在Spring应用开发中,你是否曾遇到过这样的需求:在Service层或工具类中需要获取当前的HttpServletRequest对象?常见的做法无外乎两种,要么从Controller层开始层层传递这个参数,要么使用RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()。但你是否深入思考过,这个看似能“全局”获取的Request,其背后是如何实现线程安全的?又为何会在异步调用场景下失效?本文将深入源码,并结合具体场景,为你彻底剖析RequestContextHolder的工作原理与注意事项。
一、RequestContextHolder的本质是什么?
首先给出核心结论:RequestContextHolder是Spring框架对ThreadLocal的一层封装,其主要作用是存储当前线程的HTTP请求上下文(即RequestAttributes对象)。
要理解其实现,需要查看其核心的静态成员变量:
// RequestContextHolder.java
// 普通ThreadLocal:存储当前线程的RequestAttributes
private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> requestAttributesHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
// 可继承ThreadLocal:允许子线程继承父线程的RequestAttributes
private static final InheritableThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> inheritableRequestAttributesHolder = new InheritableThreadLocal<>();
这里的RequestAttributes是Spring对HTTP请求上下文的抽象接口,其具体实现ServletRequestAttributes封装了HttpServletRequest、HttpServletResponse等原生对象。
二、源码追踪:请求上下文如何绑定到线程?
RequestContextHolder的核心逻辑嵌入在DispatcherServlet的请求处理流程中。我们从Spring MVC处理请求的核心方法DispatcherServlet#doDispatch开始分析:
1. 入口:DispatcherServlet#doDispatch
// DispatcherServlet.java
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
// ... 省略其他前置逻辑
try {
// 关键步骤:初始化并绑定请求上下文到当前线程
initContextHolders(request, response, mappedHandler);
// 实际调用Controller方法处理请求
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
// ... 省略后续视图渲染等逻辑
}
finally {
// 请求处理完毕,清理当前线程的上下文
resetContextHolders(request, response, mappedHandler);
}
}
其中,initContextHolders方法是实现上下文绑定的关键。
2. 绑定上下文:initContextHolders
// DispatcherServlet.java
private void initContextHolders(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler) {
// 将请求和响应对象封装为ServletRequestAttributes
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = new ServletRequestAttributes(request, response);
// 调用RequestContextHolder设置当前线程的上下文
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(attributes, this.detectIncludeRequest);
// ... 省略LocaleContext、ThemeSource等其他上下文的初始化
}
这里的detectIncludeRequest是一个Spring配置相关的标志(默认为false),它决定了是否使用可继承的ThreadLocal(即inheritableRequestAttributesHolder)。
3. 核心设置逻辑:RequestContextHolder#setRequestAttributes
// RequestContextHolder.java
public static void setRequestAttributes(@Nullable RequestAttributes attributes, boolean inheritable) {
if (attributes == null) {
resetRequestAttributes(); // 清空上下文
} else {
if (inheritable) {
// 使用可继承ThreadLocal,子线程可以获取父线程的上下文
inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.set(attributes);
requestAttributesHolder.remove();
} else {
// 使用普通ThreadLocal,上下文仅对当前线程可见
requestAttributesHolder.set(attributes);
inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.remove();
}
}
}
至此,当前HTTP请求的上下文就被存储到了当前线程的ThreadLocal变量中。之后在任何地方(如Service、工具类)调用RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(),本质上都是从当前线程的ThreadLocal中取出之前绑定的对象,进而可以获取HttpServletRequest:
// 工具类中获取当前请求的典型写法
public static HttpServletRequest getCurrentRequest() {
RequestAttributes attributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
return attributes != null ? ((ServletRequestAttributes) attributes).getRequest() : null;
}
三、可视化流程:UML时序图
为了更清晰地展示上述流程,以下是请求上下文绑定与获取的时序图:
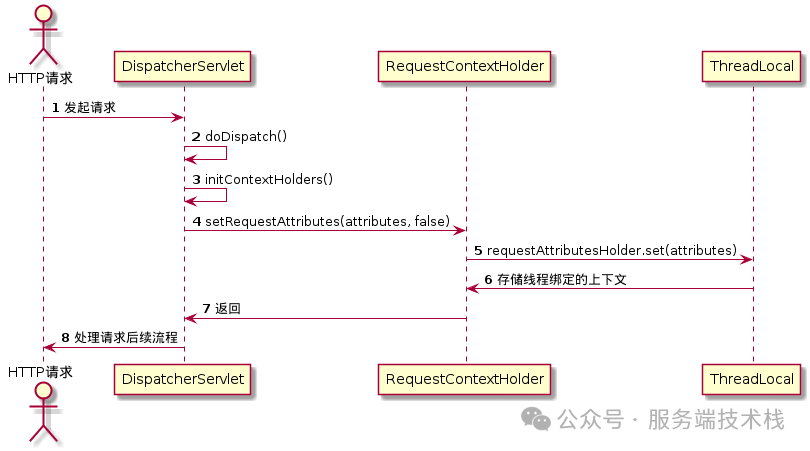
四、常见陷阱:为何异步线程中无法获取Request?
许多开发者在实践中会遇到一个典型的“坑”:在异步线程(例如使用@Async注解的方法或手动提交到线程池的任务)中,调用getRequest()方法会返回null。
其根本原因在于,普通的ThreadLocal变量存储的数据是线程隔离的,不会自动传递给新创建的子线程。示例如下:
// Controller层
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test() {
// 当前主线程(Tomcat工作线程)可以正常获取
System.out.println(RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()); // 非null
// 在新创建的异步线程中
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()); // 结果为null
});
return "ok";
}
解决此问题主要有两种思路:
- 启用可继承ThreadLocal模式:通过Spring配置(例如设置
spring.mvc.async.request-timeout或调整detectIncludeRequest策略),让RequestContextHolder使用inheritableRequestAttributesHolder。但需注意,如果使用线程池,由于线程复用,可继承ThreadLocal也可能失效。
- 使用增强型上下文传递工具:对于复杂的并发编程或线程池场景,推荐使用阿里开源的
TransmittableThreadLocal(TTL),它能够更好地解决线程池上下文传递的问题。
五、核心总结
本质上,RequestContextHolder并非什么高深的“黑魔法”,它只是Spring提供的一个基于ThreadLocal的线程上下文管理工具类。其设计目的是将HTTP请求的生命周期与处理线程绑定,使得在同一个请求处理链路上的任何位置都能便捷地获取请求上下文,从而避免了在方法参数中层层传递的繁琐。
然而,正因为其底层依赖于ThreadLocal,开发者必须清晰认知其线程作用域边界。在跨线程(尤其是异步任务、线程池任务)的场景下,默认的上下文传递会中断,需要根据具体情况采取上述的解决方案进行显式处理。理解这一机制,是构建健壮、可维护的Spring应用的重要一环。