Python 已成为数据科学领域当之无愧的首选语言,其背后强大的生态系统则由一系列功能各异的专业库构成。这些库全面覆盖了数据处理、可视化分析、机器学习、深度学习及各类工程应用,为数据科学家和分析师提供了高效、完整的Python工具链。本文将系统梳理并介绍 30 个关键的 Python 数据科学库,帮助你快速掌握其核心功能与应用场景。
1. Pandas:数据分析的“瑞士军刀”
说明:最核心的数据处理与分析库,提供了 DataFrame 和 Series 两种核心数据结构,支持数据清洗、转换、合并、分组、聚合等丰富操作。
import pandas as pd
data = {'产品': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'],
'销售额': [1200, 1500, 1300, 1800],
'成本': [800, 900, 1000, 1200]}
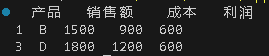
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df['利润'] = df['销售额'] - df['成本']
high_profit = df[df['利润'] > 400]
print(high_profit)
2. NumPy:科学计算基础库
说明:几乎所有数值计算库的基石,提供高效的 N 维数组对象和大量数学函数,支持大规模的矩阵与数组运算。
import numpy as np
arr1 = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
arr2 = np.ones((2, 3))
result = arr1 * arr2 + 3
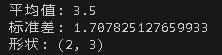
print("平均值:", np.mean(arr1))
print("标准差:", np.std(arr1))
print("形状:", arr1.shape)
3. Dask:并行计算库
说明:专为处理超出内存限制的大规模数据集而设计,能够并行化 Pandas DataFrame 和 NumPy 数组的操作。
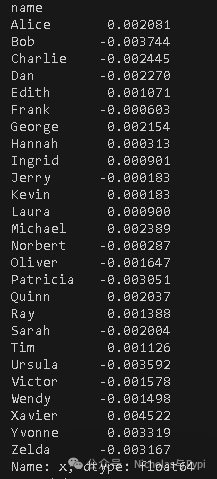
import dask.dataframe as dd
df = dd.demo.make_timeseries(npartitions=10, freq="15s", start_date="2020-01-01")
result = df.groupby('name').x.mean().compute()
print(result)
4. Polars:高性能DataFrame库
说明:采用 Rust 编写的高性能 DataFrame 库,拥有强大的查询优化器和表达式系统,在多核处理上表现优异。
import polars as pl
import numpy as np
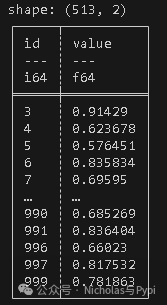
df = pl.DataFrame({
'id': range(1000),
'value': np.random.rand(1000)
})
result = df.filter(pl.col('value') > 0.5).group_by('id').agg(pl.col('value').mean())
print(result)
5. Matplotlib:基础绘图库
说明:Python 最基础的 2D 绘图库,提供了全面的图表绘制功能,是许多高级可视化库的底层依赖。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
y1 = np.sin(x)
y2 = np.cos(x)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(x, y1, label='sin(x)', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(x, y2, label='cos(x)', linestyle='--')
plt.xlabel('X轴')
plt.ylabel('Y轴')
plt.title('三角函数图')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
6. Seaborn:统计可视化库
说明:基于 Matplotlib,提供了更美观的默认样式和高级 API,特别擅长绘制复杂的统计图形。
import seaborn as sns
tips = sns.load_dataset('tips')
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, col='time', row='smoker')
g.map(sns.scatterplot, 'total_bill', 'tip', alpha=0.7)
g.add_legend()
g.fig.suptitle('小费与总账单关系图', y=1.03)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
7. Plotly:交互式可视化库
说明:功能强大的交互式图表库,支持缩放、平移、数据点悬停等丰富的交互操作,可生成网页或 Notebook 内嵌图表。
import plotly.express as px
df = px.data.gapminder().query("year == 2007")
fig = px.scatter(df, x='gdpPercap', y='lifeExp', size='pop',
color='continent', hover_name='country',
log_x=True, size_max=60,
title='2007年国家GDP与寿命关系')
fig.show()
8. Bokeh:Web交互式可视化
说明:专注于在现代 Web 浏览器中创建交互式、可缩放的可视化图表,尤其适合处理大规模或流式数据集。
from bokeh.plotting import figure, show
from bokeh.io import output_notebook
from bokeh.models import HoverTool
output_notebook()
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
y = [6, 7, 2, 4, 8]
p = figure(title='简单折线图', x_axis_label='X', y_axis_label='Y')
p.line(x, y, line_width=2, legend_label='趋势线')
p.scatter(x, y, size=10, fill_color='white')
hover = HoverTool(tooltips=[('值', '@y')])
p.add_tools(hover)
show(p)
9. Scikit-learn:经典机器学习库
说明:应用最广泛的机器学习库之一,提供了统一的 API 用于数据预处理、模型训练、评估和选择,涵盖了几乎所有经典机器学习算法。
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report
iris = load_iris()
X, y = iris.data, iris.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3)
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
print(f'准确率: {accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred):.2f}')
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred, target_names=iris.target_names))
10. XGBoost:梯度提升库
说明:高度优化的分布式梯度提升库,以出色的性能和精度在众多数据科学竞赛中脱颖而出。
import xgboost as xgb
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=10, random_state=42)
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(X, label=y)
params = {
'max_depth': 6,
'eta': 0.3,
'objective': 'binary:logistic',
'eval_metric': 'logloss'
}
model = xgb.train(params, dtrain, num_boost_round=100)
y_pred = model.predict(dtrain)
y_binary = [1 if p > 0.5 else 0 for p in y_pred]
print('预测结果:', y_binary[:10])
11. LightGBM:轻量级梯度提升机
说明:微软开发的基于决策树算法的梯度提升框架,以其极快的训练速度、高效的内存利用和良好的准确度而闻名。
import lightgbm as lgb
import numpy as np
X = np.random.rand(1000, 10)
y = np.random.randint(0, 2, 1000)
train_data = lgb.Dataset(X, label=y)
params = {
'objective': 'binary',
'metric': 'binary_logloss',
'num_leaves': 31,
'learning_rate': 0.05
}
model = lgb.train(params, train_data, num_boost_round=100)
importance = model.feature_importance()
print('特征重要性:', importance)
12. Statsmodels:统计分析库
说明:专注于传统统计学的库,提供了线性回归、时间序列分析、假设检验等丰富的统计模型和检验方法。
import statsmodels.api as sm
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(42)
X = np.random.randn(100, 2)
y = 2.5 + 1.2 * X[:,0] + 0.8 * X[:,1] + np.random.randn(100) * 0.5
X = sm.add_constant(X)
model = sm.OLS(y, X).fit()
print(model.summary())
13. TensorFlow:端到端机器学习平台
说明:由 Google 开发的开源机器学习框架,支持从研究原型设计到生产环境部署的全流程,尤其在深度学习领域应用广泛。
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers, models
import numpy as np
model = models.Sequential([
layers.Dense(64, activation='relu', input_shape=(10,)),
layers.Dropout(0.2),
layers.Dense(32, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
model.summary()
X_train = np.random.random((1000, 10))
y_train = np.random.randint(0, 2, (1000, 1))
history = model.fit(X_train, y_train, epochs=10, batch_size=32, validation_split=0.2)
14. PyTorch:灵活深度学习框架
说明:由 Facebook 开发,以其动态计算图(现已支持静态图)和直观的编程接口深受学术界和研究人员喜爱,是人工智能研究的主流工具之一。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
class SimpleNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(SimpleNN, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(10, 50)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(50, 20)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(20, 1)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = self.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.sigmoid(self.fc3(x))
return x
model = SimpleNN()
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
X = torch.randn(100, 10)
y = torch.randint(0, 2, (100, 1)).float()
for epoch in range(10):
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(X)
loss = criterion(outputs, y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if epoch % 5 == 0:
print(f'Epoch {epoch}, Loss: {loss.item():.4f}')
15. Keras:高级神经网络API
说明:作为 TensorFlow 的高级 API,Keras 提供了极其简洁直观的接口来构建和训练深度学习模型,大大降低了入门门槛。
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
model = keras.Sequential([
layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu', input_shape=(28, 28, 1)),
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'),
layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)),
layers.Flatten(),
layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
keras.utils.plot_model(model, show_shapes=True)
16. NLTK:自然语言工具包
说明:用于构建 Python 程序来处理人类语言数据的经典平台,提供了丰富的语料库和算法,非常适合教学和研究入门。
import nltk
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize, sent_tokenize
from nltk.corpus import stopwords
from nltk.stem import PorterStemmer
nltk.download('punkt')
nltk.download('stopwords')
text = "Natural language processing is a fascinating field. It helps computers understand human language."
sentences = sent_tokenize(text)
tokens = word_tokenize(text)
stop_words = set(stopwords.words('english'))
filtered_words = [word for word in tokens if word.lower() not in stop_words]
stemmer = PorterStemmer()
stemmed = [stemmer.stem(word) for word in filtered_words]
print("句子分割:", sentences)
print("词语分割:", tokens)
print("去除停用词:", filtered_words)
print("词干提取:", stemmed)
17. spaCy:工业级NLP库
说明:专为生产环境设计的自然语言处理库,提供了预训练模型和高效的流水线,在速度和精度上都有出色表现。
import spacy
nlp = spacy.load('en_core_web_sm')
text = "Apple is looking at buying U.K. startup for $1 billion. The meeting happened in New York."
doc = nlp(text)
print("命名实体识别:")
for ent in doc.ents:
print(f"{ent.text} - {ent.label_} - {spacy.explain(ent.label_)}")
print("\n词性标注:")
for token in doc:
print(f"{token.text} - {token.pos_} - {spacy.explain(token.pos_)}")
18. Gensim:主题建模库
说明:专注于无监督主题建模和文档语义相似度计算的库,能够高效处理大规模的文本语料。
from gensim import corpora
from gensim.models import LdaModel
from gensim.parsing.preprocessing import preprocess_string
documents = [
"Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence",
"Deep learning uses neural networks with multiple layers",
"Natural language processing helps computers understand text",
"Computer vision enables machines to interpret images"
]
processed_docs = [preprocess_string(doc) for doc in documents]
dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(processed_docs)
corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(doc) for doc in processed_docs]
lda_model = LdaModel(corpus=corpus, id2word=dictionary,
num_topics=2, random_state=42, passes=10)
for idx, topic in lda_model.print_topics():
print(f"主题 {idx}: {topic}")
19. OpenCV:计算机视觉库
说明:功能强大的开源计算机视觉和机器学习软件库,包含数千种优化算法,涵盖图像处理、物体识别、视频分析等。
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
image = np.zeros((300, 300), dtype=np.uint8)
for i in range(300):
image[:, i] = i * 255 / 299
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(image, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
edges = cv2.Canny(image, 100, 200)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(15, 5))
axes[0].imshow(image, cmap='gray')
axes[0].set_title('原图')
axes[1].imshow(thresh, cmap='gray')
axes[1].set_title('阈值处理')
axes[2].imshow(edges, cmap='gray')
axes[2].set_title('边缘检测')
for ax in axes:
ax.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
20. Pillow:图像处理库
说明:Python 图像处理库 PIL 的友好分支,支持广泛的图像文件格式,并提供了基本的图像处理功能。
from PIL import Image, ImageFilter, ImageDraw, ImageFont
img = Image.new('RGB', (400, 300), color='lightblue')
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
draw.rectangle([50, 50, 200, 150], fill='red', outline='darkred')
draw.ellipse([250, 100, 350, 200], fill='green', outline='darkgreen')
try:
font = ImageFont.truetype("arial.ttf", 24)
except:
font = ImageFont.load_default()
draw.text((150, 250), "Pillow示例", fill='black', font=font)
filtered_img = img.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR)
img.show()
filtered_img.show()
21. Requests:HTTP库
说明:人性化、简单易用的 HTTP 库,让发送 HTTP/1.1 请求变得异常简单,是进行网络 API 调用的首选。
import requests
import json
response = requests.get(' https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts')
if response.status_code == 200:
posts = response.json()
for i, post in enumerate(posts[:3]):
print(f"{i+1}. 标题: {post['title']}")
print(f" 内容: {post['body'][:50]}...")
print()
new_post = {
'title': '测试标题',
'body': '测试内容',
'userId': 1
}
response = requests.post(' https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts', json=new_post)
print(f"POST响应状态: {response.status_code}")
22. Scrapy:网络爬虫框架
说明:一个快速、高层次的 Web 爬取框架,用于抓取网站数据并从网页中提取结构化数据,广泛应用于数据挖掘和监测。
import scrapy
from scrapy.crawler import CrawlerProcess
class QuoteSpider(scrapy.Spider):
name = 'quotes'
start_urls = [' http://quotes.toscrape.com/page/1/' ]
def parse(self, response):
for quote in response.css('div.quote'):
yield {
'text': quote.css('span.text::text').get(),
'author': quote.css('small.author::text').get(),
'tags': quote.css('div.tags a.tag::text').getall()
}
next_page = response.css('li.next a::attr(href)').get()
if next_page is not None:
yield response.follow(next_page, self.parse)
process = CrawlerProcess(settings={
'FEED_FORMAT': 'json',
'FEED_URI': 'quotes.json'
})
process.crawl(QuoteSpider)
process.start()
23. SQLAlchemy:数据库ORM
说明:Python 中最著名的 SQL 工具包和对象关系映射(ORM)库,提供了企业级的持久化模式,能够高效、灵活地操作多种数据库/中间件。
from sqlalchemy import create_engine, Column, Integer, String
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
Base = declarative_base()
class User(Base):
__tablename__ = 'users'
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True)
name = Column(String(50))
email = Column(String(100))
def __repr__(self):
return f"<User(name='{self.name}', email='{self.email}')>"
engine = create_engine('sqlite:///example.db')
Base.metadata.create_all(engine)
Session = sessionmaker(bind=engine)
session = Session()
new_user = User(name='张三', email='zhangsan@example.com')
session.add(new_user)
session.commit()
users = session.query(User).all()
for user in users:
print(user)
24. Jupyter:交互式计算环境
说明:开源的 Web 应用程序,允许你创建和共享包含实时代码、数学公式、可视化及叙述性文本的文档,是数据探索和教学的绝佳工具。
# 在Jupyter Notebook中运行
%matplotlib inline
%timeit [x**2 for x in range(1000)]
from IPython.core.interactiveshell import InteractiveShell
InteractiveShell.ast_node_interactivity = "all"
from ipyparallel import Client
rc = Client()
view = rc[:]
result = view.map(lambda x: x**2, range(10))
print("并行计算结果:", result.get())
25. SciPy:科学计算库
说明:基于 NumPy 构建,提供用于数学、科学和工程计算的模块,包括优化、线性代数、积分、插值、信号处理等。
from scipy import optimize
import numpy as np
def f(x):
return x**2 + 10*np.sin(x)
result = optimize.minimize(f, x0=0)
print("最小值:", result.x)
print("函数值:", result.fun)
26. BeautifulSoup:网页解析库
说明:用于从 HTML 和 XML 文件中提取数据的 Python 库,它能将复杂的文档转换为复杂的树形结构,便于遍历和搜索。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """<html><head><title>测试页面</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>测试文档</b></p>
<p class="content">这是一个测试段落。</p>
</body></html>"""
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'html.parser')
print("标题:", soup.title.string)
print("段落:", soup.find('p', class_='content').text)
27. PyMySQL:MySQL客户端库
说明:一个纯 Python 实现的 MySQL 客户端库,用于连接和操作 MySQL 数据库。
import pymysql
# 连接数据库
connection = pymysql.connect(
host='localhost',
user='username',
password='password',
database='test_db'
)
try:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
# 创建表
cursor.execute("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (id INT, name VARCHAR(50))")
# 插入数据
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO users VALUES (1, '张三')")
connection.commit()
print("数据插入成功")
finally:
connection.close()
28. Os:操作系统交互库
说明:Python 标准库中的模块,提供了丰富的方法来处理文件和目录,与操作系统进行交互。
import os
# 获取当前工作目录
print("当前目录:", os.getcwd())
# 列出目录内容
print("目录内容:", os.listdir('.'))
# 创建目录
os.makedirs('test_dir', exist_ok=True)
print("目录创建成功")
# 环境变量
print("PATH环境变量:", os.getenv('PATH'))
29. Sys:系统相关功能库
说明:提供对 Python 解释器密切相关的一些变量和函数的访问,如命令行参数、模块搜索路径等。
import sys
# Python版本信息
print("Python版本:", sys.version)
# 命令行参数
print("命令行参数:", sys.argv)
# 模块搜索路径
print("模块路径:", sys.path[:3])
# 退出程序
# sys.exit(0)
30. Re:正则表达式库
说明:Python 的标准库,提供了 Perl 风格的正则表达式操作,是进行复杂字符串匹配、查找和替换的强大工具。
import re
text = "我的电话是123-4567-8901,邮箱是test@example.com"
# 匹配电话号码
phone_pattern = r'\d{3}-\d{4}-\d{4}'
phones = re.findall(phone_pattern, text)
print("电话号码:", phones)
# 匹配邮箱
email_pattern = r'\b[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z|a-z]{2,}\b'
emails = re.findall(email_pattern, text)
print("邮箱地址:", emails)
# 替换文本
new_text = re.sub(phone_pattern, '***-****-****', text)
print("替换后文本:", new_text)
总结与建议
Python 数据科学库生态繁荣,覆盖了从数据获取、清洗、分析到建模、可视化乃至部署的完整链条。合理选择和组合使用这些工具,能极大提升工作效率。
- 根据任务规模选型:处理中小型数据,Pandas 是首选;面对超出内存的大数据,可考虑 Dask 或 Polars 等并行/高性能方案。
- 掌握核心,逐步扩展:优先精通 NumPy、Pandas、Matplotlib、Scikit-learn 等核心库,再根据项目需求学习其他领域专用库。
- 善用文档与社区:优秀的开源库通常拥有完善的文档和活跃的社区,遇到问题时这是最好的学习资源。
- 实践出真知:理论学习结合项目实践是掌握这些工具最快、最有效的方式。