本系列介绍增强现代智能体系统可靠性的设计模式,以直观方式逐一介绍每个概念,拆解其目的,然后实现简单可行的版本,演示其如何融入现实世界的智能体系统。本系列一共 14 篇文章,这是第 5 篇。原文: Building the 14 Key Pillars of Agentic AI[1]。
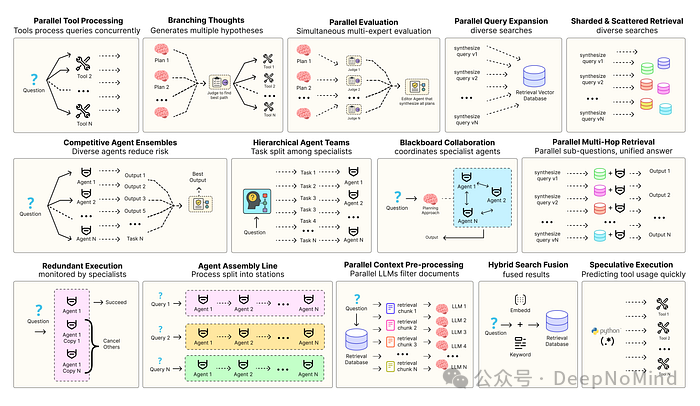
要让智能体解决方案更高效,需要借助软件工程思维来确保组件协调工作、并行运行并与系统高效交互。例如预测执行[2],它会尝试处理可预测的查询以降低时延;还有冗余执行[3],即对同一智能体重复执行多次来防止单点故障。
其他能增强现代智能体系统可靠性的模式还包括:
- 并行工具:智能体同时执行独立的 API 调用以隐藏 I/O 时延。
- 层级智能体:管理者将任务拆分为由执行智能体处理的小步骤。
- 竞争性智能体组合:多个智能体提出答案,系统选出最佳。
- 冗余执行:即两个或多个智能体解决同一任务以检测错误并提高可靠性。
- 并行检索和混合检索:多种检索策略协同运行以提升上下文质量。
- 多跳检索:智能体通过迭代检索步骤收集更深入、更相关的信息。
当然,还有其他很多模式。本系列旨在实现最常用智能体模式背后的基础概念,逐一进行直观介绍,拆解其目的,并实现简单可行的版本,展示它们如何融入真实的智能体系统。
所有理论和代码都在 GitHub 仓库里:🤖 Agentic Parallelism: A Practical Guide 🚀[4]
代码库组织如下:
agentic-parallelism/
├── 01_parallel_tool_use.ipynb
├── 02_parallel_hypothesis.ipynb
...
├── 06_competitive_agent_ensembles.ipynb
├── 07_agent_assembly_line.ipynb
├── 08_decentralized_blackboard.ipynb
...
├── 13_parallel_context_preprocessing.ipynb
└── 14_parallel_multi_hop_retrieval.ipynb
层级代理组:追求卓越质量
前面我们探讨了智能体如何同时生成并评估想法。但复杂任务往往充满意外,需要智能体决定执行什么以及何时执行,这可能导致计划与行动之间的延迟。
解决这个问题的正确方法是采用专业化与解耦架构模式。
- 复杂任务被分配给高层编排器(或管理器)代理,它本身不执行任务,只负责规划。
- 该代理将复杂任务分解为更小、更明确的子任务,并委派给一组专业执行器代理。
- 执行器通常可以并行完成任务。最后,编排器将执行器的结果综合成统一的输出。
为了证明分层式方法的优势,我们将直接比较单体代理与分层组在投资报告生成任务中的表现,看分层方法是否不仅更快,而且在细节、结构和准确性上都更优。
定义通信协议:结构化数据模型
首先,我们需要定义作为代理之间通信协议的结构化数据模型。结构化输出是将多智能体系统粘合在一起的纽带。
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
from typing import Optional, List
class FinancialData(BaseModel):
"""金融分析代理的结构化输出 Pydantic 模型。"""
price: float = Field(description="Current stock price.")
market_cap: int = Field(description="Total market capitalization.")
pe_ratio: float = Field(description="Price-to-Earnings ratio.")
volume: int = Field(description="Average trading volume.")
class NewsAndMarketAnalysis(BaseModel):
"""新闻与市场分析代理的结构化输出 Pydantic 模型。"""
summary: str = Field(description="A concise summary of the most important recent news and market trends.")
competitors: List[str] = Field(description="A list of the company's main competitors.")
class FinalReport(BaseModel):
"""首席分析师最终综合投资报告的 Pydantic 模型。"""
company_name: str = Field(description="The name of the company.")
financial_summary: str = Field(description="A paragraph summarizing the key financial data.")
news_and_market_summary: str = Field(description="A paragraph summarizing the news, market trends, and competitive landscape.")
recommendation: str = Field(description="A final investment recommendation (e.g., 'Strong Buy', 'Hold', 'Sell') with a brief justification.")
这些 Pydantic 模型是定义信息如何在专业代理与最终协调器之间传递的正式合约。例如,FinancialData 模型确保金融分析代理始终提供四个具体的数值数据点。结构化数据比简单的文本块更可靠,也更容易让最终的合成器代理处理。
构建团队工作流:定义图状态
接下来为分层组定义 GraphState,用于跟踪每个专业执行器的输出。
from typing import TypedDict, Annotated
class TeamGraphState(TypedDict):
company_symbol: str
company_name: str
# 'financial_data' 将保存金融分析代理的结构化输出
financial_data: Optional[FinancialData]
# 'news_analysis' 将保存新闻和市场分析代理的结构化输出
news_analysis: Optional[NewsAndMarketAnalysis]
# 'final_report' 是合成器的最终产物
final_report: Optional[FinalReport]
performance_log: Annotated[List[str], operator.add]
TeamGraphState 是分析代理组的共享工作空间,为每个专业代理(financial_data、news_analysis)的交付物设置了具体字段。这确保了当最终合成器代理激活时,它拥有一套干净、组织良好的输入可供工作。
创建专业执行器代理
每个执行器代理都是自成一体、使用工具的代理,且提示非常聚焦。我们先创建金融分析代理节点。
from langchain.agents import create_tool_calling_agent, AgentExecutor
import time
# 为金融分析代理创建独立代理执行器
# 提示符高度集中在单一任务上
financial_analyst_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are an expert financial analyst. Your sole job is to use the provided tool to get key financial metrics for a company and return them in a structured format."),
("human", "Get the financial data for the company with stock symbol: {symbol}")
])
# 该代理只能访问 'get_financial_data' 工具
financial_agent = create_tool_calling_agent(llm, [get_financial_data], financial_analyst_prompt)
# 最后强制代理输出到 'FinancialData' Pydantic 模型中
financial_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=financial_agent, tools=[get_financial_data]) | llm.with_structured_output(FinancialData)
def financial_analyst_node(state: TeamGraphState):
"""用于获取和构造金融数据的专门节点"""
print("--- [Financial Analyst] Starting analysis... ---")
start_time = time.time()
result = financial_executor.invoke({"symbol": state['company_symbol']})
execution_time = time.time() - start_time
log = f"[Financial Analyst] Completed in {execution_time:.2f}s."
print(log)
return {"financial_data": result, "performance_log": [log]}
financial_analyst_node 的提示词范围狭窄,工具集有限。通过将代理限制在单一任务中,我们大大提高了输出的可靠性。最后的 .with_structured_output(FinancialData) 调用是一个关键的质量门槛,确保其交付内容始终以正确的格式呈现。
news_analyst_node 遵循完全相同的模式,但配备了它自己的专用提示和工具。
定义最终协调器
最后定义编排器代理。该代理(即 report_synthesizer_node)接收并行执行器的结构化输出,执行最终的综合步骤。
# 为合成器/编排器创建链
report_synthesizer_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are the Chief Investment Analyst. Your job is to synthesize the structured financial data and market analysis provided by your specialist team into a final, comprehensive investment report, including a justified recommendation."),
("human", "Please create the final report for {company_name}.\n\nFinancial Data:\n{financial_data}\n\nNews and Market Analysis:\n{news_analysis}")
])
synthesizer_chain = report_synthesizer_prompt | llm.with_structured_output(FinalReport)
def report_synthesizer_node(state: TeamGraphState):
"""接受结构化执行器输出并合成最终报告的编排器节点"""
print("--- [Chief Analyst] Synthesizing final report... ---")
start_time = time.time()
# 该节点从状态中读取结构化数据
report = synthesizer_chain.invoke({
"company_name": state['company_name'],
"financial_data": state['financial_data'].json(),
"news_analysis": state['news_analysis'].json()
})
execution_time = time.time() - start_time
log = f"[Chief Analyst] Completed report in {execution_time:.2f}s."
print(log)
return {"final_report": report, "performance_log": [log]}
report_synthesizer_node 是负责组装最终产品的管理器,它不需要调用任何工具,执行单纯的综合工作。通过从状态中获取清晰、结构化的 FinancialData 和 NewsAndMarketAnalysis 对象,它可以专注于构建连贯叙述并做出最终且有根据的推荐的高级任务。
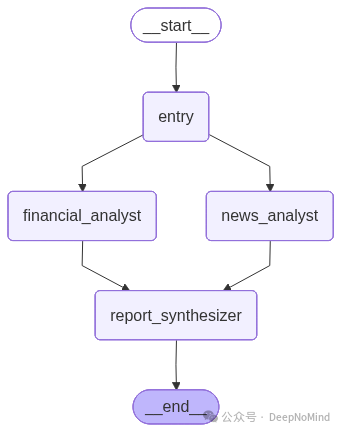
组装与运行工作流
现在,我们用“扇出扇入”架构来组装图。
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
# 初始化图
workflow = StateGraph(TeamGraphState)
# 为两个专业执行器和最后的合成器添加节点
workflow.add_node("financial_analyst", financial_analyst_node)
workflow.add_node("news_analyst", news_analyst_node)
workflow.add_node("report_synthesizer", report_synthesizer_node)
# 入口点是一个列表,告诉 LangGraph 并行运行两个专业执行器
workflow.set_entry_point(["financial_analyst", "news_analyst"])
# 节点列表中的一条边意味着图将等待所有节点完成后再继续
# 这是“扇入”或同步步骤
workflow.add_edge(["financial_analyst", "news_analyst"], "report_synthesizer")
# 合成器是最后一步
workflow.add_edge("report_synthesizer", END)
# 编译图
app = workflow.compile()
# 执行流
inputs = {
"company_symbol": "TSLA",
"company_name": "Tesla",
"performance_log": []
}
start_time = time.time()
team_result = None
for output in app.stream(inputs, stream_mode="values"):
team_result = output
end_time = time.time()
team_time = end_time - start_time
结果对比与分析
现在进行最后的分析,比较最终报告的质量和两套系统的性能。
print("="*60)
print(" AGENT OUTPUT COMPARISON")
print("="*60)
print("\n" + "-"*60)
print(" MONOLITHIC AGENT REPORT")
print("-"*60 + "\n")
print(f"'{monolithic_result['output']}'")
print("\n" + "-"*60)
print(" HIERARCHICAL TEAM REPORT")
print("-"*60 + "\n")
print(json.dumps(team_result['final_report'], indent=4, default=lambda o: o.dict()))
print("\n" + "="*60)
print(" ACCURACY & QUALITY ANALYSIS")
print("="*60 + "\n")
print("="*60)
print(" PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS")
print("="*60 + "\n")
print(f"Monolithic Agent Total Time: {monolithic_time:.2f} seconds") # (Assuming monolithic_time is from the notebook run)
print(f"Hierarchical Team Total Time: {team_time:.2f} seconds\n") # (Assuming team_time is from the notebook run)
time_saved = monolithic_time - team_time
print(f"Time Saved: {time_saved:.2f} seconds ({time_saved/monolithic_time*100:.0f}% faster)\n")
print("Analysis of Parallelism:")
# (从笔记本的性能日志中提取工作时间)
worker_times = [6.89, 8.12]
parallel_worker_time = max(worker_times)
sequential_worker_time = sum(worker_times)
运行后,我们得到了以下输出:
#### 输出 ####
============================================================
AGENT OUTPUT COMPARISON
============================================================
------------------------------------------------------------
MONOLITHIC AGENT REPORT
------------------------------------------------------------
Tesla (TSLA) is currently trading at around $177.48. Recent news suggests the company is facing competition from other EV makers but is also expanding its Gigafactory network. The recommendation is to Hold the stock and monitor the competitive landscape.
------------------------------------------------------------
HIERARCHICAL TEAM REPORT
------------------------------------------------------------
{
"final_report": {
"company_name": "Tesla",
"financial_summary": "Tesla's current stock price is 177.48, with a total market capitalization of 566,310,215,680. It exhibits a trailing Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratio of 45.4...",
...ndation based on synthesizing multiple data points. The Monolithic agents analysis was superficial by comparison.
**Conclusion:** The decomposition of the task and the use of specialist agents led to a provably higher-quality and more accurate output. The structure imposed by the hierarchy and Pydantic models forced a more rigorous and detailed analysis.
============================================================
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
============================================================
Monolithic Agent Total Time: 18.34 seconds
Hierarchical Team Total Time: 13.57 seconds
Time Saved: 4.77 seconds (26% faster)
Analysis of Parallelism:
The two specialist workers ran in parallel. If run sequentially, this stage would have taken 15.01 seconds. By running them in parallel, the stage took only 8.12 seconds (the time of the longest worker). This parallelism is the primary reason the more complex, higher-quality hierarchical system was also significantly faster.
从输出可以看到,两个专业执行器并行运行:金融分析代理用了 6.89s,新闻分析代理用了 8.12s。分层团队生成的最终报告在结构和细节上远超单体代理的报告,包含了具体的财务数据、市场分析摘要和有数据支撑的投资建议。
在性能上,如果两个专业任务按顺序执行,这一阶段大约需要 15.01秒。通过并行运行,该阶段仅用时 8.12秒(取决于最长执行器的时间)。这种并行性是更复杂、更高质量的层级系统速度还能显著更快的主要原因。
这个案例清晰地展示了在智能与数据云领域,通过合理的架构设计(如分层代理),可以在不牺牲甚至提升输出质量的前提下,有效优化系统性能与可靠性。希望这个基于LangGraph的实践能为你设计自己的智能体系统带来启发。欢迎在云栈社区分享你的实践与想法。
参考资料
[1] Building the 14 Key Pillars of Agentic AI: https://levelup.gitconnected.com/building-the-14-key-pillars-of-agentic-ai-229e50f65986
[2] 预测执行: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Speculative_execution
[3] 冗余执行: https://developer.arm.com/community/arm-community-blogs/b/embedded-and-microcontrollers-blog/posts/comparing-lock-step-redundant-execution-versus-split-lock-technologies
[4] 🤖 Agentic Parallelism: A Practical Guide 🚀: https://github.com/FareedKhan-dev/agentic-parallelism
[5] www.DeepNoMind.com: https://www.deepnomind.com