SQL,包含最终SQL和参数映射
二、SQL解析模块整体架构
SQL解析模块采用分层设计,从XML/注解到最终SQL的转换过程清晰明了。
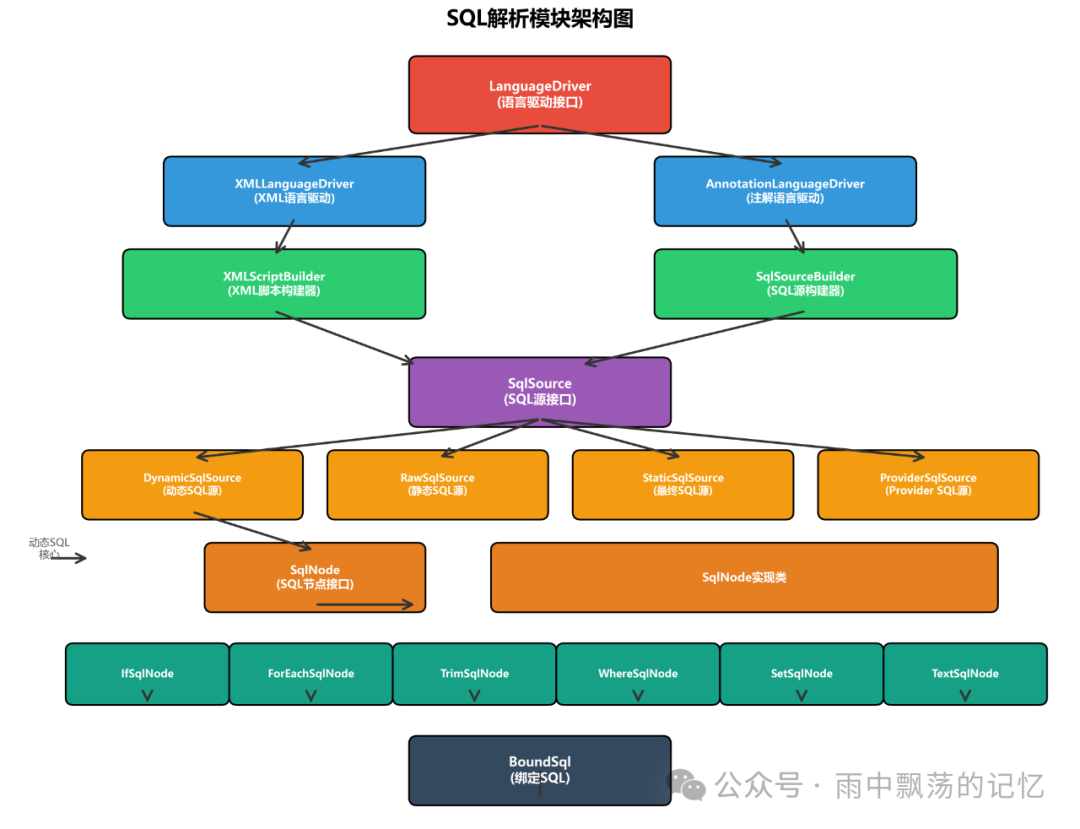
解析流程概览
SQL解析的整体流程可以分为四个阶段:
- 阶段1:配置解析 — 从Mapper XML或注解中读取SQL语句
- 阶段2:SqlSource创建 — 根据SQL是否包含动态标签,创建相应的SqlSource
- 阶段3:SQL构建 — 运行时根据参数信息构建可执行SQL
- 阶段4:参数绑定 — 将Java对象参数绑定到SQL占位符
核心接口详解
LanguageDriver接口
LanguageDriver是SQL解析的顶层接口,定义了创建SqlSource和ParameterHandler的方法:
public interface LanguageDriver {
// 创建ParameterHandler
ParameterHandler createParameterHandler(
MappedStatement mappedStatement,
Object parameterObject,
BoundSql boundSql);
// 创建SqlSource(从XML)
SqlSource createSqlSource(
Configuration configuration,
XNode script,
Class<?> parameterType);
// 创建SqlSource(从注解)
SqlSource createSqlSource(
Configuration configuration,
String script,
Class<?> parameterType);
}
SqlSource接口
SqlSource是SQL的抽象表示,是SQL解析模块的核心接口:
public interface SqlSource {
// 根据参数对象获取BoundSql
BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
}
SqlSource有三个主要实现类:
- DynamicSqlSource — 包含动态SQL标签的SQL源
- RawSqlSource — 静态SQL源,在配置解析时已完成解析
- StaticSqlSource — 最终的静态SQL,SQL和参数都已确定
BoundSql类
BoundSql表示绑定后的SQL,包含了执行SQL所需的所有信息:
public class BoundSql {
private final String sql; // 最终的SQL语句
private final List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings; // 参数映射
private final Object parameterObject; // 参数对象
private final Map<String, Object> additionalParameters; // 额外参数
}
三、动态SQL标签处理
动态SQL是MyBatis最强大的特性之一,通过OGNL表达式实现条件判断和循环等功能。
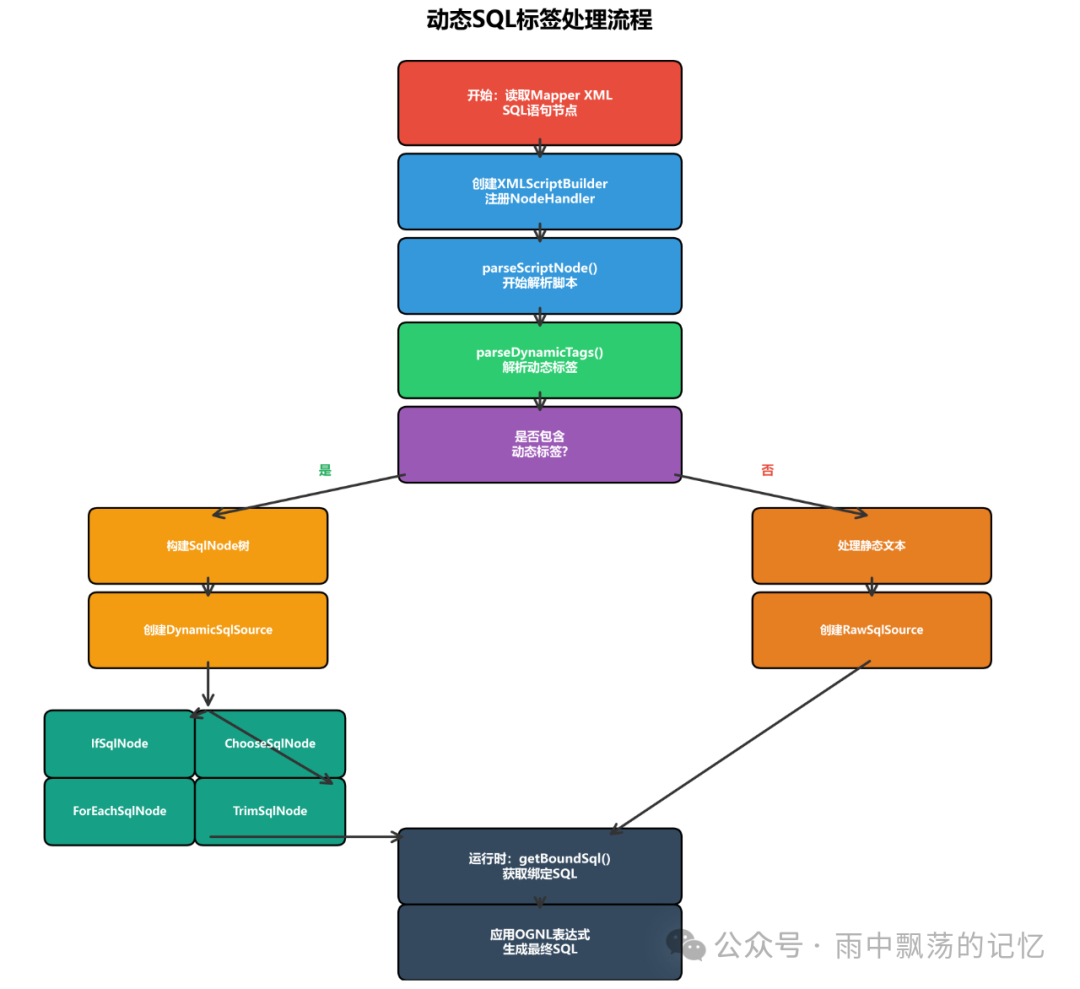
动态SQL标签类型
MyBatis提供了丰富的动态SQL标签:
| 标签 |
功能 |
使用场景 |
| if |
条件判断 |
单条件分支 |
| choose/when/otherwise |
多条件选择 |
多分支选择 |
| trim/where/set |
去除多余关键字 |
动态WHERE/SET子句 |
| foreach |
循环处理 |
IN查询、批量插入 |
| bind |
创建变量 |
绑定变量到上下文 |
XMLScriptBuilder解析器
XMLScriptBuilder负责将XML中的SQL脚本解析为SqlNode树:
public class XMLScriptBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private final XNode context;
private final Map<String, NodeHandler> nodeHandlerMap;
public XMLScriptBuilder(Configuration configuration, XNode context) {
super(configuration);
this.context = context;
// 注册各种节点处理器
this.nodeHandlerMap = new HashMap<>();
nodeHandlerMap.put("trim", new TrimHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("where", new WhereHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("set", new SetHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("foreach", new ForEachHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("if", new IfHandler());
nodeHandlerMap.put("choose", new ChooseHandler());
// ...更多处理器
}
// 解析SQL脚本
public SqlSource parseScriptNode() {
MixedSqlNode rootSqlNode = parseDynamicTags(context);
SqlSource sqlSource;
if (isDynamic) {
sqlSource = new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode);
} else {
sqlSource = new RawSqlSource(configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
return sqlSource;
}
}
SqlNode体系
SqlNode是SQL节点的抽象,每个动态标签都对应一个SqlNode实现:
public interface SqlNode {
// 应用当前节点,生成SQL片段
boolean apply(DynamicContext context);
}
核心SqlNode实现
1. IfSqlNode — 处理if条件判断
public class IfSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final String test;
private final SqlNode contents;
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 使用OGNL表达式判断条件
if (evaluator.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings())) {
contents.apply(context);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
2. ForEachSqlNode — 处理foreach循环
public class ForEachSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final String collection;
private final String item;
private final String separator;
private final SqlNode contents;
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 获取集合参数
Iterable<?> iterable = evaluator.evaluateIterable(
collection, context.getBindings());
Iterator<?> i = iterable.iterator();
int index = 0;
while (i.hasNext()) {
Object item = i.next();
// 绑定item和index变量
context.bind(this.item, item);
context.bind(this.index, index);
// 应用子节点
contents.apply(context);
// 添加分隔符
if (i.hasNext()) {
context.appendSql(separator);
}
index++;
}
return true;
}
}
动态SQL综合示例
下面是一个综合使用动态SQL的实际案例:
<select id="findUserList" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT * FROM t_user
<where>
<if test="userName != null and userName != ''">
AND user_name LIKE CONCAT('%', #{userName}, '%')
</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
AND email = #{email}
</if>
<if test="status != null">
AND status = #{status}
</if>
</where>
<choose>
<when test="orderBy != null and orderBy != ''">
ORDER BY ${orderBy}
</when>
<otherwise>
ORDER BY id DESC
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
对应的SqlNode树结构:
MixedSqlNode
├── StaticTextSqlNode: "SELECT * FROM t_user"
├── WhereSqlNode
│ └── MixedSqlNode
│ ├── IfSqlNode (userName)
│ ├── IfSqlNode (email)
│ └── IfSqlNode (status)
└── ChooseSqlNode
├── IfSqlNode (when)
└── OtherwiseSqlNode
四、SqlSource解析流程
SqlSource的创建和使用是SQL解析的核心流程。
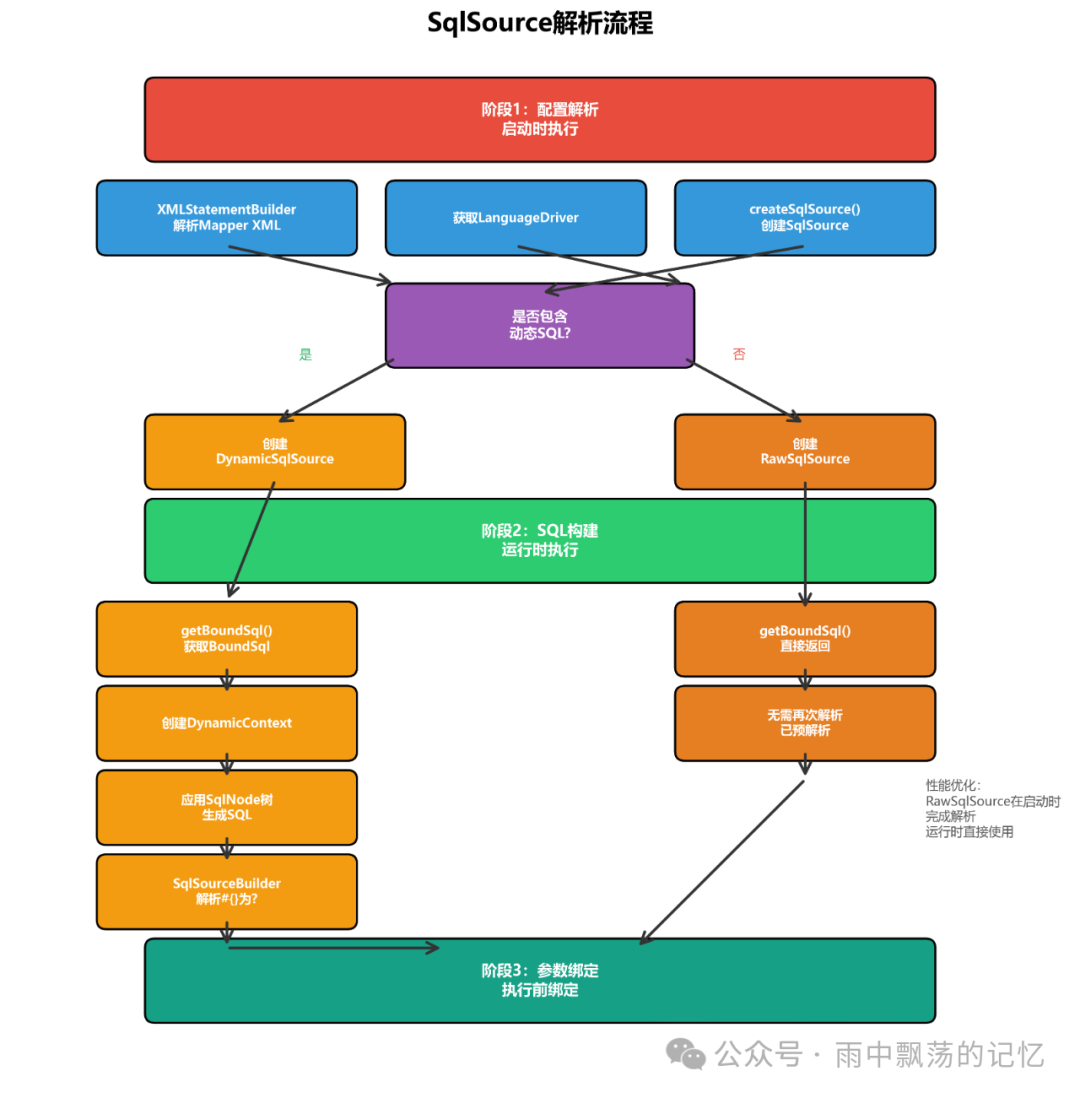
DynamicSqlSource详解
DynamicSqlSource用于处理包含动态SQL标签的SQL:
public class DynamicSqlSource implements SqlSource {
private final Configuration configuration;
private final SqlNode rootSqlNode;
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 1. 创建DynamicContext
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(
configuration, parameterObject);
// 2. 应用SqlNode树,生成SQL
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
// 3. 将#{}替换为?
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser =
new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(
context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
// 4. 创建BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 5. 添加额外参数
context.getBindings().forEach(
boundSql::setAdditionalParameter);
return boundSql;
}
}
RawSqlSource详解
RawSqlSource用于处理静态SQL,在配置解析时完成参数解析:
public class RawSqlSource implements SqlSource {
private final SqlSource sqlSource;
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration,
SqlNode rootSqlNode,
Class<?> parameterType) {
// 一次性解析,后续不再解析
this.sqlSource = getSqlSource(
configuration, rootSqlNode, parameterType);
}
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// 直接返回已解析的SqlSource的BoundSql
return sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
}
性能优化提示:RawSqlSource在启动时完成解析,运行时性能更好,适合静态SQL场景!
五、参数绑定机制
参数绑定是将Java对象参数转换为SQL参数的关键过程。
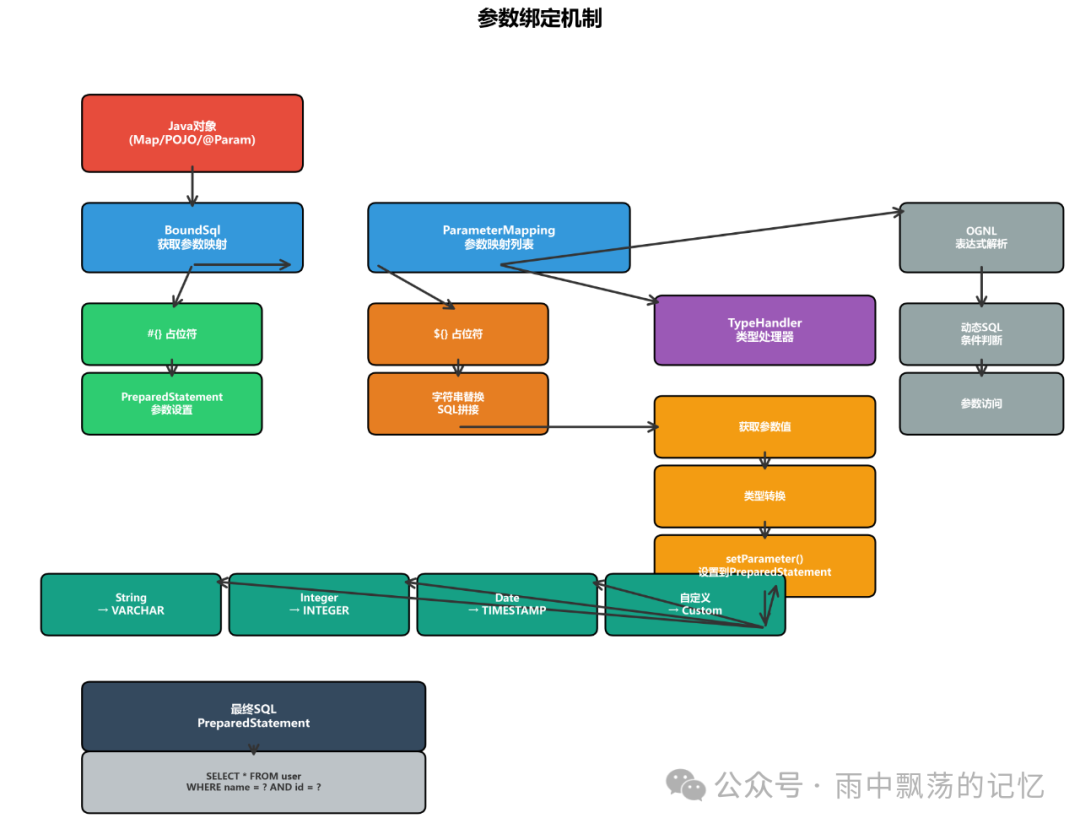
参数占位符对比
MyBatis支持两种参数占位符:
| 占位符 |
类型 |
安全性 |
说明 |
| #{} |
PreparedStatement |
✅ 安全 |
使用预编译参数 |
| ${} |
字符串替换 |
⚠️ 不安全 |
直接替换SQL |
安全建议:优先使用#{},避免SQL注入风险!
ParameterMapping详解
ParameterMapping描述了一个参数的完整映射信息:
public class ParameterMapping {
private final String property; // 参数属性名
private final ParameterMode mode; // 参数模式(IN/OUT/INOUT)
private final Class<?> javaType; // Java类型
private final JdbcType jdbcType; // JDBC类型
private final TypeHandler<?> typeHandler; // 类型处理器
}
参数绑定流程
参数绑定的核心代码:
// DefaultParameterHandler中
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings =
boundSql.getParameterMappings();
for (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {
ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);
// 1. 获取参数值
Object value = getParameterValue(
parameterObject, parameterMapping);
// 2. 获取TypeHandler
TypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();
// 3. 设置参数
typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);
}
}
实战案例
案例1:简单参数绑定
// 方法签名
User findUserByNameAndEmail(
@Param("userName") String userName,
@Param("email") String email);
// SQL配置
<select id="findUserByNameAndEmail" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT * FROM t_user
WHERE user_name = #{userName}
AND email = #{email}
</select>
// 生成后的SQL
SELECT * FROM t_user
WHERE user_name = ?
AND email = ?
案例2:集合参数绑定(foreach)
// 方法签名
List<User> findByIds(@Param("ids") List<Long> ids);
// SQL配置
<select id="findByIds" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
SELECT * FROM t_user
WHERE id IN
<foreach collection="ids" item="id"
open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</select>
// 假设ids=[1,2,3],生成的SQL
SELECT * FROM t_user
WHERE id IN (?, ?, ?)
// 参数映射
ParameterMapping[0] {property: __frch_id_0}
ParameterMapping[1] {property: __frch_id_1}
ParameterMapping[2] {property: __frch_id_2}
六、SQL生成与执行
SQL的最终生成和执行是整个解析流程的收官环节。
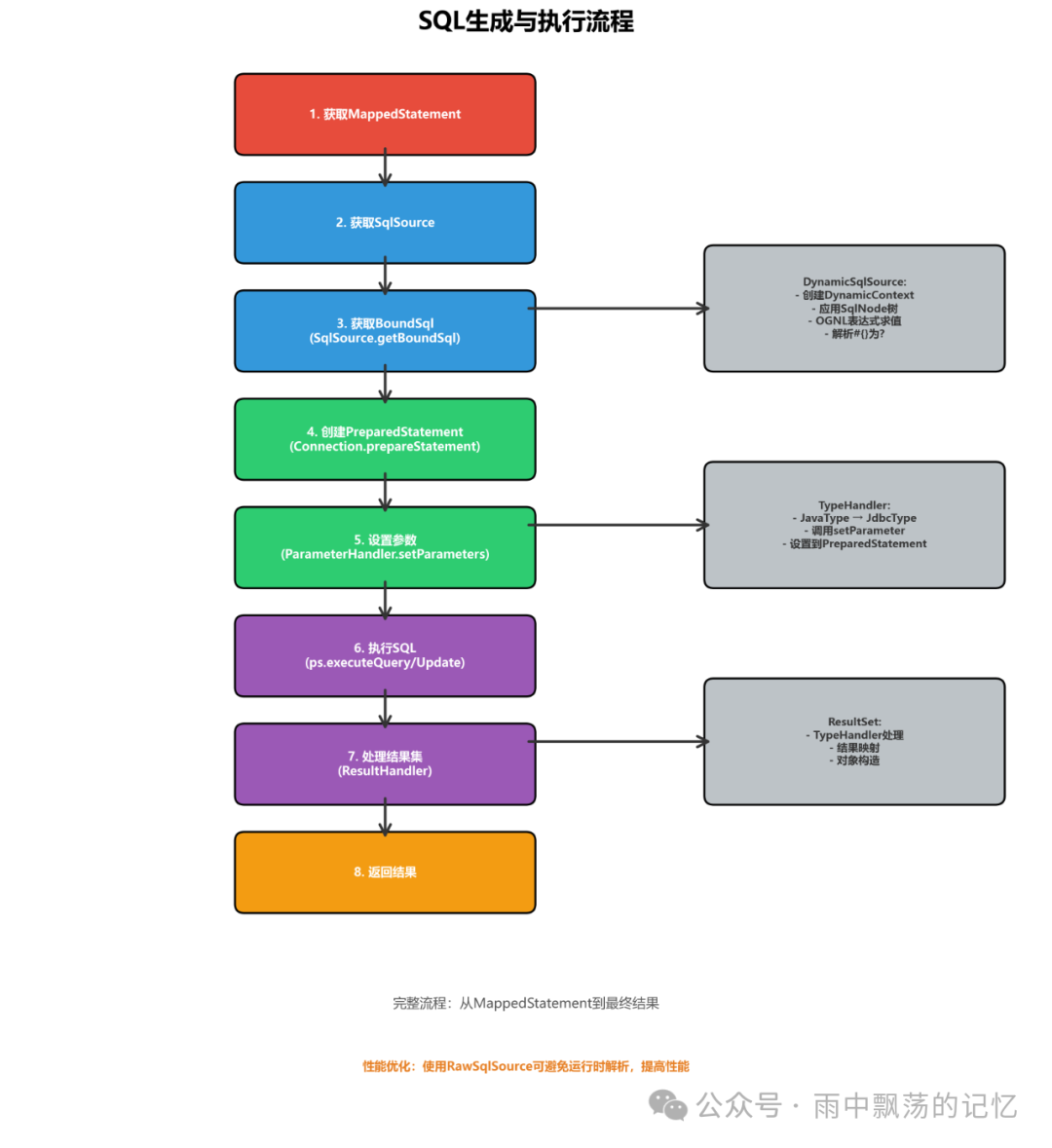
SQL生成完整流程
从SqlSource到可执行SQL的六个步骤:
// 1. 获取SqlSource
SqlSource sqlSource = mappedStatement.getSqlSource();
// 2. 获取BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 3. 获取最终SQL
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// 4. 创建PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
// 5. 设置参数
parameterHandler.setParameters(ps);
// 6. 执行SQL
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
OGNL表达式解析
MyBatis使用OGNL表达式语言来处理动态SQL的条件判断:
// OgnlCache中
public static Object getValue(String expression, Object root) {
try {
Map<Object, Object> context = new HashMap<>();
// 解析表达式
Object value = Ognl.getValue(
parseExpression(expression), context, root);
return value;
} catch (OgnlException e) {
throw new BuilderException(
"Error evaluating expression '" + expression + "'", e);
}
}
常用OGNL表达式示例
<!-- 对象属性访问 -->
<if test="user.name != null">
<!-- 集合操作 -->
<if test="list != null and list.size() > 0">
<!-- 比较运算 -->
<if test="age >= 18">
<!-- 逻辑运算 -->
<if test="status == 1 or status == 2">
<!-- 方法调用 -->
<if test="userName != null and userName.trim() != ''">
TypeHandler的作用
TypeHandler负责Java类型和JDBC类型之间的双向转换:
public interface TypeHandler<T> {
// 设置参数(Java → JDBC)
void setParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i,
T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType);
// 获取结果(JDBC → Java)
T getResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName);
}
示例:StringTypeHandler
public class StringTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<String> {
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps,
int i, String parameter,
JdbcType jdbcType) {
ps.setString(i, parameter);
}
@Override
public String getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) {
return rs.getString(columnName);
}
}
七、最佳实践
动态SQL使用建议
✅ 优先使用#{}而非${}避免SQL注入风险,除非必须使用动态表名或列名
✅ 合理使用where和set标签简化WHERE和SET子句的处理,自动去除多余的AND/OR
✅ foreach注意性能大批量数据时考虑分批处理,避免SQL过长
✅ OGNL表达式简化复杂的判断逻辑放到Java代码中,保持SQL简洁
参数绑定建议
✅ 使用@Param注解提高可读性,避免参数混乱
// 推荐写法
User findUser(@Param("name") String name, @Param("age") int age);
// 不推荐
User findUser(String name, int age);
✅ 提供JDBC类型对于null值,明确指定jdbcType
#{createTime, jdbcType=TIMESTAMP}
✅ 自定义TypeHandler处理特殊类型的转换
✅ 参数对象设计使用专门的DTO封装复杂参数
性能优化建议
- 减少动态SQL复杂度简单场景优先使用静态SQL
- 利用RawSqlSource静态SQL在启动时解析,提高运行时性能
- 合理使用二级缓存避免重复解析相同的SQL
- 批量操作优化使用BATCH执行器处理批量数据
常见问题解决
问题1:OGNL表达式报错
<!-- ❌ 错误写法 -->
<if test="userName == 'admin'">
<!-- ✅ 正确写法 -->
<if test='userName == "admin"'>
<!-- ✅ 或使用转义 -->
<if test="userName == "admin"">
问题2:foreach集合参数为null
<!-- ❌ 错误:直接遍历会导致NPE -->
<select id="findByIds">
WHERE id IN
<foreach collection="ids"...>
</select>
<!-- ✅ 正确:添加判断 -->
<select id="findByIds">
<where>
<if test="ids != null and ids.size() > 0">
AND id IN
<foreach collection="ids"...>
</if>
</where>
</select>
问题3:Date类型参数绑定
<!-- 指定jdbcType避免类型推断错误 -->
#{createTime, jdbcType=TIMESTAMP}
或自定义TypeHandler:
@MappedTypes(Date.class)
@MappedJdbcTypes(JdbcType.TIMESTAMP)
public class MyDateTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<Date> {
// 自定义转换逻辑
}
八、总结
MyBatis的SQL解析模块是整个框架的核心组件,通过精心设计的SqlSource、SqlNode等抽象,实现了强大的动态SQL功能。
核心要点
- 分层设计LanguageDriver → SqlSource → BoundSql,职责清晰
- 动态SQL通过SqlNode树和OGNL表达式实现灵活的条件判断
- 参数绑定TypeHandler机制实现类型安全转换
- 性能优化RawSqlSource预解析,DynamicSqlSource运行时解析
深入理解这些底层机制,不仅能帮助我们更高效地使用MyBatis,也能在遇到复杂场景时快速定位和解决问题。希望本文对你理解MyBatis的SQL解析模块有所帮助。