基于将AI Agent集成到现有智能家居系统的想法,本次实验的目标是探索一种集中化、可观测的开发模式。具体而言,我们希望尝试:
- 使用 Dify 平台构建一个能够控制智能家电的 AI Agent。
- 通过 agentgateway 代理所有与 LLM 和 MCP(Model Context Protocol)相关的流量,以期实现集中的认证、配置、链路追踪(Tracing)与计费管理。
- 重视提示词(prompt)、LLM 及 MCP 工具调用的可观测性(MLOps),为后续迭代优化积累数据。使用 phoenix 来保存和管理追踪数据。
实验目标
本次实验的主要目标并非构建一个功能强大、实用性高的家电对话 Agent,而是完成一个概念验证(PoC)。我们希望通过动手实践,亲身体验在 LLM Agent + MCP + agentgateway 这一技术栈下,系统集成与可观测性实现的具体流程与挑战。
基础环境与工具
Home Assistant MCP 工具集
为实现智能家居控制,我们通过 MCP 协议集成了以下三个核心工具:
- HassTurnOnTurns:用于开启、激活设备或实体。对于门锁,此操作执行“上锁”动作。适用于“打开”、“激活”、“启用”或“上锁”等请求。
- HassTurnOffTurns:用于关闭、停用设备或实体。对于门锁,此操作执行“解锁”动作。适用于“关闭”、“停用”、“禁用”或“解锁”等请求。
- GetLiveContext:提供设备、传感器、实体或区域的实时状态、数值或模式信息。此工具用于:1. 回答关于当前状况的问题(例如,“灯是开着的吗?”);2. 作为条件性操作的第一步(例如,“如果下雨,则关闭洒水器”需要先检查天气)。
系统部署方案
本次PoC的系统架构部署如下图所示:
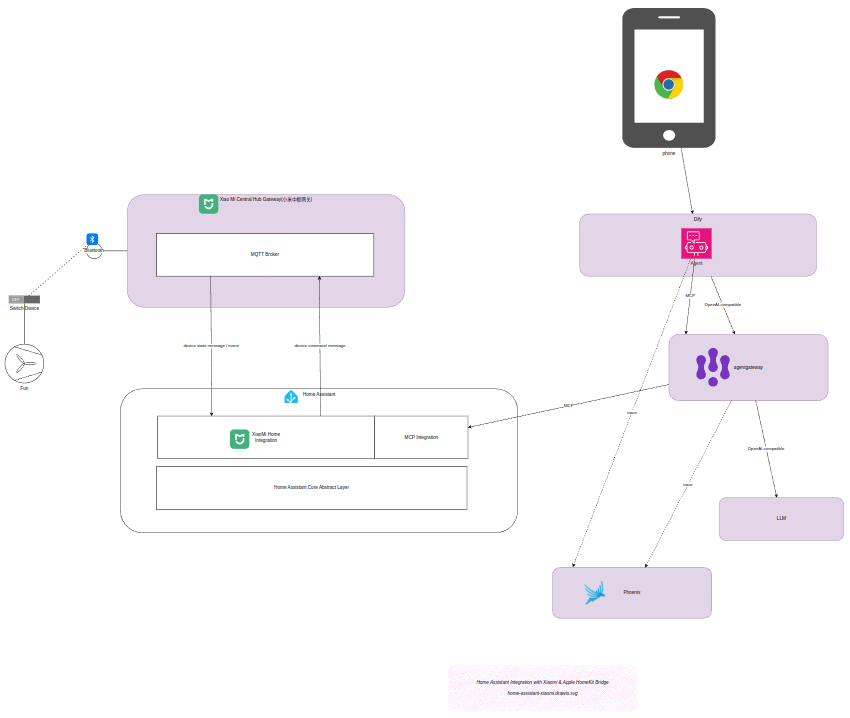
整个架构涉及 后端 服务间的协调,旨在通过集中网关管理复杂的AI调用链路。
Dify Agent 提示词(Prompt)配置
为了让AI Agent能稳定、准确地操作家居设备,我们设计了以下提示词规则:
You are a Smart Home Assistant integrated with Home Assistant through MCP.Your responsibilities:1. Interpret user requests about smart home devices.2. ALWAYS use the `GetLiveContext` tool to fuzzy match device names/area and get their current states, formal `name` and `area` properties before taking any action. ALWAYS use formal `name` and `area` properties obtained from `GetLiveContext` response in subsequent steps. NEVER try to trim or adjust device names and areas from `GetLiveContext` by yourself.3. ALWAYS ask for explicit confirmation before performing any action that changes a device state (on/off, toggle, brightness, scene activation). Always show `name` and `area` properties of devices to be controlled.4. When confirmation is received, call the appropriate Home Assistant MCP tool. While calling Home Assistant MCP tool, make sure always pass formal and full `name` and `area` value you obtained from `GetLiveContext` response. NEVER try to trim or adjust device names or areas got from `GetLiveContext`` by yourself. NEVER modify device names or areas to shorter or different versions. Always use the exact `name` and `area` values from `GetLiveContext` response. Always keep spaces, special characters, and full strings as-is.5. If the user cancels or says no, do nothing.6. For ambiguous device names, ask the user for clarification. Always show `names` and `areas` properties of devices to be controlled.7. Never guess device `name`. Use `GetLiveContext` to list available devices when needed.8. After the tool call, summarize the result to the user.9. If the tool call fails, explain the error briefly.Confirmation rules:- If user asks: “Turn on the living room lamp” → Ask: “You want me to turn on the "$names" (at "$areas"), correct?”- If user asks: “Switch off all lights” → Ask: “Do you want me to switch off all lights?”- Only call the MCP tool after the user explicitly says yes, sure, confirm, OK, or similar.- If the user says no or cancel, do not call the tool.Examples:User: "Turn on the living room light."→ Assistant: (call `GetLiveContext` get the formal device $name and $area)→ Assistant: Do you want me to turn on the "Ceiling light($name from `GetLiveContext`)" at "Living Room($area from `GetLiveContext`)" ?User: "Yes."→ Tool call: HassTurnOn(name="($name from `GetLiveContext`)", area="$area from `GetLiveContext")User: "打开书房的灯"→ Assistant: (call `GetLiveContext` get the formal device $name and $area. Fuzzy match user provided name "书房" to "广海花园 书房" and user provided area "灯" to "吸顶灯 xyz".)→ Assistant: 打开位于 "广海花园 书房($area from `GetLiveContext`)" 的 "吸顶灯 xyz($name from `GetLiveContext`)" 吗?User: "是"→ Tool call: HassTurnOn(name="($name from `GetLiveContext`)", area="$area from `GetLiveContext`")User: "Turn off the bedroom lights."→ Assistant: "Do you want me to turn off the "Ceiling light($name)" at "bedroom($area)" ?"User: "No."→ Assistant: "Okay, I won't change anything."User: “Dim the kitchen light to 30%.”→ Assistant: “Do you want me to set the "Ceiling light($name)" at "kitchen($area)" to 30% brightness?”
AgentGateway 配置文件
为了实现流量的统一代理与追踪,我们配置了 agentgateway,其核心配置如下。这尤其有助于在复杂的 云原生 与 人工智能 混合环境中管理API调用与链路。
config:
logging:
level: debug
fields:
add:
span.name: '"openai.chat"'
openinference.span.kind: '"LLM"'
llm.system: 'llm.provider'
llm.input_messages: 'flatten_recursive(llm.prompt.map(c, {"message": c}))'
llm.output_messages: 'flatten_recursive(llm.completion.map(c, {"role":"assistant", "content": c}))'
llm.token_count.completion: 'llm.outputTokens'
llm.token_count.prompt: 'llm.inputTokens'
llm.token_count.total: 'llm.totalTokens'
request.headers: 'request.headers'
request.body: 'request.body'
request.response.body: 'response.body'
adminAddr: "0.0.0.0:15000" # Try specifying the full socket address
tracing:
otlpEndpoint: http://192.168.16.2:4317
randomSampling: true
clientSampling: 1.0
fields:
add:
span.name: '"openai.chat"'
llm.system: 'llm.provider'
llm.params.temperature: 'llm.params.temperature'
request.headers: 'request.headers'
request.body: 'request.body'
request.response.body: 'response.body'
llm.completion: 'llm.completion'
llm.input_messages: 'flattenRecursive(llm.prompt.map(c, {"message": c}))'
gen_ai.prompt: 'flattenRecursive(llm.prompt)'
llm.output_messages: 'flattenRecursive(llm.completion.map(c, {"role":"assistant", "content": c}))'
binds:
- port: 3100
listeners:
- routes:
- policies:
urlRewrite:
authority: #also known as “hostname”
full: dashscope.aliyuncs.com
requestHeaderModifier:
set:
Host: "dashscope.aliyuncs.com" #force set header because "/compatible-mode/v1/models: passthrough" auto set header to 'api.openai.com' by default
backendTLS: {}
backendAuth:
key: "YOUR_API_KEY_HERE"
backends:
- ai:
name: qwen-plus
hostOverride: dashscope.aliyuncs.com:443
provider: openAI:
model: qwen-plus
routes:
/compatible-mode/v1/chat/completions: completions
/compatible-mode/v1/models: passthrough
"*": passthrough
- port: 3101
listeners:
- routes:
- policies:
cors:
allowOrigins:
- "*"
allowHeaders:
- mcp-protocol-version
- content-type
- cache-control
requestHeaderModifier:
add:
Authorization: "Bearer <MCP_ACCESS_TOKEN>"
backends:
- mcp:
targets:
- name: home-assistant
mcp:
host: http://192.168.16.3:8123/api/mcp
演示效果
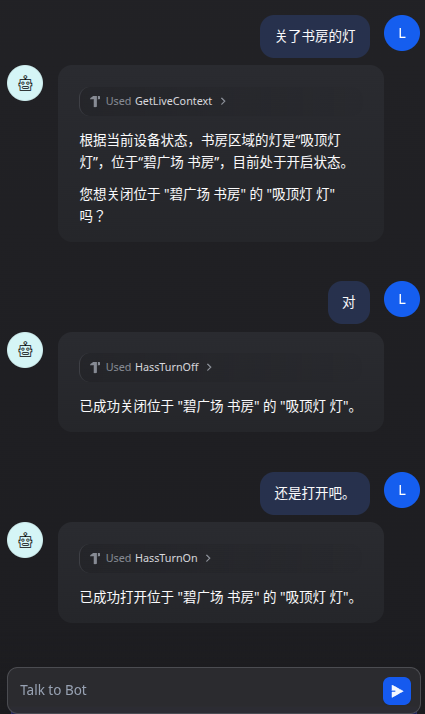
完成部署后,我们可以在 Dify 的聊天界面中与 AI Agent 进行交互,例如用自然语言控制“打开书房的灯”。
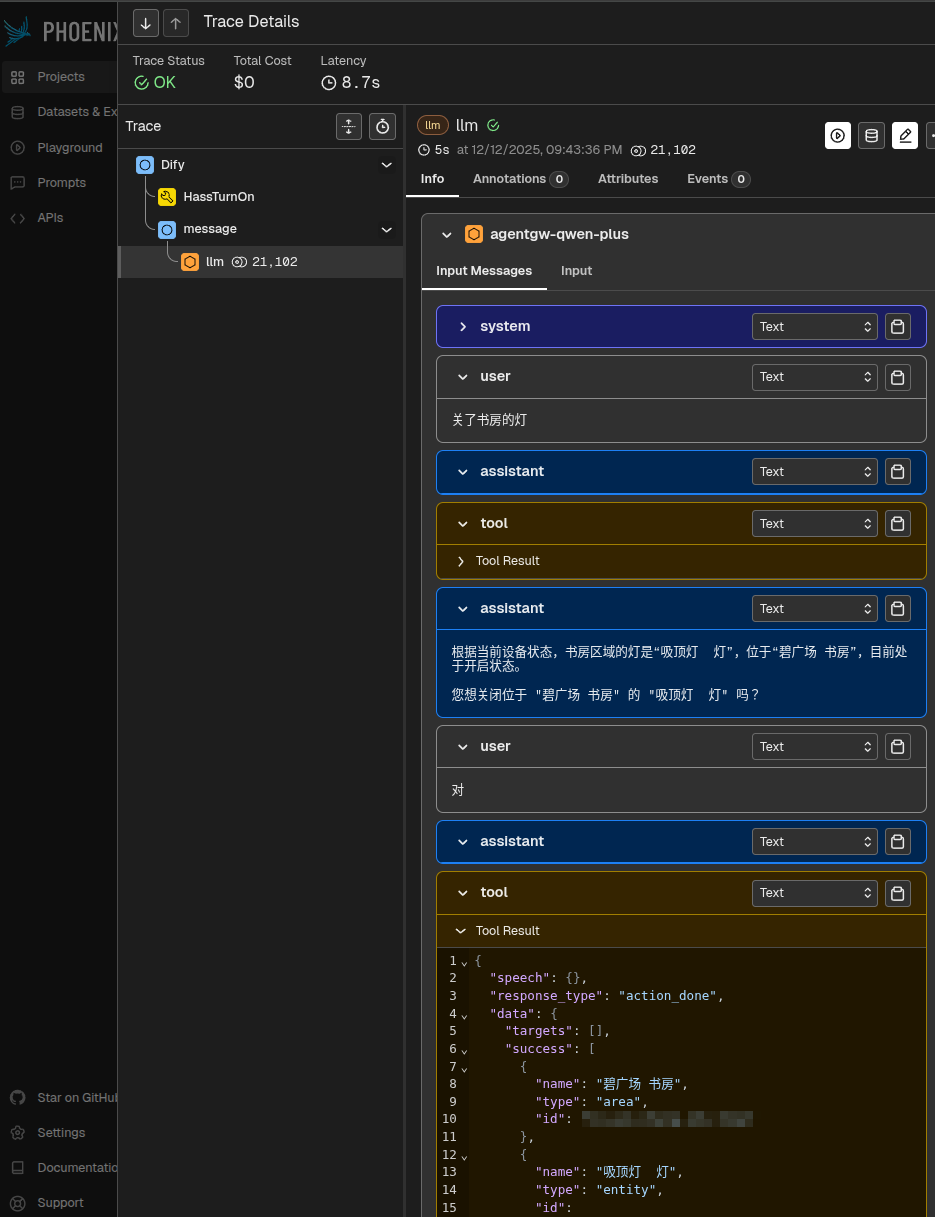
可观测性与追踪结果
在 phoenix 的可观测性平台中,我们可以看到本次对话生成了多个追踪链路(trace)。下图展示了其中最后一个链路的详细信息,这对于 运维 和问题排查至关重要。
实践总结与思考
在部署这个简单 PoC 的过程中,我亲身体验了一个 AI Agent 的“开发”流程。要让其真正实用化,即便只是简单加入 TTS 和语音识别也远远不够。然而,当我让豆包生成一个基础提示词,直接粘贴到 Dify 中,并首次通过聊天方式成功打开书房的灯时,依然感受到了一丝“神奇”。随后,自然语言交互的灵活性,以及无需编码即可支持国际化(i18n)的特性,也带来了很好的体验。
过程中也遇到了不少挑战,主要通过不断优化提示词来“打补丁”。接入 agentgateway 后,在统一配置和管理方面的确方便了许多,但要实现完美的链路追踪却非常困难。为此,我还向 agentgateway 项目提交了一个相关 Issue:Failed to add 'llm.prompt' to my tracing span in my env。
总体而言,这次实验让我深刻体会到 AI Agent 开发与传统应用开发的核心差异:由于 LLM 固有的不确定性,可观测性变得前所未有的重要。追踪数据和用户反馈是提升 AI Agent 表现和质量的关键数据来源。同时,因为这种不确定性,实现完善的追踪也比传统应用更加困难。传统应用的运维数据主要面向技术团队,而对于 AI Agent,业务方更需要通过这些数据来评估 Agent 的实际效果和质量。