做后端开发时,你一定遇到过「接口调用超时」「第三方服务偶发失败」的问题——重试是解决这类问题的常用手段。但你知道Spring Retry是如何帮你把「重试逻辑」封装成可复用组件的吗?这篇文章从RetryTemplate的核心流程入手,拆解Spring Retry的执行脉络,帮你搞懂「重试规则」「回退策略」是如何在Spring框架中配合工作的。
1. RetryTemplate:重试流程的「总指挥」
Spring Retry的核心入口是RetryTemplate,所有重试逻辑都围绕它的execute方法展开。我们先看最核心的doExecute方法——它是重试流程的「执行引擎」。
// RetryTemplate.java 核心方法简化
protected <T, E extends Throwable> T doExecute(
RetryCallback<T, E> retryCallback,
RecoveryCallback<T> recoveryCallback,
RetryState state) throws E, ExhaustedRetryException {
// 1. 初始化重试上下文
RetryContext context = open(retryCallback, state);
try {
// 2. 循环执行重试逻辑
while (canRetry(context)) {
try {
// 3. 执行业务回调(doWithRetry)
return retryCallback.doWithRetry(context);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
// 4. 记录异常,更新重试状态
registerThrowable(context, throwable);
// 5. 执行回退策略(如固定等待、指数退避)
backOff(context);
}
}
// 6. 重试耗尽,执行恢复逻辑
return recoveryCallback != null ? recoveryCallback.recover(context) : null;
} finally {
// 7. 关闭上下文
close(context);
}
}
关键逻辑说明:
open(...):创建重试上下文(RetryContext),保存重试次数、异常等状态;canRetry(context):委托给RetryPolicy判断是否继续重试(比如超过最大次数则返回false);retryCallback.doWithRetry(context):执行业务代码(比如调用第三方接口);registerThrowable(...):更新上下文的异常信息,供RetryPolicy判断;backOff(context):委托给BackOffPolicy执行回退(比如等待1秒后再重试)。
2. RetryPolicy:重试的「规则裁判」
RetryPolicy决定了「什么时候该重试」,Spring提供了SimpleRetryPolicy(固定次数)、TimeoutRetryPolicy(超时时间)等实现。我们以最常用的SimpleRetryPolicy为例,看它的canRetry方法:
// SimpleRetryPolicy.java 核心逻辑
public boolean canRetry(RetryContext context) {
// 1. 从上下文获取已重试次数
Integer retryCount = context.getRetryCount();
// 2. 判断是否超过最大重试次数(默认3次)
return retryCount < this.maxAttempts;
}
// 记录异常的方法(更新重试次数)
public void registerThrowable(RetryContext context, Throwable throwable) {
// 1. 标记异常是否是可重试的(比如忽略RuntimeException以外的异常)
boolean retryable = isRetryable(throwable);
if (retryable) {
// 2. 重试次数+1
context.registerThrowable(throwable);
} else {
// 3. 不可重试的异常,直接标记为耗尽
context.setExhaustedOnly();
}
}
关键结论:RetryPolicy通过「重试次数」和「异常类型」两个维度,决定是否继续重试。比如如果业务抛出NullPointerException,SimpleRetryPolicy默认会重试;但如果抛出IllegalStateException(需配置),则直接终止。
3. BackOffPolicy:重试的「节奏控制器」
BackOffPolicy决定了「重试之间该等多久」,避免频繁重试压垮服务。Spring提供FixedBackOffPolicy(固定等待)、ExponentialBackOffPolicy(指数退避)等实现。以FixedBackOffPolicy为例:
// FixedBackOffPolicy.java 核心逻辑
public void backOff(BackOffContext backOffContext) throws BackOffInterruptedException {
// 1. 从上下文获取等待时间(默认1000ms)
long backOffPeriod = ((FixedBackOffContext) backOffContext).getBackOffPeriod();
if (backOffPeriod > 0) {
try {
// 2. 睡眠指定时间
Thread.sleep(backOffPeriod);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new BackOffInterruptedException("Thread interrupted while backing off", e);
}
}
}
注意:BackOffContext保存了回退的状态(比如指数退避的当前乘数),确保每次回退的时间符合策略。
4. 完整流程:从调用到结束的时序脉络
为了更清晰展示整个流程,我们绘制了UML时序图(点击查看高清图):
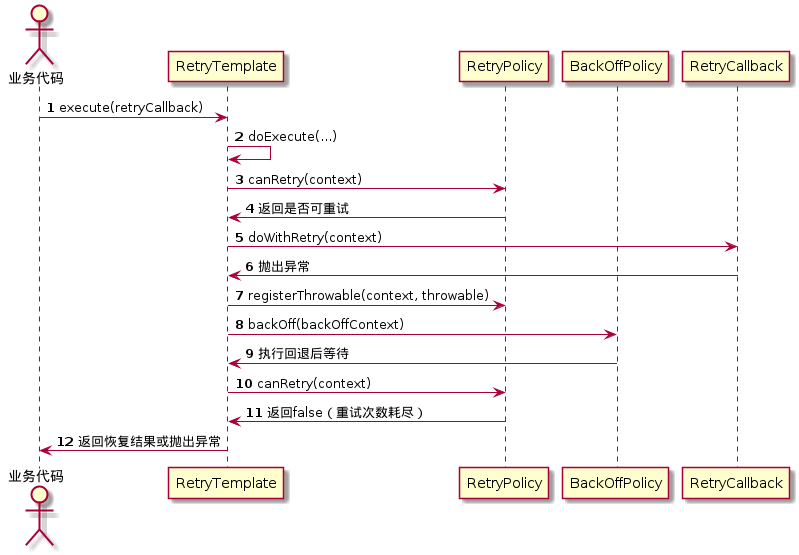
流程说明:
- 业务代码调用
RetryTemplate.execute(...);
RetryTemplate初始化上下文,进入循环;- 委托
RetryPolicy判断是否可重试;
- 执行业务回调(
doWithRetry),若抛出异常则记录并执行回退;
- 回退后再次判断是否可重试,直到次数耗尽;
- 重试耗尽后,执行恢复逻辑(或抛出异常)。
5. 实战:如何自定义重试策略?
如果默认的SimpleRetryPolicy满足不了需求(比如需要「失败3次后,第4次等待5秒再重试」),我们可以自定义RetryPolicy:
// 自定义RetryPolicy:前3次立即重试,第4次等待5秒
public class CustomRetryPolicy implements RetryPolicy {
private int maxAttempts = 4;
private long backOffPeriod = 5000;
@Override
public boolean canRetry(RetryContext context) {
int retryCount = context.getRetryCount();
if (retryCount < 3) return true;
// 第4次重试前等待5秒
if (retryCount == 3) {
try {
Thread.sleep(backOffPeriod);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 其他方法(open、close、registerThrowable)省略...
}
使用时,只需将CustomRetryPolicy注入RetryTemplate即可:
@Bean
public RetryTemplate retryTemplate() {
RetryTemplate template = new RetryTemplate();
template.setRetryPolicy(new CustomRetryPolicy());
return template;
}
结尾:重试不是「银弹」,但要懂它的「脉络」
Spring Retry的核心逻辑其实很简单——用RetryTemplate串联RetryPolicy和BackOffPolicy,通过上下文管理重试状态。但真正理解它,需要从源码看清楚「每一步是谁在做决策」:RetryPolicy管「能不能重试」,BackOffPolicy管「重试前等多久」,RetryTemplate管「流程的串联」。
最后需要强调的是,重试并非越多越好。例如在调用支付接口等网络请求时,无脑重试可能导致重复扣款。因此,在实际的高并发或分布式场景中应用重试,必须结合业务幂等性设计来规避副作用。理解框架的执行脉络,才能更好地驾驭它。