在Java开发中,MyBatis作为主流的持久层框架,其日志模块为SQL调试和性能优化提供了关键支持。本文将深入解析MyBatis日志模块的设计原理、配置方法及实战应用。
一、整体架构:日志模块的战略位置
通过MyBatis的整体架构图,我们可以看到日志模块位于基础支撑层,负责记录系统运行的关键时刻。
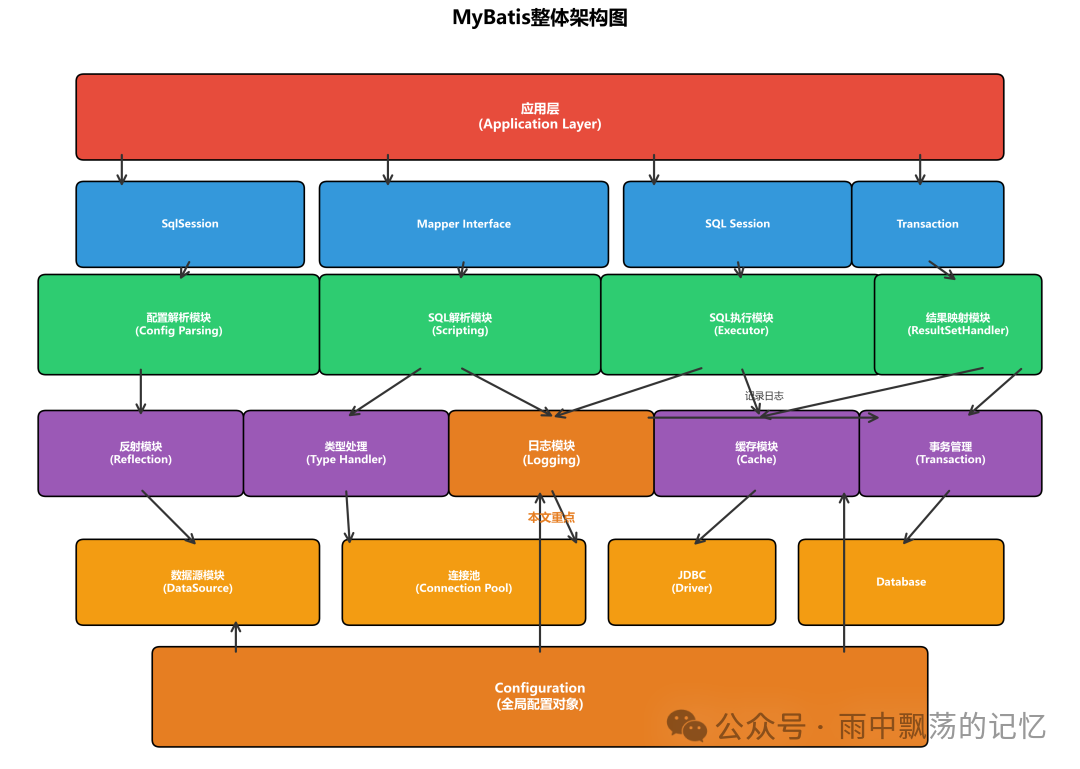
日志模块的六大核心职责
- 记录SQL执行日志 - 完整捕获执行的SQL语句
- 记录参数日志 - 追踪SQL参数的传递过程
- 记录结果日志 - 可选的查询结果记录
- 记录性能日志 - 精准统计SQL执行耗时
- 记录异常日志 - 详尽的错误信息捕获
- 集成日志框架 - 无缝适配主流日志组件
为什么日志如此重要?
在实际开发中,日志扮演着三个关键角色:
开发调试阶段
- 查看实际执行的SQL语句
- 检查参数绑定是否正确
- 快速排查SQL语法错误
性能优化阶段
- 识别执行缓慢的SQL查询
- 分析SQL执行频率分布
- 指导索引优化方向
生产运维阶段
- 问题快速定位与追踪
- 数据操作行为审计
- 业务数据深度分析
MyBatis日志的五大特点
| 特性 |
说明 |
| 自动集成 |
智能检测并使用项目中的日志框架 |
| 多框架支持 |
支持SLF4J、Log4j、Log4j2、JDK Logging等 |
| 分级记录 |
支持DEBUG、INFO、WARN、ERROR等级别 |
| 性能考虑 |
使用延迟加载,避免不必要的字符串拼接 |
| JDBC日志 |
专门记录JDBC操作的详细日志 |
二、接口架构:统一而灵活的设计
MyBatis采用接口+适配器的经典设计模式,实现了与日志框架的解耦。
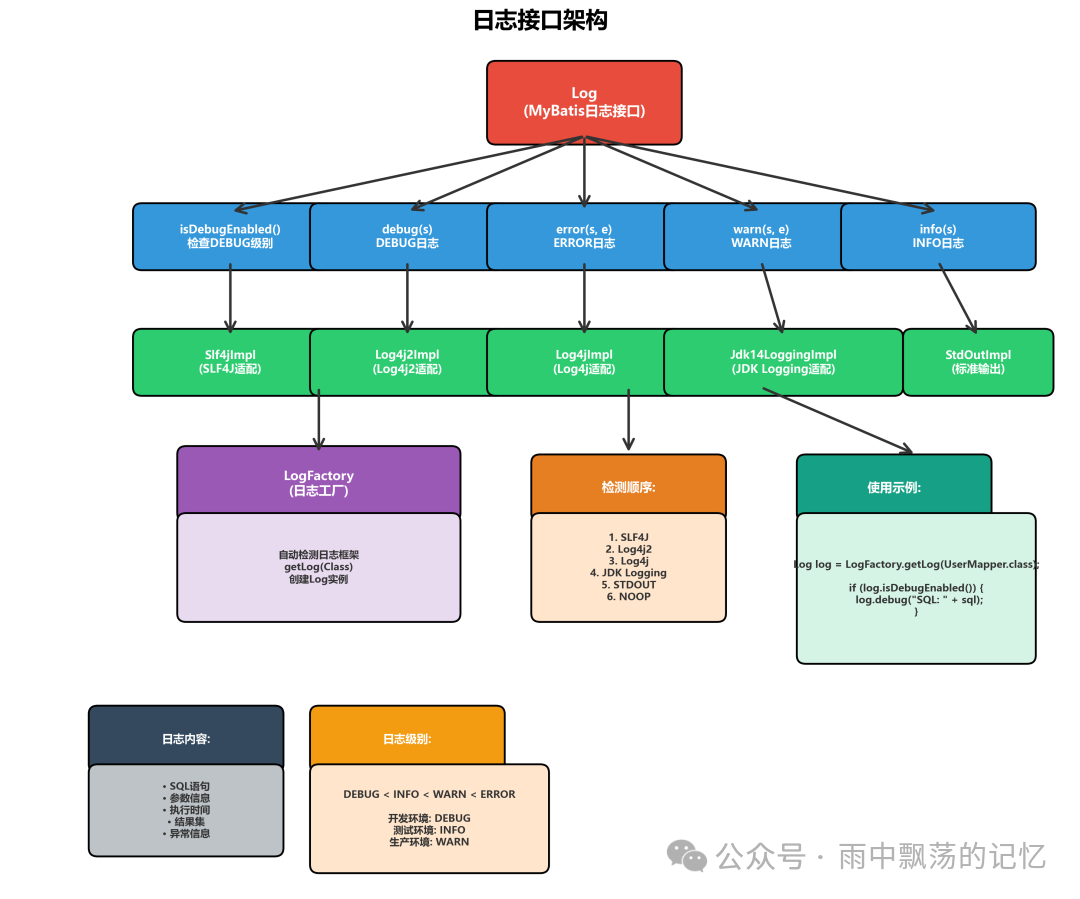
核心接口:Log
MyBatis定义了简洁而强大的日志接口:
public interface Log {
// 是否启用DEBUG级别
boolean isDebugEnabled();
// 是否启用ERROR级别
boolean isErrorEnabled();
// DEBUG级别日志
void debug(String s);
// ERROR级别日志
void error(String s);
// ERROR级别日志(带异常)
void error(String s, Throwable e);
// WARN级别日志(带异常)
void warn(String s, Throwable e);
}
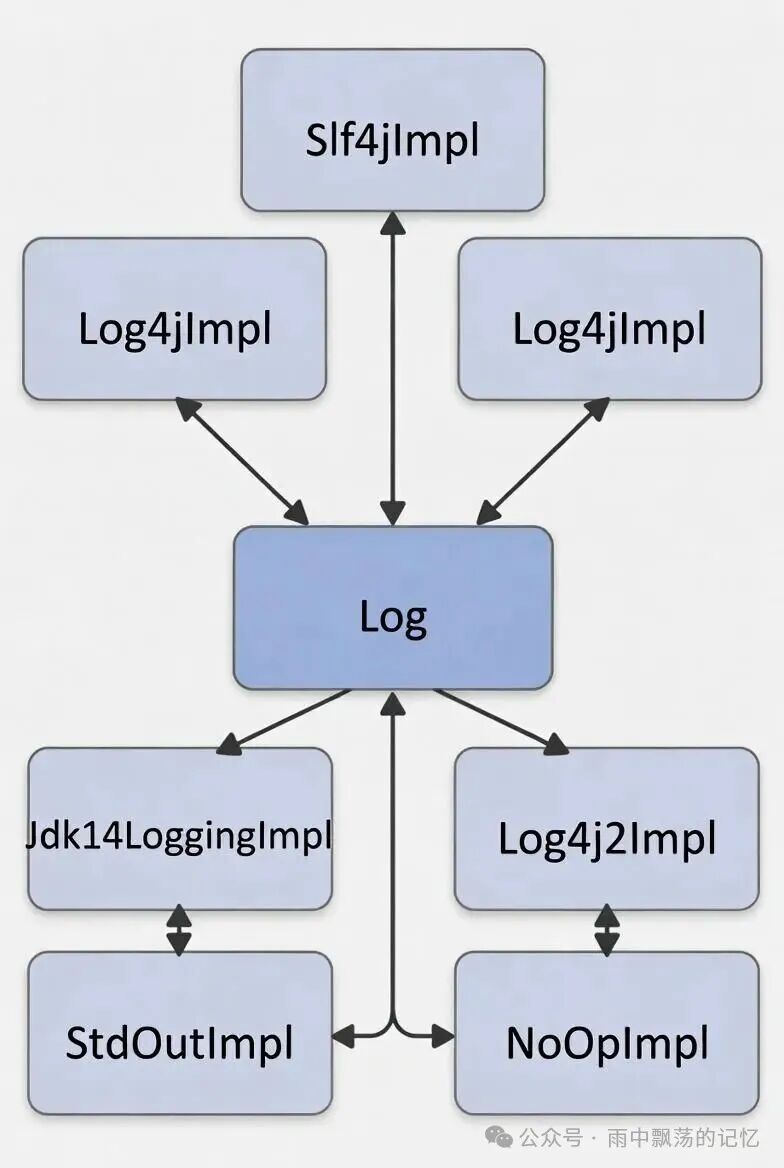
日志框架适配器家族
MyBatis通过适配器模式支持多种主流日志框架:
Slf4jImpl实现示例
public class Slf4jImpl implements Log {
private final Logger log;
public Slf4jImpl(String clazz) {
// 通过SLF4J工厂创建Logger
log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(clazz);
}
@Override
public boolean isDebugEnabled() {
return log.isDebugEnabled();
}
@Override
public void debug(String s) {
log.debug(s);
}
@Override
public void error(String s, Throwable e) {
log.error(s, e);
}
@Override
public void warn(String s, Throwable e) {
log.warn(s, e);
}
}
LogFactory工厂类:智能选择最佳日志框架
LogFactory负责按照优先级自动检测并创建合适的Log实现:
public final class LogFactory {
private static Constructor<? extends Log> logConstructor;
static {
// 按优先级依次尝试加载日志框架
// 1. 优先尝试SLF4J
tryImplementation(Slf4jImpl.class, "SLF4J");
// 2. 然后尝试Log4j2
tryImplementation(Log4j2Impl.class, "Log4j 2");
// 3. 继续尝试Log4j
tryImplementation(Log4jImpl.class, "Log4j");
// 4. 尝试JDK内置日志
tryImplementation(Jdk14LoggingImpl.class, "JDK logging");
// 5. 降级到标准输出
tryImplementation(StdOutImpl.class, "stdout");
// 6. 最后使用空实现
tryImplementation(NoOpImpl.class, "noop");
}
// 获取Log实例
public static Log getLog(Class<?> clazz){
return getLog(clazz.getName());
}
public static Log getLog(String logger){
try {
return logConstructor.newInstance(logger);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error creating logger for " + logger, t);
}
}
// 支持自定义日志实现
public static synchronized void useCustomLogging(
Class<? extends Log> clazz) {
setImplementation(clazz);
}
}
三、日志配置:灵活多样的配置方式
MyBatis提供了多种配置方式,满足不同场景需求。
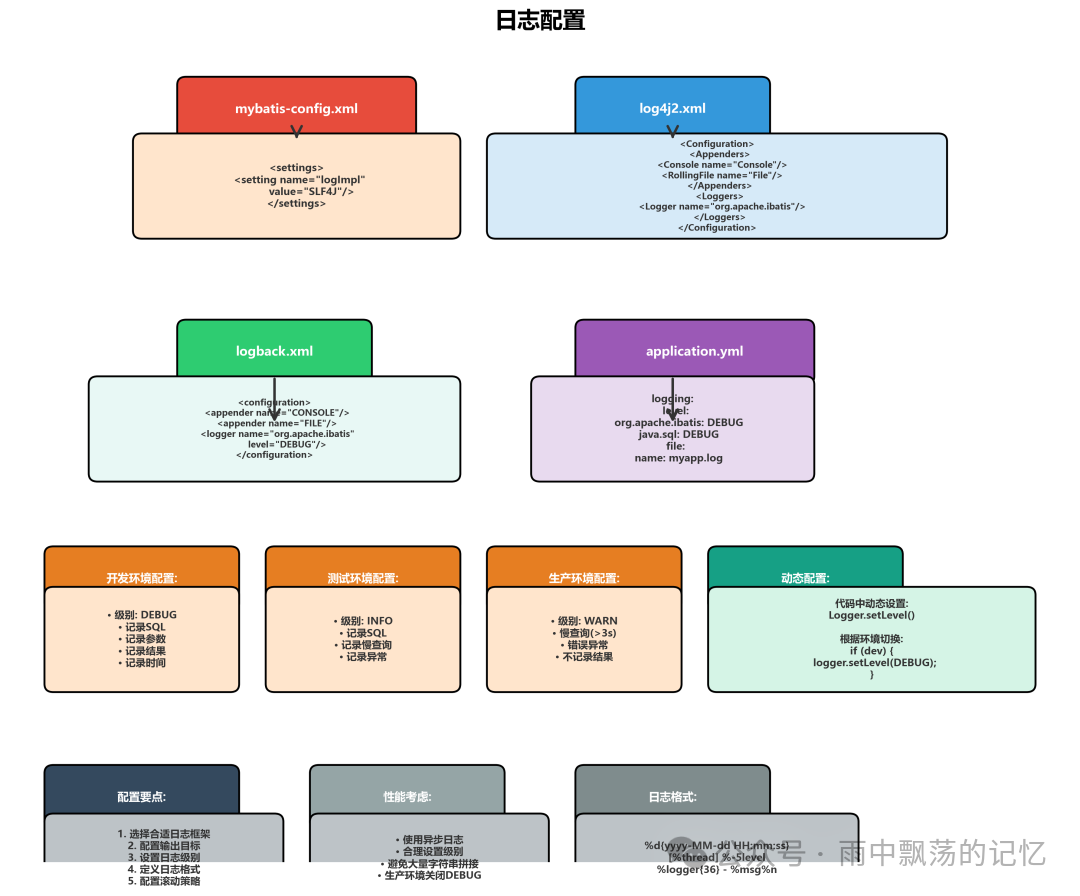
方式1:mybatis-config.xml配置
<configuration>
<settings>
<!-- 可选:显式指定日志实现 -->
<!-- <setting name="logImpl" value="SLF4J"/> -->
<!-- <setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J2"/> -->
<!-- <setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/> -->
</settings>
</configuration>
方式2:Log4j2详细配置
log4j2.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Configuration status="WARN">
<Appenders>
<!-- 控制台输出 -->
<Console name="Console" target="SYSTEM_OUT">
<PatternLayout
pattern="%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%t] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n"/>
</Console>
<!-- 文件输出(滚动策略) -->
<RollingFile name="RollingFile"
fileName="logs/mybatis.log"
filePattern="logs/mybatis-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}-%i.log.gz">
<PatternLayout
pattern="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%t] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n"/>
<Policies>
<!-- 每天滚动 -->
<TimeBasedTriggeringPolicy interval="1"/>
<!-- 单文件最大100MB -->
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="100 MB"/>
</Policies>
<!-- 最多保留30天 -->
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="30"/>
</RollingFile>
</Appenders>
<Loggers>
<!-- MyBatis核心日志 -->
<Logger name="org.apache.ibatis" level="DEBUG" additivity="false">
<AppenderRef ref="Console"/>
<AppenderRef ref="RollingFile"/>
</Logger>
<!-- SQL语句日志 -->
<Logger name="org.apache.ibatis.jdbc.SQL"
level="DEBUG" additivity="false">
<AppenderRef ref="Console"/>
</Logger>
<!-- Root Logger -->
<Root level="INFO">
<AppenderRef ref="Console"/>
<AppenderRef ref="RollingFile"/>
</Root>
</Loggers>
</Configuration>
方式3:Logback配置
logback.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<!-- 控制台输出 -->
<appender name="CONSOLE"
class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- 文件输出 -->
<appender name="FILE"
class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>logs/mybatis.log</file>
<rollingPolicy
class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>logs/mybatis-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</fileNamePattern>
<maxHistory>30</maxHistory>
</rollingPolicy>
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- MyBatis日志配置 -->
<logger name="org.apache.ibatis" level="DEBUG"/>
<logger name="java.sql.Connection" level="DEBUG"/>
<logger name="java.sql.Statement" level="DEBUG"/>
<logger name="java.sql.PreparedStatement" level="DEBUG"/>
<!-- Root配置 -->
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="CONSOLE"/>
<appender-ref ref="FILE"/>
</root>
</configuration>
方式4:Spring Boot配置
application.yml:
# 日志配置
logging:
level:
# MyBatis SQL日志
org.apache.ibatis: DEBUG
java.sql.Connection: DEBUG
java.sql.Statement: DEBUG
java.sql.PreparedStatement: DEBUG
java.sql.ResultSet: WARN
# 日志文件配置
file:
path: logs
name: myapp.log
max-size: 100MB
max-history: 30
# 日志格式
pattern:
console: "%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n"
file: "%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n"
四、JDBC日志:细粒度的操作追踪
MyBatis提供了专门的JDBC日志记录机制,可以追踪每一个JDBC操作的细节。
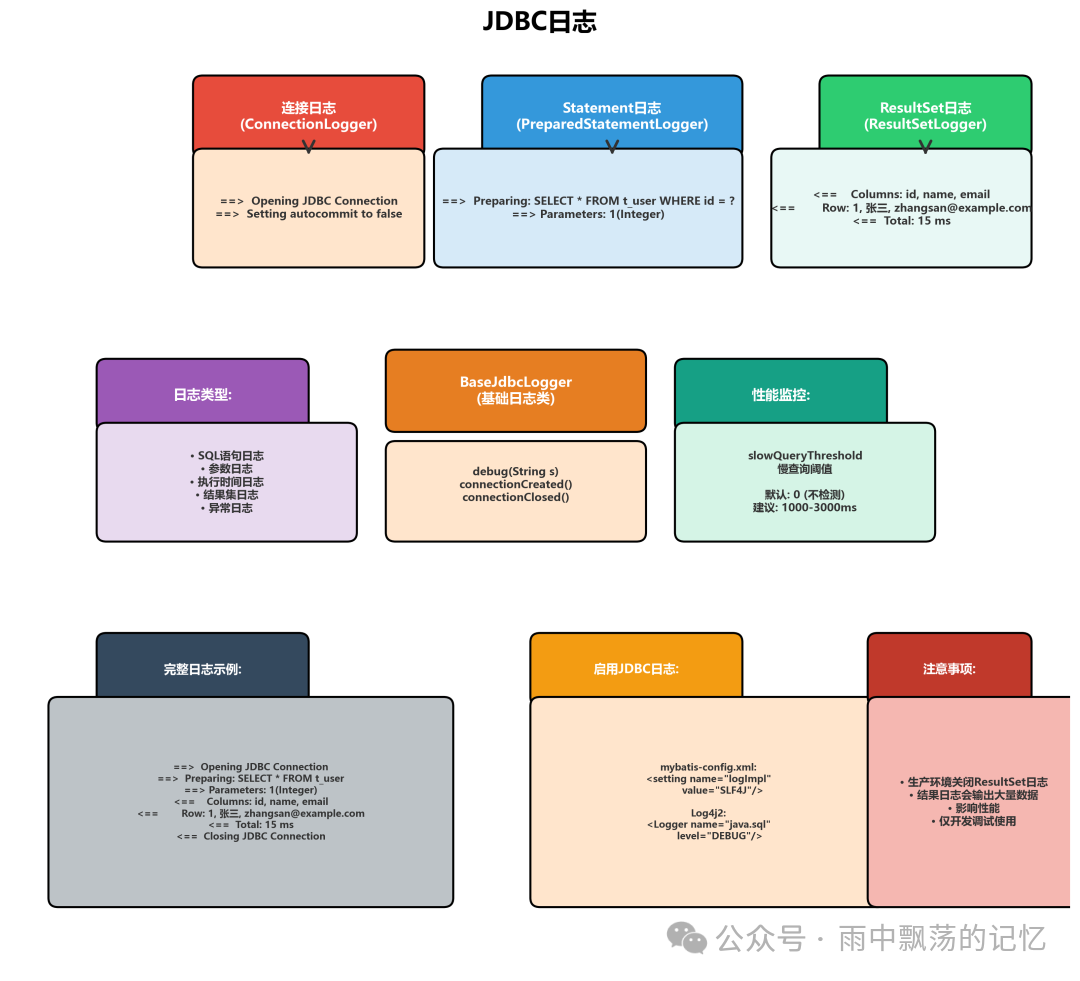
JDBC日志记录内容

BaseJdbcLogger基础类
public abstract class BaseJdbcLogger {
// 日志对象
protected Log statementLog;
protected Log connectionLog;
// 调试开关
protected boolean isDebugEnabled;
// 慢查询阈值(毫秒)
protected int slowQueryThreshold;
public BaseJdbcLogger(Log log, int queryThreshold) {
this.statementLog = log;
this.connectionLog = log;
this.isDebugEnabled = log.isDebugEnabled();
this.slowQueryThreshold = queryThreshold;
}
// 记录SQL执行
protected void debug(String s, boolean isSql) {
if (this.isDebugEnabled) {
this.statementLog.debug(s);
}
}
// 记录连接创建
protected void connectionCreated(Connection conn) {
if (this.connectionLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.connectionLog.debug("==> Opening JDBC Connection");
}
}
// 记录连接关闭
protected void connectionClosed(Connection conn) {
if (this.connectionLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.connectionLog.debug("<== Closing JDBC Connection");
}
}
}
ConnectionLogger连接日志
public class ConnectionLogger extends BaseJdbcLogger
implements InvocationHandler {
private final Connection connection;
public ConnectionLogger(Connection conn, Log log,
int queryThreshold) {
super(log, queryThreshold);
this.connection = conn;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
// 记录PreparedStatement创建
if ("prepareStatement".equals(methodName) ||
"prepareCall".equals(methodName)) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
debug("Preparing: " +
removeBreakingWhitespace((String) args[0]), true);
}
}
// 记录连接关闭
if ("close".equals(methodName)) {
connectionClosed(connection);
return null;
}
// 执行原方法
return method.invoke(connection, args);
}
}
PreparedStatementLogger语句日志
public class PreparedStatementLogger extends BaseJdbcLogger
implements InvocationHandler {
private final PreparedStatement statement;
private final String sql;
private final Object[] parameterValues;
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
// 记录参数设置
if ("setString".equals(methodName) ||
"setInt".equals(methodName) ||
"setLong".equals(methodName)) {
if (args.length == 2) {
int paramIndex = (Integer) args[0];
Object paramValue = args[1];
parameterValues[paramIndex - 1] = paramValue;
if (isDebugEnabled) {
debug("Parameters: " + paramIndex +
" => " + paramValue, true);
}
}
}
// 记录SQL执行
if ("execute".equals(methodName) ||
"executeUpdate".equals(methodName) ||
"executeQuery".equals(methodName)) {
if (isDebugEnabled) {
debug("==> Executing: " + sql, true);
debug("==> Parameters: " +
getParameterString(), true);
}
// 计时执行
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = method.invoke(statement, args);
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
if (isDebugEnabled) {
debug("<== Total: " + cost + " ms", true);
}
// 慢查询告警
if (slowQueryThreshold > 0 && cost > slowQueryThreshold) {
connectionLog.warn("Slow query detected: " +
cost + " ms");
}
return result;
}
return method.invoke(statement, args);
}
private String getParameterString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < parameterValues.length; i++) {
if (i > 0) sb.append(", ");
sb.append(i + 1).append(" => ").append(parameterValues[i]);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
ResultSetLogger结果集日志
public class ResultSetLogger extends BaseJdbcLogger
implements InvocationHandler {
private final ResultSet resultSet;
private final List<String> columnNames = new ArrayList<>();
private final List<String> columnValues = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
String methodName = method.getName();
// 记录列名
if ("next".equals(methodName)) {
if (columnNames.isEmpty()) {
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
columnNames.add(metaData.getColumnName(i));
}
}
}
// 记录结果值
if ("getString".equals(methodName) ||
"getInt".equals(methodName) ||
"getObject".equals(methodName)) {
Object result = method.invoke(resultSet, args);
if (isDebugEnabled && result != null) {
String columnName = columnNames.isEmpty() ?
"?" : columnNames.get(columnValues.size());
columnValues.add(columnName + " = " + result);
}
return result;
}
// 记录结果集关闭
if ("close".equals(methodName)) {
if (isDebugEnabled && !columnValues.isEmpty()) {
debug("<== Columns: " + columnNames, true);
debug("<== Row: " + columnValues, true);
}
return null;
}
return method.invoke(resultSet, args);
}
}
五、日志适配器:优雅的框架集成
MyBatis通过适配器模式实现了与各种日志框架的无缝集成。
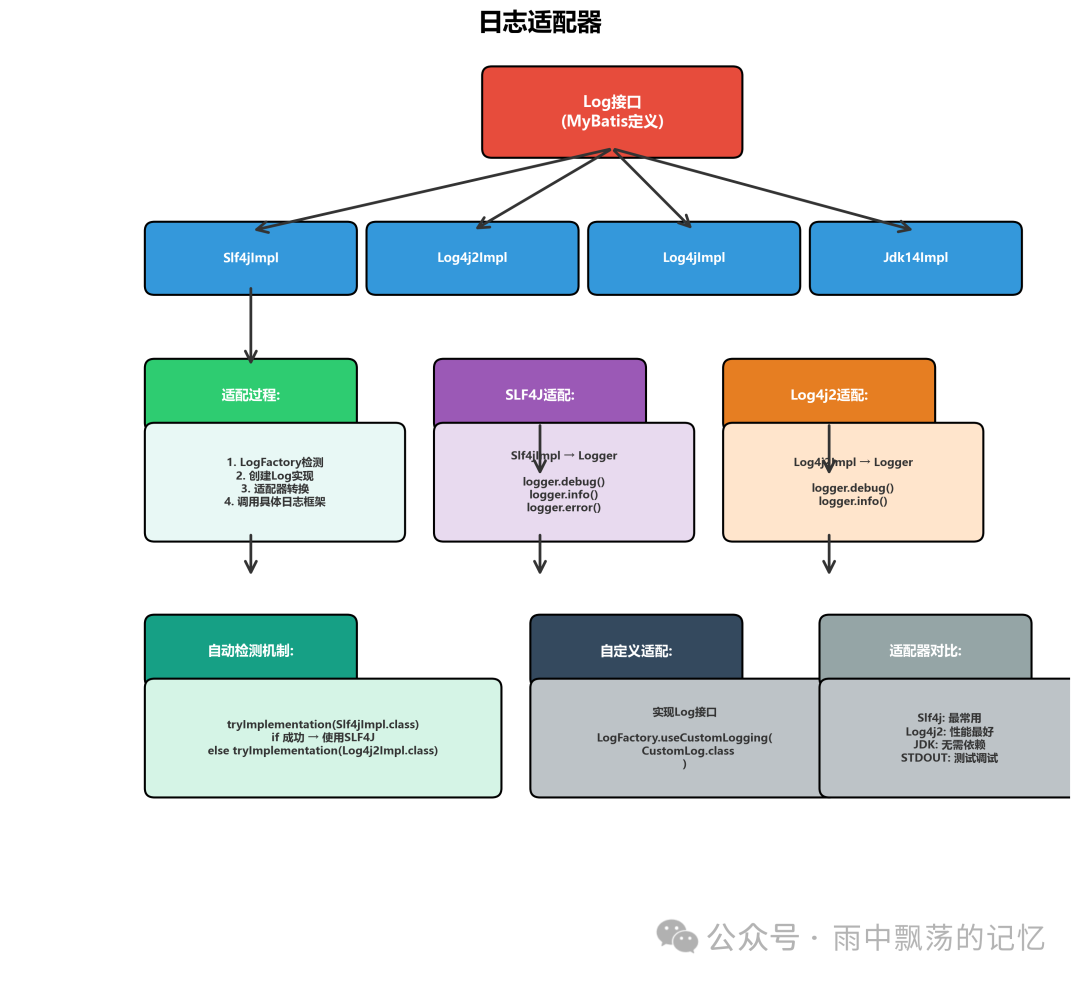
日志适配器的工作流程
MyBatis Log接口
↓
日志适配器 (Log4j2Impl)
↓
Log4j2 Logger
↓
日志输出(控制台/文件)
LogFactory按照优先级自动检测并选择日志框架:
- SLF4J (优先级最高)
- Log4j2
- Log4j
- JDK Logging
- STDOUT (标准输出)
- NOOP (无日志)
自定义日志适配器
如果需要使用自定义日志框架,可以轻松扩展:
public class CustomLog implements Log {
private final CustomLogger logger;
public CustomLog(String clazz) {
this.logger = CustomLoggerFactory.getLogger(clazz);
}
@Override
public boolean isDebugEnabled() {
return logger.isDebugEnabled();
}
@Override
public void debug(String s) {
logger.debug(s);
}
@Override
public void error(String s, Throwable e) {
logger.error(s, e);
}
@Override
public void warn(String s, Throwable e) {
logger.warn(s, e);
}
}
// 使用自定义日志
LogFactory.useCustomLogging(CustomLog.class);
主流日志框架对比
| 日志框架 |
优点 |
缺点 |
适用场景 |
| SLF4J |
统一日志门面,性能优秀 |
需要绑定实现 |
大型项目 |
| Log4j2 |
性能最佳,功能强大 |
配置相对复杂 |
高并发系统 |
| Log4j |
成熟稳定,社区活跃 |
性能一般 |
老项目维护 |
| JDK Logging |
无需额外依赖,简单轻量 |
功能有限 |
简单项目 |
| STDOUT |
配置简单,即开即用 |
无格式化,不可配置 |
开发测试 |
六、实战应用:日志在开发中的运用
让我们通过实际场景看看日志如何帮助我们解决问题。
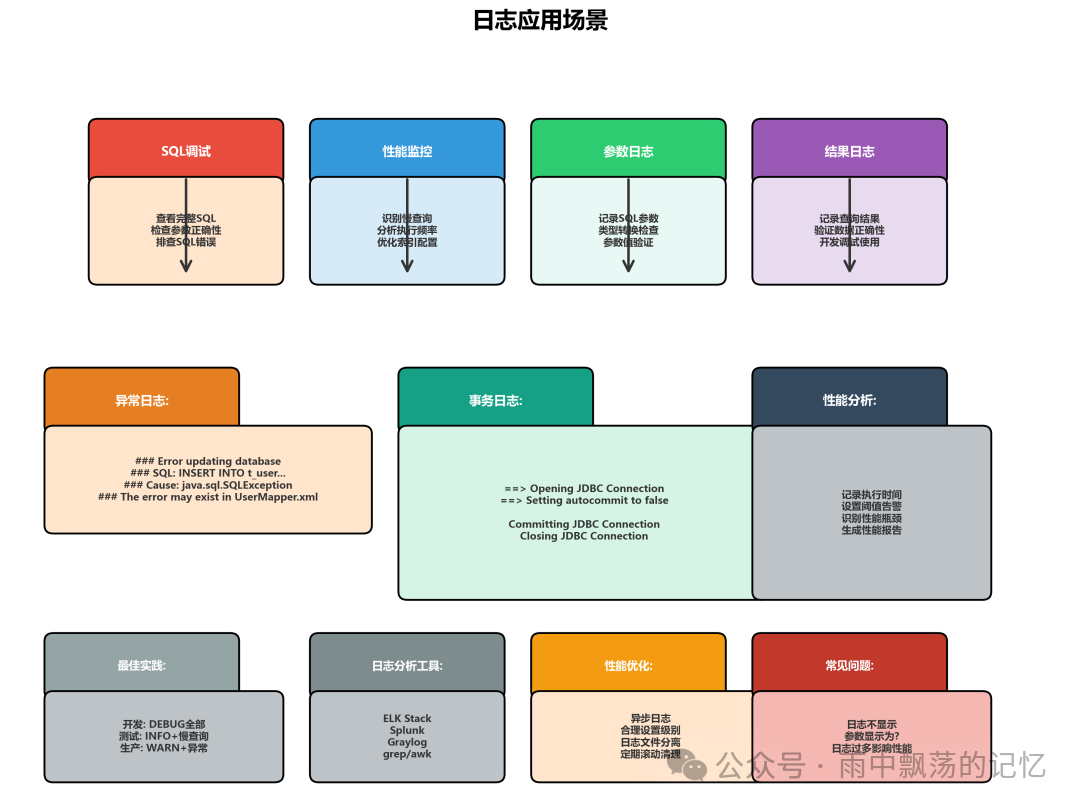
场景1:SQL调试日志
记录完整的SQL语句和参数,快速定位问题:
// 执行查询
User user = userMapper.selectById(1L);
// 控制台输出:
==> Preparing: SELECT * FROM t_user WHERE id = ?
==> Parameters: 1(Integer)
<== Columns: id, name, email, age, create_time
<== Row: 1, 张三, zhangsan@example.com, 25, 2024-01-01 10:00:00
<== Total: 15 ms
场景2:性能监控日志
识别慢查询,优化系统性能:
@Override
public Object query(...) throws SQLException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
return result;
} finally {
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
// 慢查询告警
if (cost > slowQueryThreshold) {
logger.warn("Slow query: {} ms - SQL: {}",
cost, sql);
}
if (isDebugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Query cost: {} ms", cost);
}
}
}
场景3:参数日志
检查参数绑定是否正确:
// 查询用户
List<User> users = userMapper.selectByCondition("张", 25);
// 日志输出:
==> Preparing: SELECT * FROM t_user
WHERE name LIKE CONCAT('%', ?, '%') AND age = ?
==> Parameters: 张(String), 25(Integer)
<== Total: 22 ms
<== Rows: 5
场景4:结果日志(开发环境)
// 日志输出:
<== Columns: id, name, email
<== Row: 1, 张三, zhangsan@example.com
<== Row: 2, 李四, lisi@example.com
<== Row: 3, 王五, wangwu@example.com
<== Total: 3 rows
场景5:异常日志
详细记录SQL执行异常:
try {
userMapper.insert(user);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 日志输出:
==> Preparing: INSERT INTO t_user (name, email) VALUES (?, ?)
==> Parameters: 张三(String), invalid-email(String)
### Error updating database.
### Cause: java.sql.SQLException: Incorrect string value
### The error may exist in UserMapper.xml
### The error may involve UserMapper.insert
### SQL: INSERT INTO t_user (name, email) VALUES (?, ?)
### Cause: java.sql.SQLException: Incorrect string value
}
场景6:事务日志
追踪事务的完整生命周期:
// 开启事务
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 日志输出:
==> Opening JDBC Connection
==> Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection
// 提交事务
session.commit();
// 日志输出:
==> Committing JDBC Connection
<== Closing JDBC Connection
七、最佳实践
不同环境的日志配置策略
开发环境配置
logging:
level:
org.apache.ibatis: DEBUG
# 启用DEBUG级别
# 记录SQL和参数
# 记录结果集
# 记录执行时间
测试环境配置
logging:
level:
org.apache.ibatis: INFO
# 启用INFO级别
# 记录SQL和参数
# 记录慢查询(>1秒)
# 记录异常信息
生产环境配置
logging:
level:
org.apache.ibatis: WARN
# 启用WARN级别
# 仅记录慢查询(>3秒)
# 记录错误和异常
性能优化
1️⃣ 合理设置日志级别
<!-- 生产环境使用INFO或WARN级别 -->
<logger name="org.apache.ibatis" level="WARN"/>
2️⃣ 使用异步日志
<!-- Log4j2异步日志配置 -->
<Async name="AsyncAppender">
<AppenderRef ref="RollingFile"/>
</Async>
3️⃣ SQL日志单独存储
<!-- SQL日志独立文件 -->
<RollingFile name="SqlLog" fileName="logs/sql.log">
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} - %msg%n"/>
</RollingFile>
<Logger name="org.apache.ibatis.jdbc" level="DEBUG">
<AppenderRef ref="SqlLog"/>
</Logger>
4️⃣ 日志文件滚动策略
<Policies>
<!-- 每天滚动 -->
<TimeBasedTriggeringPolicy interval="1"/>
<!-- 单文件最大100MB -->
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="100 MB"/>
</Policies>
<!-- 最多保留30天 -->
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="30"/>
八、总结
MyBatis的日志模块为开发调试和性能优化提供了强大的支持,其核心设计包括:
- Log接口 - MyBatis定义的统一日志接口,实现与框架解耦
- 日志适配器 - 通过适配器模式支持多种日志框架
- JDBC日志 - 细粒度的JDBC操作日志记录
- 灵活配置 - 支持多种配置方式,适应不同场景
- 性能监控 - 通过日志识别性能瓶颈
掌握MyBatis日志模块的配置和使用,能有效提升开发调试和系统监控效率。更多Java和数据库相关技术讨论,欢迎访问云栈社区。