随着大型语言模型驱动的自主智能体从理论研究走向实际应用,确保其行为的可靠、安全与可控,已成为决定其能否在真实世界关键任务中成功落地的核心挑战。尽管模型能力不断增强,但其输出仍可能存在错误或不准确之处。当智能体被授权执行高风险或敏感操作时,微小的失误也可能引发不可预知的风险。因此,引入“人工干预”机制至关重要,它能在关键决策点暂停智能体,将控制权交还人类,借助人类的智慧来弥补模型的不足,为应用加上一道安全锁。
什么是Multi-Agent系统?
简单来说,Multi-Agent系统并非依赖一个“全能”的超级AI,而是通过多个具备特定角色和能力的相对简单的自主智能体协同工作,共同完成复杂任务。每个智能体拥有自己的专长(通过不同的提示词、工具和知识库定义),它们之间可以沟通、协作、反馈甚至辩论,最终合力交付高质量的成果。
核心特征包括:
- 任务分解:将宏大、模糊的任务拆解为具体、可执行的子任务。
- 角色专长:每个智能体都有明确的职责和擅长的技能(例如,网络搜索、代码执行)。
- 智能协作:智能体通过信息交换来协调工作,例如程序员完成代码后交由测试员。
- 运行自主:每个智能体可在其职责范围内独立判断和操作,无需人类步步干预。
Multi-Agent中为何需要人工干预?
人工干预,简而言之,就是让人类能够深度参与到AI的工作流程中,实时审查、编辑甚至批准其决策和行动。在大语言模型驱动的应用场景中,这种机制尤为关键。
引入的必要性在于:
LLM虽能胜任写作、编码等多种任务,但并非完美。当智能体被授权执行预订酒店、调用付费API、修改数据库或处理法律、医疗等高风险领域的敏感操作时,若拥有完全自主性,微小的错误也可能带来巨大风险。因此,我们需要一个“暂停按钮”,在关键节点将控制权交还给人类,结合人类的判断力、专业知识和经验为AI工作提供额外保障,从而提升应用的准确性与可靠性。
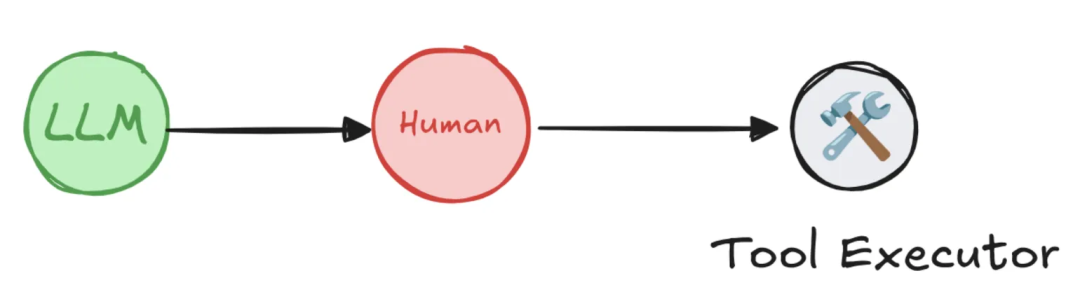
LangGraph的人工干预机制剖析
LangGraph 框架通过其创新的 interrupt(中断) 机制,使得构建需要人工审查、编辑和批准的“人机协同”工作流成为可能。当工作流执行到预设的中断点时,它会保存所有当前状态并暂停,直到接收到人类输入指令后再从断点处恢复,为构建可靠、安全且透明的智能体应用奠定了基石。
该机制允许在工作流的任何阶段进行干预,尤其适用于需要验证、更正或补充模型输出的场景。它主要包含两种中断类型:动态中断和静态中断。
核心能力
- 持久化执行状态:这是实现异步、无时间限制人工审查的基础。LangGraph 利用其持久化层,在工作流的每一步执行后创建检查点,完整保存所有状态。这意味着中断后,人类可在任意时间返回处理,系统能从中断点无缝恢复,不丢失任何信息。
- 灵活的中断机制:
- 动态中断:在特定节点内部根据运行状态条件性触发暂停,如同设置了一个条件判断,实现按需暂停。
- 静态中断:在编译时于预定义节点的前后固定设置中断点,流程运行到这些“关卡”时必须暂停等待人工干预。
四大典型应用模式
基于上述能力,可以构建出多种典型的人工干预场景。
-
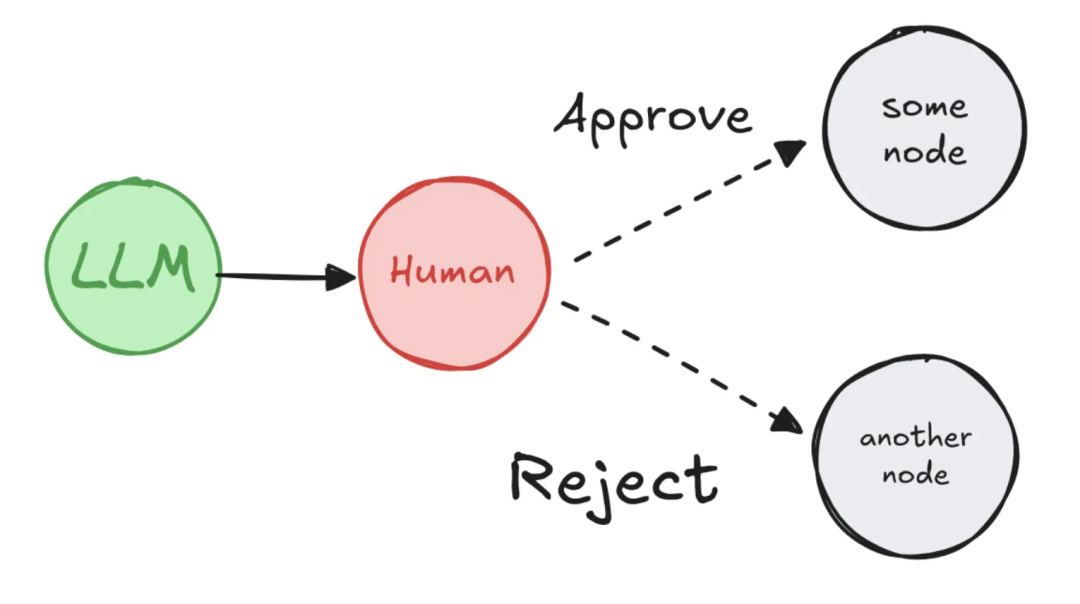
模式一:批准/拒绝
在高风险操作执行前暂停,等待人工审核。根据批准或拒绝的决策,工作流可走向不同的分支。
- 应用场景:API调用审批、敏感操作确认(如财务交易)。
- 价值:降低风险,防止错误操作。
-
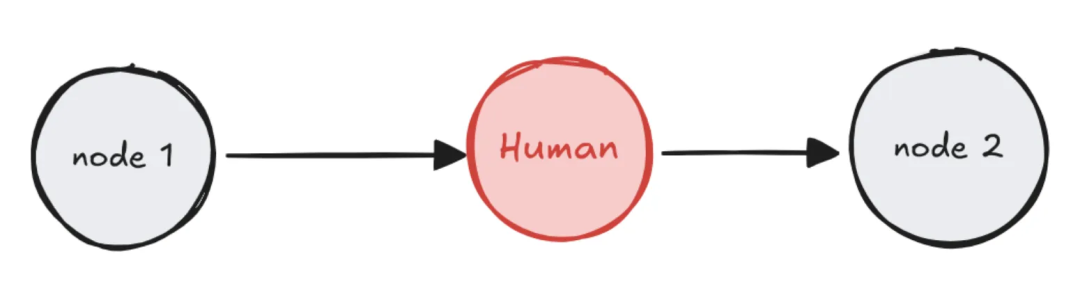
模式二:编辑图状态
暂停后允许人工直接修改工作流的状态数据,然后再继续执行。
- 应用场景:纠正AI生成的错误信息、补充缺失内容、更新上下文。
- 价值:修正错误,完善信息,提升后续步骤的准确性。
-
模式三:审查工具调用
在智能体决定调用某个工具(如搜索API、数据库查询)时强制中断,等待人工确认工具选择及参数的正确性。
- 应用场景:审核API请求参数、验证工具选择的合理性。
- 价值:确保工具调用的正确性和安全性,是保障智能体安全的终极防线之一。
-
模式四:验证人工输入
在流程中需要用户提供特定格式的输入时,使用循环中断反复请求,直至输入有效为止。
- 应用场景:用户输入验证、表单数据校验。
- 价值:确保数据质量,防止无效或错误输入影响后续流程。

LangGraph人工干预核心工作流详解
实现一次完整的人机交互闭环,其工作流遵循清晰的四步模式,理解其核心机制“恢复即重跑”至关重要。
-
配置持久化层:中断的本质是状态的保存与恢复,因此编译图时必须指定一个检查点存储器。
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
graph = graph_builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)
-
在节点中调用 interrupt():在需要干预的节点函数中调用此函数,它会立即暂停执行,并可向用户传递需要审查的数据。
from langgraph.types import interrupt
def human_review_node(state: State):
# 中断执行,将摘要文本交给用户审查
edited_data = interrupt({
"task": "请审查并编辑下面的摘要",
"summary_to_review": state["summary"]
})
# 恢复后,edited_data 将是用户输入的新内容
return {"summary": edited_data["edited_summary"]}
-
运行并触发中断:使用唯一的 thread_id 运行图。遇到 interrupt() 时,图会暂停,返回结果中包含中断的详细信息。
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "some-unique-id"}}
result = graph.invoke({"summary": "初步生成的摘要..."}, config=config)
# 检查中断信息
print(result['__interrupt__'])
-
使用 Command 恢复执行:用户完成审查并提供输入后,通过传入 Command(resume=...) 对象来恢复图的执行。
from langgraph.types import Command
# 用户提供了编辑后的摘要
user_input = {"edited_summary": "这是经过人工编辑的最终摘要。"}
final_result = graph.invoke(Command(resume=user_input), config=config)
⚠️ 核心机制警示:恢复即重跑
恢复执行并非从 interrupt() 调用的那一行代码继续,而是从包含 interrupt() 的那个节点的开头重新执行整个节点。在重跑期间,再次遇到 interrupt() 时不会暂停,而是直接返回 Command(resume=...) 中提供的值。这意味着,任何位于 interrupt() 调用之前的、具有副作用的操作(如API调用、数据库写入)都会被重复执行。最佳实践是将副作用操作置于 interrupt() 之后,或放在一个独立的后续节点中。
实战演练:Interrupt的四大经典模式
要在图中使用 interrupt,你需要:1) 指定检查点;2) 在适当位置调用 interrupt();3) 使用线程ID运行图直至命中中断;4) 使用 invoke/stream 恢复执行。以下选取两个模式进行详解。
模式一:审批或否决实战
在执行高风险操作前,强制要求人工批准,并根据决策路由到不同分支。
1. 定义状态与节点函数
from typing import Literal, TypedDict
import uuid
from langgraph.constants import END
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
from langgraph.types import interrupt, Command
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
class State(TypedDict):
llm_output: str
decision: str
def generate_llm_output(state: State) -> State:
print("\n--- 步骤1:AI生成内容 ---")
return {"llm_output": "这是AI生成的一段需要审批的文本。"}
def human_approval(state: State) -> Command[Literal["approved_path", "rejected_path"]]:
print("\n--- 暂停:等待人工审批 ---")
# 暂停执行,等待人类决策
decision = interrupt({
"question": "请审批以下内容,回复 'approve' 或 'reject':",
"llm_output": state["llm_output"]
})
# 根据决策返回不同的路由指令
if decision == "approve":
print("\n--- 决策:批准 ---")
return Command(goto="approved_path", update={"decision": "approved"})
else:
print("\n--- 决策:拒绝 ---")
return Command(goto="rejected_path", update={"decision": "rejected"})
def approved_node(state: State) -> State:
print("--- 步骤2 (分支A): 已进入批准流程。---")
return state
def rejected_node(state: State) -> State:
print("--- 步骤2 (分支B): 已进入拒绝流程。---")
return state
2. 构建图
builder = StateGraph(State)
builder.add_node("generate_llm_output", generate_llm_output)
builder.add_node("human_approval", human_approval)
builder.add_node("approved_path", approved_node)
builder.add_node("rejected_path", rejected_node)
builder.set_entry_point("generate_llm_output")
builder.add_edge("generate_llm_output", "human_approval")
builder.add_edge("approved_path", END)
builder.add_edge("rejected_path", END)
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
graph = builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)
3. 首次运行并触发中断
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": f"thread-{uuid.uuid4()}"}}
print("首次调用,启动审批流程...")
result = graph.invoke({}, config=config)
print("\n图已暂停,等待审批...")
运行结果示意:

4. 传入决策恢复执行
print("\n--- 恢复执行:传入 'approve' 决策 ---")
final_result = graph.invoke(Command(resume="approve"), config=config)
print("\n流程执行完毕,最终状态如下:")
print(final_result)
运行结果示意(批准分支):

模式三:审查工具调用实战
这是保障智能体安全的关键模式。我们通过一个酒店查询Agent的例子,展示如何在工具调用前强制中断,等待人工确认。
1. 环境准备与模型初始化
pip install -U langgraph langchain langchain_openai
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
# 假设使用Venus AI平台
BASE_URL="http://v2.xxxxxx.com/llmproxy"
TOKEN="your_token"
MODEL_NAME="gpt-4o"
model = init_chat_model(
model=MODEL_NAME,
model_provider="openai",
base_url=BASE_URL,
api_key=TOKEN,
temperature=0,
)
2. 定义工具与通用人工干预包装器
from typing import Callable
from langchain_core.tools import BaseTool, tool as create_tool
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableConfig
from langgraph.types import interrupt
from langgraph.prebuilt.interrupt import HumanInterruptConfig, HumanInterrupt
def search_hotel(hotel_name: str):
"""根据酒店名称查询酒店信息"""
return f"为您查询{hotel_name}."
def add_human_in_the_loop(
tool: Callable | BaseTool,
*,
interrupt_config: HumanInterruptConfig = None,
) -> BaseTool:
"""高阶函数:为任何工具添加人工审核层"""
if not isinstance(tool, BaseTool):
tool = create_tool(tool)
if interrupt_config is None:
interrupt_config = {"allow_accept": True, "allow_edit": True, "allow_respond": True}
@create_tool(tool.name, description=tool.description, args_schema=tool.args_schema)
def call_tool_with_interrupt(config: RunnableConfig, **tool_input):
request: HumanInterrupt = {
"action_request": {"action": tool.name, "args": tool_input},
"config": interrupt_config,
"description": "Please review the tool call"
}
response = interrupt([request])[0] # 触发中断
if response["type"] == "accept":
tool_response = tool.invoke(tool_input, config) # 批准后调用原工具
elif response["type"] == "edit":
tool_input = response["args"]["args"] # 使用编辑后的参数
tool_response = tool.invoke(tool_input, config)
elif response["type"] == "response":
tool_response = response["args"] # 直接使用人工反馈作为结果
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported interrupt response type: {response['type']}")
return tool_response
return call_tool_with_interrupt
3. 创建带有人工干预的Agent
from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import InMemorySaver
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
# 关键:使用包装器封装原始工具
search_agent = create_react_agent(
model=model,
tools=[add_human_in_the_loop(search_hotel)], # 传入封装后的工具
checkpointer=checkpointer,
name="search_assistant",
prompt="你是一个酒店查询助手"
)
4. 运行Agent并触发中断
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}}
# Turn 0: 查询意图,工具参数不全,不会触发中断
for chunk in agent.stream({"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "我要查酒店"}]}, config):
print(chunk)
print("\n")
# Turn 1: 提供具体酒店名,工具参数完备,触发中断
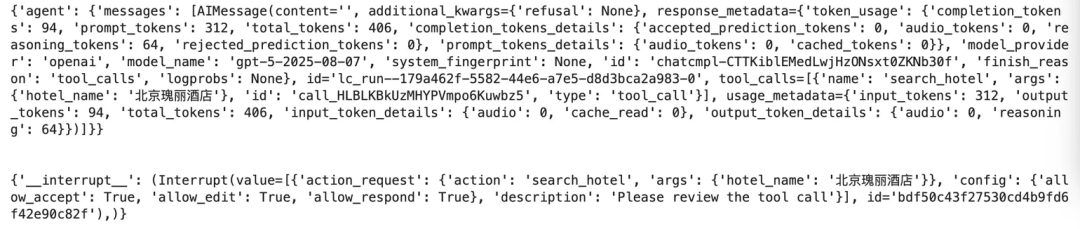
for chunk in agent.stream({"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "帮我查下北京瑰丽酒店的信息"}]}, config):
print(chunk)
print("\n")
运行结果示意(触发中断):
5. 人工批准后恢复执行
from langgraph.types import Command
for chunk in agent.stream(Command(resume=[{"type": "accept"}]), config):
print(chunk)
print("\n")
运行结果示意(批准后执行工具):

进阶实战:集成MCP协议实现真实搜索工具的中断
本示例展示如何为通过MCP协议接入的真实网络搜索工具添加人工干预层。
1. 初始化模型与MCP客户端
# 初始化模型(同上,略)
# 创建MCP客户端连接智能搜索工具
from langchain_mcp_adapters.client import MultiServerMCPClient
url = "your_mcp_server_sse_url" # 从Venus MCP server市场获取
search_client = MultiServerMCPClient({
"other_search": {
"url": url,
"headers": {"Authorization": f"Bearer {TOKEN}"},
"transport": "sse"
}
})
search_tools = await search_client.get_tools() # 获取工具列表
2. 定义异步版人工干预包装器
由于MCP工具调用是异步的,需要调整包装器。
def add_human_in_the_loop_async(
tool: BaseTool,
interrupt_config: HumanInterruptConfig = None
) -> BaseTool:
if interrupt_config is None:
interrupt_config = {"allow_accept": True, "allow_edit": True, "allow_respond": True}
@create_tool(tool.name, description=tool.description, args_schema=tool.args_schema)
async def call_tool_with_interrupt(config: RunnableConfig, **tool_input): # 异步函数
request: HumanInterrupt = {
"action_request": {"action": tool.name, "args": tool_input},
"config": interrupt_config,
"description": "Please review the tool call"
}
response = interrupt([request])[0]
if response["type"] == "accept":
tool_response = await tool.ainvoke(tool_input, config) # 异步调用
elif response["type"] == "edit":
tool_input = response["args"]["args"]
tool_response = await tool.ainvoke(tool_input, config)
elif response["type"] == "response":
tool_response = response["args"]
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported response type: {response['type']}")
return tool_response
return call_tool_with_interrupt
3. 创建并运行带人工干预的搜索Agent
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
checkpointer = InMemorySaver()
# 为所有搜索工具添加中断功能
wrapped_search_tools = [add_human_in_the_loop_async(tool) for tool in search_tools]
agent = create_react_agent(
model=model,
tools=wrapped_search_tools,
checkpointer=checkpointer,
name="search_assistant",
prompt="你是一个能搜索各种信息的助手..."
)
import asyncio
async def run_agent():
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "2"}}
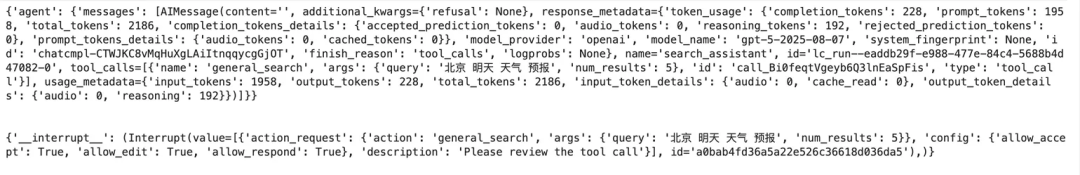
async for chunk in agent.astream(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "查明天北京的天气"}]},
config
):
print(chunk)
print("\n")
await run_agent()
运行结果示意(触发中断):
4. 人工批准后获取搜索结果
from langgraph.types import Command
async def run_response():
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "2"}}
print("--- Resuming with 'accept' ---")
async for chunk in agent.astream(Command(resume=[{"type": "accept"}]), config):
print(chunk)
print("\n")
await run_response()
运行结果示意(批准后执行搜索):

总结
LangGraph的人工干预机制通过 interrupt 将“暂停-保存-恢复-重执行”的流程无缝集成到智能体工作流中,为开发者提供了强大的控制力。借助持久化状态、动态/静态中断以及灵活的集成点,我们可以实现审批、编辑、工具审查、输入验证等多种模式,从而构建出既能发挥大模型强大能力,又能在关键时刻接受人类指导的复杂、可靠且安全的智能应用。这无疑是推动AI Agent在真实业务场景中落地的重要保障。
END---