
OpenClaw 是目前全球用户规模最大的自托管个人 AI 助手。从 AI Agent 开发者的视角来看,它不仅仅是一个工具,更是一个极具参考价值的真实世界 Agent 设计范例。它能够帮助我们在构建 Agent 时,形成更加成熟和系统化的设计思路。在 云栈社区 的技术讨论中,我们经常探讨如何将这类优秀实践应用于自己的项目。
在本文中,我将深入探索 OpenClaw 的内部设计,并最终构建出一个揭示其运作原理的概念模型。
概念模型
下图是我构建的 OpenClaw 概念模型:
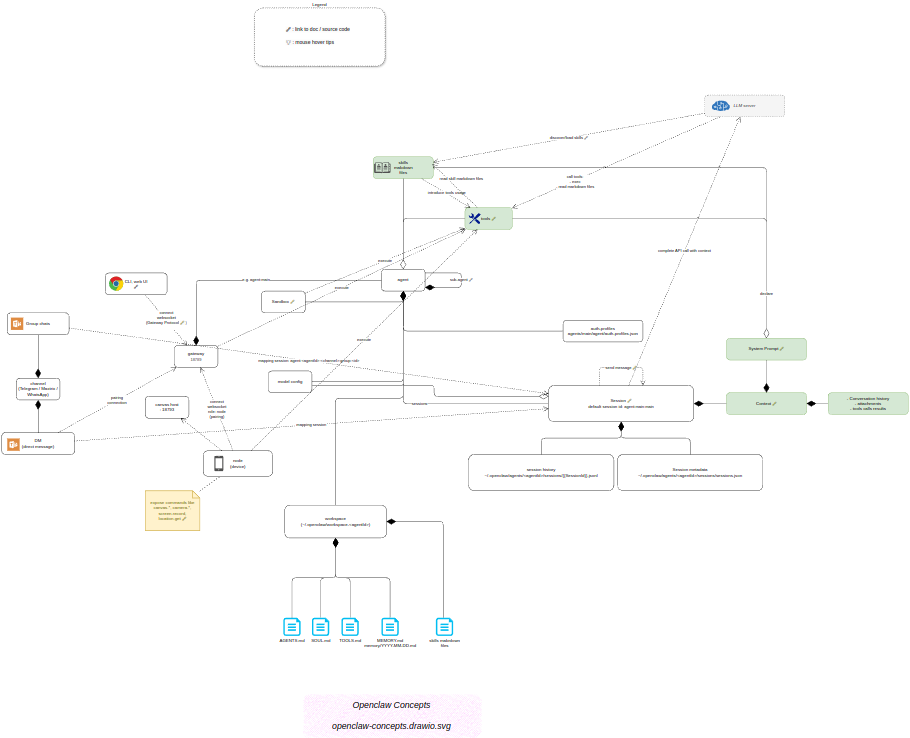
OpenClaw 概念模型(使用 Draw.io 打开[1])
该模型基于两个“事实来源”(source of truth):
文档分析
官方文档[3] 内容十分丰富,但其组织方式并非“循序渐进式”的概念教学结构。因此,在阅读过程中,我经常会在文档页面之间迷失方向。
问题的核心在于:文档缺乏一个整体性的概念地图,以及各个概念之间清晰、显式的关系描述。 在通读文档后,我尝试尽可能地提炼并还原这些概念之间的关联。这个过程本身,就是对一个复杂 人工智能 系统进行逆向工程的有趣实践。
掌握 Prompt 追踪
绝大多数 AI 应用的“核心秘密”,都隐藏在其 LLM Prompt 之中。但对 LLM 流量进行追踪,往往就像掉进了一个由非结构化数据组成的兔子洞。
有效的可观测性通常依赖两种主要方法:Tracing(追踪) 和 Sampling(采样)。
在我的实验环境中,我使用 OpenRouter[4] 作为 LLM 网关。它支持一种名为 Broadcast 的追踪复制机制(文档[5])。我将其配置为把追踪数据发送到我对外开放的、自托管的 Langfuse[6] 服务。
环境准备
为了演示 Prompt 追踪,我们需要一个会触发 OpenClaw 执行特定 Skill 的场景。
我选择了自己自托管的 Home Assistant 实例(用于管理智能家居设备)作为目标环境。为了完成集成,我从以下地址安装了所需的 Skill:https://clawhub.ai/dbhurley/homeassistant[7],并将其放置到目录:
~/.openclaw/workspace/skills/homeassistant
同时,别忘了设置环境变量(通常配置在 ~/.openclaw/.env 中):
HA_URL=http://your-ha-host:8123
HA_TOKEN=your_ha_token
理解 Agent Skill 的“魔法”
打开 OpenClaw Dashboard,新建一个聊天会话,并输入以下 Prompt:
Any smart home device in my study room?
为什么要使用 OpenClaw Dashboard,而不是 IM 客户端?
虽然 OpenClaw 支持 Telegram、WhatsApp 等主流即时通讯工具,但在开发和调试阶段,原生 Dashboard 更具优势。与普通聊天界面不同,Dashboard 提供了一个高可见度的“检查模式”,能够实时展示 Agent 即将调用的 tool 及其参数、系统返回的原始执行结果。这种透明性对于验证 Agent 行为至关重要。
接下来,打开 Langfuse Dashboard,进入 Tracing 页面。你将看到捕获到的一系列 Trace。这为我们深入理解其内部数据流提供了绝佳的 运维/DevOps/SRE 观测窗口。我们按时间顺序分析前两个 Trace,以理解 Skill 的发现、加载与调用机制。
1. Skill 发现
LLM 输入 —— Messages:
You are a personal assistant running inside OpenClaw.
...
## Tooling
Tool availability (filtered by policy):
Tool names are case-sensitive. Call tools exactly as listed.
- read: Read file contents
- write: Create or overwrite files
...
## Skills (mandatory)
Before replying: scan <available_skills><description> entries.
- If exactly one skill clearly applies: read its SKILL.md at <location> with `read`, then follow it.
- If multiple could apply: choose the most specific one, then read/follow it.
- If none clearly apply: do not read any SKILL.md.
Constraints: never read more than one skill up front; only read after selecting.
The following skills provide specialized instructions for specific tasks.
Use the read tool to load a skill‘s file when the task matches its description.
<available_skills>
...
<skill>
<name>homeassistant</name>
<description>Control Home Assistant - smart plugs, lights, scenes, automations.</description>
<location>~/.openclaw/workspace/skills/homeassistant/SKILL.md</location>
</skill>
</available_skills>
LLM 输入 —— Tool 声明:
tools: [
{
type: "function",
function: {
name: "read",
description: "Read the contents of a file...",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
path: { "type": "string" },
...
file_path: { "type": "string" }
}
}
}
}
]
LLM 输出:
completion: "read{\"path\": \"~/.openclaw/workspace/skills/homeassistant/SKILL.md\"}",
reasoning: "用户在询问书房里的智能家居设备,这与 Home Assistant Skill 完全匹配,因此需要加载该 Skill 的说明文档。"
此时,LLM 主动调用 read 工具,读取对应 Skill 的 SKILL.md 文件。
2. Skill 加载
Agent 接收到 LLM 的 Tool Call 后,执行 read,并将 SKILL.md 内容返回给 LLM。
LLM 输入(节选):
messages: [
...
{
role: "tool"
content: "---
name: homeassistant
description: Control Home Assistant - smart plugs, lights, scenes, automations.
homepage: https://www.home-assistant.io/
metadata: {"clawdis":{"emoji":"🏠","requires":{"bins":["curl"],"env":["HA_TOKEN"]},"primaryEnv":"HA_TOKEN"}}
---
# Home Assistant
Control smart home devices via Home Assistant API.
## Setup
Set environment variables:
- `HA_URL`: Your Home Assistant URL (e.g., `http://192.168.1.100:8123`)
- `HA_TOKEN`: Long-lived access token (create in HA → Profile → Long-Lived Access Tokens)
## Quick Commands
### List entities by domain
```bash
curl -s \"$HA_URL/api/states\" -H \"Authorization: Bearer $HA_TOKEN\" | \
jq -r '.[] | select(.entity_id | startswith(\"switch.\")) | .entity_id'
...
"
随后,**LLM 输出**:
```json
completion: "exec{\"command\": \"curl -s \\\"$HA_URL/api/states\\\" -H \\\"Authorization: Bearer $HA_TOKEN\\\" | jq -r '.[] | select(.attributes.area_name // .attributes.room // .entity_id | contains(\\\"study\\\")) | {entity_id: .entity_id, name: .attributes.friendly_name, state: .state, area: (.attributes.area_name // \\\"N/A\\\")}' | head -20\"}"
在理解了 homeassistant Skill 的文档后,LLM 发起了一个 exec Tool Call,通过命令行访问 Home Assistant 的 HTTP API。
这里最巧妙的设计点在于安全性:
Agent 不会 将真实的 Token 或凭据直接传递给 LLM。 Skill 使用环境变量来注入敏感信息,从而确保这些秘密:不会暴露在 LLM 的上下文中、不会被记录在 Trace 历史里。
这是一个值得借鉴的 Agent 安全设计模式。当然,OpenClaw 的设计哲学中也包含了一些被业界认为不够安全的实践,所以,参考时还需结合具体场景多加甄别。
参考资料
[1] 使用 Draw.io 打开: https://app.diagrams.net/?ui=sketch#Uhttps%3A%2F%2Fblog.mygraphql.com%2Fen%2Fposts%2Fai%2Fai-personal-assistant%2Fopenclaw-concepts%2Fopenclaw-concepts.drawio.svg
[2] https://docs.openclaw.ai/: https://docs.openclaw.ai/
[3] 官方文档: https://docs.openclaw.ai/
[4] OpenRouter: https://openrouter.ai/
[5] 文档: https://openrouter.ai/docs/guides/features/broadcast/overview
[6] Langfuse: https://langfuse.com/
[7] https://clawhub.ai/dbhurley/homeassistant: https://clawhub.ai/dbhurley/homeassistant