打 Backdoor 的 skernel 时,在 Tplus 大佬那里学习了一个在不能使用 userfaultfd 和 FUSE 的情况下完成对地址访问阻塞的攻击方法,个人觉得非常好用。限于篇幅,本篇文章主要聚焦于 punch hole 的原理。(当然我也不能确定 punch hole 是预期打法)
环境说明
- 本文中关于 Linux 源码的分析均基于:Linux 6.12.32 版本
- 题目内核版本:Linux 6.18.0
题目
struct __fixed struct_3 // sizeof=0x18
{ // XREF: module_ioctl/r
int index; // XREF: module_ioctl+25/w
// module_ioctl+60/r ...
int field_4;
__int64 length; // XREF: module_ioctl+2E/w
// module_ioctl+6B/r ...
__int64 buf; // XREF: module_ioctl+37/w
// module_ioctl+169/r ...
};
__int64 __fastcall module_ioctl(__int64 a1, int a2, __int64 a3)
{
__int64 v4; // rbx
__int64 v5; // rax
__int64 v7; // rdx
__int64 v8; // rdi
struct_3 v9; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-70h] BYREF
_BYTE v10[64]; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-58h] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v11; // [rsp+60h] [rbp-18h]
v11 = __readgsqword((unsigned int)&_ref_stack_chk_guard);
memset(&v9, 0, sizeof(v9));
mutex_lock(&skernel_mutex);
if ( copy_from_user(&v9, a3, 24) )
{
v4 = -14;
goto LABEL_10;
}
if ( v9.index > 7u )
{
v4 = -22;
goto LABEL_10;
}
v4 = -22;
if ( (unsigned __int64)(v9.length - 1) > 0x3F )
{
LABEL_10:
mutex_unlock(&skernel_mutex);
return v4;
}
mutex_unlock(&skernel_mutex);
switch ( a2 )
{
case 322376504:
memset(v10, 0, sizeof(v10));
v7 = allocated_objects[v9.index];
if ( !v7 )
return -1;
v4 = 0;
kfree(v7);
copy_from_user(v10, v9.buf, 64);
allocated_objects[v9.index] = 0;
return v4;
case 322376505:
v8 = allocated_objects[v9.index];
if ( !v8 )
return -1;
if ( v9.length > 0x7FFFFFFFuLL )
BUG();
return -(copy_from_user(v8, v9.buf, v9.length) != 0);
case 322376503:
if ( allocated_objects[v9.index] )
return -1;
v4 = 0;
v5 = _kmalloc_cache_noprof(kmalloc_caches[6], 3520, 64);
allocated_objects[v9.index] = v5;
return v4;
}
return module_ioctl_cold();
}
可以看见我们在 free 后虽然进行了置空,但是在那之前有 copy_from_user(v10, v9.buf, 64);。所以我们可以通过类似于 userfaultfd 的方式延长这个 copy_from_user 的环节,从而让已经 free 后的 obj 残留在数组中。在这期间我们可以通过 write 实现 UAF 或者通过 free 实现 double-free。
Punch hole
这题目环境并不支持 userfaultfd 和 FUSE。所以我们可以用 StarLabs 博客 中提及的 punch hole 方式,替代这两种方式,实现条件竞争。当然 punch hole 也不能完美替代这两种方案,本质只是延长了访问的时间,而不是可以实现任意控制的延长。
攻击方式其实就是将我们的 buf 地址对应的内存通过 fallocate 丢弃,制造内存空洞。从而让 copy_from_user 函数访问这个地址的时候会发生缺页中断(#PF),然后去处理对应内容。由于 fallocate 会给已经丢弃的内容上锁,后续读写会等待打洞完成。(后文将重点解释为什么 fallocate 后的内存访问流程会进入等待)
核心数据结构
struct shmem_falloc {
wait_queue_head_t *waitq; // 等待队列(用于同步)
pgoff_t start; // 打洞起始页号
pgoff_t next; // 打洞结束页号(下一个页号)
pgoff_t nr_falloced; // 已分配的页数(用于普通 fallocate)
pgoff_t nr_unswapped; // 已交换的页数(用于普通 fallocate)
};
fallocate
fallocate() 用于预分配或释放文件空间。
- Mode:
FALLOC_FL_PUNCH_HOLE | FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE(后文主要以这个调用链为主)
FALLOC_FL_PUNCH_HOLE:在文件中打洞,释放指定范围的磁盘块 FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE:保持文件大小不变(不改变 inode->i_size)
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(fallocate, int, fd, int, mode, loff_t, offset, loff_t, len)
{
return ksys_fallocate(fd, mode, offset, len);
}
流程
- 设置阶段:创建等待队列,设置
inode->i_private 标记(这样后续只需要检查 i_private 即可)
- 取消映射:
unmap_mapping_range() 取消所有 VMA 中的映射
- 截断缓存:
shmem_truncate_range() → shmem_undo_range() 删除页面缓存和交换条目
- 清理阶段:清除标记,唤醒等待的 page fault 线程
vfs_fallocate
- 模式验证:
FALLOC_FL_PUNCH_HOLE 必须与 FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE 一起使用
- 权限检查:需要写权限(
FMODE_WRITE)
- 文件类型:必须是普通文件或块设备
- 最终调用:
file->f_op->fallocate(file, mode, offset, len),有多种实现路径
int vfs_fallocate(struct file *file, int mode, loff_t offset, loff_t len)
{
struct inode *inode = file_inode(file);
long ret;
loff_t sum;
if (offset < 0 || len <= 0)
return -EINVAL;
if (mode & ~(FALLOC_FL_MODE_MASK | FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE))
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
/*
* Modes are exclusive, even if that is not obvious from the encoding
* as bit masks and the mix with the flag in the same namespace.
*
* To make things even more complicated, FALLOC_FL_ALLOCATE_RANGE is
* encoded as no bit set.
*/
switch (mode & FALLOC_FL_MODE_MASK) {
case FALLOC_FL_ALLOCATE_RANGE:
case FALLOC_FL_UNSHARE_RANGE:
case FALLOC_FL_ZERO_RANGE:
break;
case FALLOC_FL_PUNCH_HOLE:
if (!(mode & FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE))
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
break;
case FALLOC_FL_COLLAPSE_RANGE:
case FALLOC_FL_INSERT_RANGE:
if (mode & FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE)
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
break;
default:
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
}
if (!(file->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE))
return -EBADF;
/*
* On append-only files only space preallocation is supported.
*/
if ((mode & ~FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE) && IS_APPEND(inode))
return -EPERM;
if (IS_IMMUTABLE(inode))
return -EPERM;
/*
* We cannot allow any fallocate operation on an active swapfile
*/
if (IS_SWAPFILE(inode))
return -ETXTBSY;
/*
* Revalidate the write permissions, in case security policy has
* changed since the files were opened.
*/
ret = security_file_permission(file, MAY_WRITE);
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = fsnotify_file_area_perm(file, MAY_WRITE, &offset, len);
if (ret)
return ret;
if (S_ISFIFO(inode->i_mode))
return -ESPIPE;
if (S_ISDIR(inode->i_mode))
return -EISDIR;
if (!S_ISREG(inode->i_mode) && !S_ISBLK(inode->i_mode))
return -ENODEV;
/* Check for wraparound */
if (check_add_overflow(offset, len, &sum))
return -EFBIG;
if (sum > inode->i_sb->s_maxbytes)
return -EFBIG;
if (!file->f_op->fallocate)
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
file_start_write(file);
// 最终调用 f_op->fallocate
ret = file->f_op->fallocate(file, mode, offset, len);
/*
* Create inotify and fanotify events.
* To keep the logic simple always create events if fallocate succeeds.
* This implies that events are even created if the file size remains
* unchanged, e.g. when using flag FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE.
*/
if (ret == 0)
fsnotify_modify(file);
file_end_write(file);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(vfs_fallocate);
ext4 文件实现
也就是我们正常创建的文件。
ext4_fallocate(ext4 文件系统实现)
具体根据不同 file->f_op->fallocate 的实现为主,这里用 ext4 文件系统举例。
- 检查加密文件系统限制
- 验证支持的模式
ext4_punch_hole 最后调用
/*
* preallocate space for a file. This implements ext4's fallocate file
* operation, which gets called from sys_fallocate system call.
* For block-mapped files, posix_fallocate should fall back to the method
* of writing zeroes to the required new blocks (the same behavior which is
* expected for file systems which do not support fallocate() system call).
*/
long ext4_fallocate(struct file *file, int mode, loff_t offset, loff_t len)
{
struct inode *inode = file_inode(file);
loff_t new_size = 0;
unsigned int max_blocks;
int ret = 0;
int flags;
ext4_lblk_t lblk;
unsigned int blkbits = inode->i_blkbits;
/*
* Encrypted inodes can't handle collapse range or insert
* range since we would need to re-encrypt blocks with a
* different IV or XTS tweak (which are based on the logical
* block number).
*/
if (IS_ENCRYPTED(inode) &&
(mode & (FALLOC_FL_COLLAPSE_RANGE | FALLOC_FL_INSERT_RANGE)))
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
/* Return error if mode is not supported */
if (mode & ~(FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE | FALLOC_FL_PUNCH_HOLE |
FALLOC_FL_COLLAPSE_RANGE | FALLOC_FL_ZERO_RANGE |
FALLOC_FL_INSERT_RANGE))
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
inode_lock(inode);
ret = ext4_convert_inline_data(inode);
inode_unlock(inode);
if (ret)
goto exit;
if (mode & FALLOC_FL_PUNCH_HOLE) {
ret = ext4_punch_hole(file, offset, len);
goto exit;
}
if (mode & FALLOC_FL_COLLAPSE_RANGE) {
ret = ext4_collapse_range(file, offset, len);
goto exit;
}
if (mode & FALLOC_FL_INSERT_RANGE) {
ret = ext4_insert_range(file, offset, len);
goto exit;
}
if (mode & FALLOC_FL_ZERO_RANGE) {
ret = ext4_zero_range(file, offset, len, mode);
goto exit;
}
trace_ext4_fallocate_enter(inode, offset, len, mode);
lblk = offset >> blkbits;
max_blocks = EXT4_MAX_BLOCKS(len, offset, blkbits);
flags = EXT4_GET_BLOCKS_CREATE_UNWRIT_EXT;
inode_lock(inode);
/*
* We only support preallocation for extent-based files only
*/
if (!ext4_test_inode_flag(inode, EXT4_INODE_EXTENTS)) {
ret = -EOPNOTSUPP;
goto out;
}
if (!(mode & FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE) &&
(offset + len > inode->i_size ||
offset + len > EXT4_I(inode)->i_disksize)) {
new_size = offset + len;
ret = inode_newsize_ok(inode, new_size);
if (ret)
goto out;
}
/* Wait all existing dio workers, newcomers will block on i_rwsem */
inode_dio_wait(inode);
ret = file_modified(file);
if (ret)
goto out;
ret = ext4_alloc_file_blocks(file, lblk, max_blocks, new_size, flags);
if (ret)
goto out;
if (file->f_flags & O_SYNC && EXT4_SB(inode->i_sb)->s_journal) {
ret = ext4_fc_commit(EXT4_SB(inode->i_sb)->s_journal,
EXT4_I(inode)->i_sync_tid);
}
out:
inode_unlock(inode);
trace_ext4_fallocate_exit(inode, offset, max_blocks, ret);
exit:
return ret;
}
ext4_punch_hole(核心函数)
- 边界检查
- 如果
offset >= inode->i_size,直接返回
- 如果超出文件大小,调整长度
- 对齐处理
- 将偏移量和长度对齐到块边界(
round_up/round_down)
- 清除页面缓存
int ext4_punch_hole(struct file *file, loff_t offset, loff_t length)
{
struct inode *inode = file_inode(file);
struct super_block *sb = inode->i_sb;
ext4_lblk_t first_block, stop_block;
struct address_space *mapping = inode->i_mapping;
loff_t first_block_offset, last_block_offset, max_length;
struct ext4_sb_info *sbi = EXT4_SB(inode->i_sb);
handle_t *handle;
unsigned int credits;
int ret = 0, ret2 = 0;
trace_ext4_punch_hole(inode, offset, length, 0);
inode_lock(inode);
/* No need to punch hole beyond i_size */
if (offset >= inode->i_size)
goto out_mutex;
/*
* If the hole extends beyond i_size, set the hole
* to end after the page that contains i_size
*/
if (offset + length > inode->i_size) {
length = inode->i_size +
PAGE_SIZE - (inode->i_size & (PAGE_SIZE - 1)) -
offset;
}
/*
* For punch hole the length + offset needs to be within one block
* before last range. Adjust the length if it goes beyond that limit.
*/
max_length = sbi->s_bitmap_maxbytes - inode->i_sb->s_blocksize;
if (offset + length > max_length)
length = max_length - offset;
if (offset & (sb->s_blocksize - 1) ||
(offset + length) & (sb->s_blocksize - 1)) {
/* Attach jinode to inode for jbd2 if we do any zeroing of
* partial block
*/
ret = ext4_inode_attach_jinode(inode);
if (ret < 0)
goto out_mutex;
}
/* Wait all existing dio workers, newcomers will block on i_rwsem */
inode_dio_wait(inode);
ret = file_modified(file);
if (ret)
goto out_mutex;
/*
* Prevent page faults from reinstantiating pages we have released from
* page cache.
*/
filemap_invalidate_lock(mapping);
ret = ext4_break_layouts(inode);
if (ret)
goto out_dio;
first_block_offset = round_up(offset, sb->s_blocksize);
last_block_offset = round_down((offset + length), sb->s_blocksize) - 1;
/* Now release the pages and zero block aligned part of pages*/
if (last_block_offset > first_block_offset) {
ret = ext4_update_disksize_before_punch(inode, offset, length);
if (ret)
goto out_dio;
ret = ext4_truncate_page_cache_block_range(inode,
first_block_offset, last_block_offset + 1);
if (ret)
goto out_dio;
}
if (ext4_test_inode_flag(inode, EXT4_INODE_EXTENTS))
credits = ext4_writepage_trans_blocks(inode);
else
credits = ext4_blocks_for_truncate(inode);
handle = ext4_journal_start(inode, EXT4_HT_TRUNCATE, credits);
if (IS_ERR(handle)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(handle);
ext4_std_error(sb, ret);
goto out_dio;
}
/* Zeroize partial blocks */
ret = ext4_zero_partial_blocks(handle, inode, offset,
length);
if (ret)
goto out_stop;
first_block = (offset + sb->s_blocksize - 1) >> EXT4_BLOCK_SIZE_BITS(sb);
stop_block = (offset + length) >> EXT4_BLOCK_SIZE_BITS(sb);
/* If there are blocks to remove, do it */
if (stop_block > first_block) {
ext4_lblk_t hole_len = stop_block - first_block;
down_write(&EXT4_I(inode)->i_data_sem);
ext4_discard_preallocations(inode);
ext4_es_remove_extent(inode, first_block, hole_len);
// Delete blocks from extent tree or indirect blocks
if (ext4_test_inode_flag(inode, EXT4_INODE_EXTENTS))
ret = ext4_ext_remove_space(inode, first_block,
stop_block - 1);
else
ret = ext4_ind_remove_space(handle, inode, first_block,
stop_block);
// Mark as HOLE in extent status tree
ext4_es_insert_extent(inode, first_block, hole_len, ~0,
EXTENT_STATUS_HOLE, 0);
up_write(&EXT4_I(inode)->i_data_sem);
}
ext4_fc_track_range(handle, inode, first_block, stop_block);
if (IS_SYNC(inode))
ext4_handle_sync(handle);
inode_set_mtime_to_ts(inode, inode_set_ctime_current(inode));
ret2 = ext4_mark_inode_dirty(handle, inode);
if (unlikely(ret2))
ret = ret2;
if (ret >= 0)
ext4_update_inode_fsync_trans(handle, inode, 1);
out_stop:
ext4_journal_stop(handle);
out_dio:
filemap_invalidate_unlock(mapping);
out_mutex:
inode_unlock(inode);
return ret;
}
shmem/tmpfs 文件实现
tmpfs 文件就是 /tmp 目录下的文件 Shmem 文件就是 memfd_create 创建的 fd
流程图
用户空间: fallocate(fd, FALLOC_FL_PUNCH_HOLE | FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE, offset, len)
↓
系统调用: SYSCALL_DEFINE4(fallocate, ...)
↓
ksys_fallocate()
↓
vfs_fallocate()
↓
file->f_op->fallocate() [对于 shmem 文件,指向 shmem_fallocate]
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ shmem_fallocate() [mm/shmem.c:3376] │
│ │
│ if (mode & FALLOC_FL_PUNCH_HOLE) { │
│ ├─ 1. 设置等待队列和标记 │
│ │ └─ inode->i_private = &shmem_falloc │
│ │ │
│ ├─ 2. unmap_mapping_range() [mm/memory.c:3857] │
│ │ └─ unmap_mapping_pages() [mm/memory.c:3821] │
│ │ └─ unmap_mapping_range_tree() │
│ │ └─ unmap_mapping_range_vma() │
│ │ └─ zap_page_range_single() │
│ │ └─ 取消映射所有 VMA 中的页面 │
│ │ │
│ ├─ 3. shmem_truncate_range() [mm/shmem.c:1146] │
│ │ └─ shmem_undo_range() [mm/shmem.c:995] │
│ │ ├─ find_lock_entries() [mm/filemap.c] │
│ │ │ └─ 查找并锁定页面缓存中的 folio │
│ │ ├─ truncate_inode_folio() [mm/truncate.c] │
│ │ │ └─ 截断完整的 folio │
│ │ ├─ truncate_inode_partial_folio() [mm/truncate.c] │
│ │ │ └─ 截断部分 folio(处理跨页边界) │
│ │ ├─ shmem_free_swap() │
│ │ │ └─ 释放交换空间条目 │
│ │ └─ shmem_recalc_inode() │
│ │ └─ 重新计算 inode 的统计信息 │
│ │ │
│ └─ 4. 清除标记并唤醒等待线程 │
│ ├─ inode->i_private = NULL │
│ └─ wake_up_all(&shmem_falloc_waitq) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
shmem_fallocate(设置等待队列)
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD_ONSTACK(shmem_falloc_waitq) 在栈上创建等待队列 inode->i_private = &shmem_falloc 标记正在打洞,其他线程可通过此字段检测 shmem_falloc.start 和 shmem_falloc.next 记录打洞的页范围 - 完成后
wake_up_all() 唤醒等待线程
static long shmem_fallocate(struct file *file, int mode, loff_t offset,
loff_t len)
{
struct inode *inode = file_inode(file);
struct shmem_sb_info *sbinfo = SHMEM_SB(inode->i_sb);
struct shmem_inode_info *info = SHMEM_I(inode);
struct shmem_falloc shmem_falloc;
pgoff_t start, index, end, undo_fallocend;
int error;
// 检查模式:只支持 KEEP_SIZE 和 PUNCH_HOLE
if (mode & ~(FALLOC_FL_KEEP_SIZE | FALLOC_FL_PUNCH_HOLE))
return -EOPNOTSUPP;
// 获取 inode 锁(防止并发修改)
inode_lock(inode);
if (mode & FALLOC_FL_PUNCH_HOLE) {
struct address_space *mapping = file->f_mapping;
// 对齐到页边界:向上取整起始位置,向下取整结束位置
loff_t unmap_start = round_up(offset, PAGE_SIZE);
loff_t unmap_end = round_down(offset + len, PAGE_SIZE) - 1;
// 在栈上声明等待队列头(用于同步打洞和 page fault)
DECLARE_WAIT_QUEUE_HEAD_ONSTACK(shmem_falloc_waitq);
// 检查文件密封:如果文件被密封为只写,不允许打洞
if (info->seals & (F_SEAL_WRITE | F_SEAL_FUTURE_WRITE)) {
error = -EPERM;
goto out;
}
// 步骤1: 设置 shmem_falloc 结构
shmem_falloc.waitq = &shmem_falloc_waitq; // 等待队列
shmem_falloc.start = (u64)unmap_start >> PAGE_SHIFT; // 起始页号
shmem_falloc.next = (unmap_end + 1) >> PAGE_SHIFT; // 结束页号+1
// 步骤2: 将 shmem_falloc 保存到 inode->i_private
// 这样 shmem_fault() 可以检测到正在打洞
spin_lock(&inode->i_lock);
inode->i_private = &shmem_falloc;
spin_unlock(&inode->i_lock);
// 步骤3: 取消映射 VMA 中的页面(如果有多个进程映射)
if ((u64)unmap_end > (u64)unmap_start)
unmap_mapping_range(mapping, unmap_start,
1 + unmap_end - unmap_start, 0);
// 步骤4: 截断页面缓存和交换空间
shmem_truncate_range(inode, offset, offset + len - 1);
/* No need to unmap again: hole-punching leaves COWed pages */
// 步骤5: 清除标记并唤醒所有等待的线程
spin_lock(&inode->i_lock);
inode->i_private = NULL; // 清除标记
wake_up_all(&shmem_falloc_waitq); // 唤醒等待的 page fault 线程
WARN_ON_ONCE(!list_empty(&shmem_falloc_waitq.head));
spin_unlock(&inode->i_lock);
error = 0;
goto out;
}
unmap_mapping_range
- 将字节范围转换为页号范围
- 调用
unmap_mapping_pages() 执行取消映射
void unmap_mapping_range(struct address_space *mapping,
loff_t const holebegin, loff_t const holelen, int even_cows)
{
pgoff_t hba = (pgoff_t)(holebegin) >> PAGE_SHIFT;
pgoff_t hlen = ((pgoff_t)(holelen) + PAGE_SIZE - 1) >> PAGE_SHIFT;
// 检查溢出
if (sizeof(holelen) > sizeof(hlen)) {
long long holeend =
(holebegin + holelen + PAGE_SIZE - 1) >> PAGE_SHIFT;
if (holeend & ~(long long)ULONG_MAX)
hlen = ULONG_MAX - hba + 1;
}
// 调用实际取消映射函数
unmap_mapping_pages(mapping, hba, hlen, even_cows);
}
unmap_mapping_pages(取消映射)
- 遍历
i_mmap 树(所有映射该文件的 VMA)
- 对每个 VMA 调用
unmap_mapping_range_vma() 取消映射
void unmap_mapping_pages(struct address_space *mapping, pgoff_t start,
pgoff_t nr, bool even_cows)
{
struct zap_details details = { };
pgoff_t first_index = start;
pgoff_t last_index = start + nr - 1;
details.even_cows = even_cows; // 是否取消映射 COW 页面
if (last_index < first_index)
last_index = ULONG_MAX;
// 获取映射锁(读锁,允许多个读者)
i_mmap_lock_read(mapping);
// 如果 i_mmap 树不为空,遍历并取消映射
if (unlikely(!RB_EMPTY_ROOT(&mapping->i_mmap.rb_root)))
unmap_mapping_range_tree(&mapping->i_mmap, first_index,
last_index, &details);
i_mmap_unlock_read(mapping);
}
shmem_truncate_range(截断范围)
文件系统上下文中,“截断”指从页面缓存(page cache)中删除指定范围的页面(folio),使页面缓存与文件状态一致。
- 遍历
i_mmap 树(所有映射该文件的 VMA)
- 对每个 VMA 调用
unmap_mapping_range_vma() 取消映射
void shmem_truncate_range(struct inode *inode, loff_t lstart, loff_t lend)
{
// 调用核心实现函数
shmem_undo_range(inode, lstart, lend, false);
// 更新修改时间和变更时间
inode_set_mtime_to_ts(inode, inode_set_ctime_current(inode));
// 增加版本号(用于缓存失效)
inode_inc_iversion(inode);
}
截断前:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ address_space->i_pages (XArray) │
│ ┌─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┐ │
│ │ 0 │ 1 │ 2 │ 3 │ 4 │ │
│ └─────┴─────┴─────┴─────┴─────┘ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ ▼ ▼ ▼ ▼ ▼ │
│ folio folio folio folio folio │
│ A B C D E │
└─────────────────────────────────────────┘
执行: truncate_inode_pages_range(mapping, 4096, 12287)
范围: [1K, 12K) = 页号 [1, 3)
截断后:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ address_space->i_pages (XArray) │
│ ┌─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┐ │
│ │ 0 │NULL │NULL │NULL │ 4 │ │
│ └─────┴─────┴─────┴─────┴─────┘ │
│ │ │ │ │
│ ▼ │ │ │
│ folio │ │ │
│ A │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ [已删除] [已删除] │
│ folio B folio C │
│ folio D │
└─────────────────────────────────────────┘
操作:
- folio B, C, D 从 XArray 中删除(
xas_store(&xas, NULL))
- folio->mapping = NULL(断开关联)
- mapping->nrpages -= 3(更新统计)
- folio 引用计数减 1,如果为 0 则释放到伙伴系统
unmap_mapping_pages
void unmap_mapping_pages(struct address_space *mapping, pgoff_t start,
pgoff_t nr, bool even_cows)
{
struct zap_details details = { };
pgoff_t first_index = start;
pgoff_t last_index = start + nr - 1;
details.even_cows = even_cows; // 是否取消映射 COW 页面
if (last_index < first_index)
last_index = ULONG_MAX;
// 获取映射锁(读锁,允许多个读者)
i_mmap_lock_read(mapping);
// 如果 i_mmap 树不为空,遍历并取消映射
if (unlikely(!RB_EMPTY_ROOT(&mapping->i_mmap.rb_root)))
unmap_mapping_range_tree(&mapping->i_mmap, first_index,
last_index, &details);
i_mmap_unlock_read(mapping);
}
shmem_undo_range(核心截断实现)
- 第一阶段:批量查找并截断完整 folio
- 第二阶段:处理部分页(跨页边界)
- 第三阶段:处理剩余完整 folio
- 释放交换空间并更新统计
static void shmem_undo_range(struct inode *inode, loff_t lstart, loff_t lend,
bool unfalloc)
{
struct address_space *mapping = inode->i_mapping;
struct shmem_inode_info *info = SHMEM_I(inode);
pgoff_t start = (lstart + PAGE_SIZE - 1) >> PAGE_SHIFT;
pgoff_t end = (lend + 1) >> PAGE_SHIFT;
struct folio_batch fbatch;
pgoff_t indices[PAGEVEC_SIZE];
struct folio *folio;
bool same_folio;
long nr_swaps_freed = 0;
pgoff_t index;
int i;
if (lend == -1)
end = -1; /* unsigned, so actually very big */
// 如果是在撤销失败的 fallocate,更新 fallocend
if (info->fallocend > start && info->fallocend <= end && !unfalloc)
info->fallocend = start;
// 初始化 folio 批次
folio_batch_init(&fbatch);
index = start;
// 第一阶段:查找并锁定范围内的所有 folio
while (index < end && find_lock_entries(mapping, &index, end - 1,
&fbatch, indices)) {
for (i = 0; i < folio_batch_count(&fbatch); i++) {
folio = fbatch.folios[i];
// 如果是交换条目(xa_is_value)
if (xa_is_value(folio)) {
if (unfalloc)
continue;
// 释放交换空间
nr_swaps_freed += shmem_free_swap(mapping,
indices[i], folio);
continue;
}
// 如果是普通 folio,截断它
if (!unfalloc || !folio_test_uptodate(folio))
truncate_inode_folio(mapping, folio);
folio_unlock(folio);
}
folio_batch_remove_exceptionals(&fbatch);
folio_batch_release(&fbatch);
cond_resched(); // 让出 CPU,避免长时间占用
}
// 第二阶段:处理部分页(跨页边界的情况)
if (unfalloc)
goto whole_folios;
same_folio = (lstart >> PAGE_SHIFT) == (lend >> PAGE_SHIFT);
// 处理起始页的部分
folio = shmem_get_partial_folio(inode, lstart >> PAGE_SHIFT);
if (folio) {
same_folio = lend < folio_pos(folio) + folio_size(folio);
folio_mark_dirty(folio);
// 截断部分 folio
if (!truncate_inode_partial_folio(folio, lstart, lend)) {
start = folio_next_index(folio);
if (same_folio)
end = folio->index;
}
folio_unlock(folio);
folio_put(folio);
folio = NULL;
}
// 处理结束页的部分(如果与起始页不同)
if (!same_folio)
folio = shmem_get_partial_folio(inode, lend >> PAGE_SHIFT);
if (folio) {
folio_mark_dirty(folio);
if (!truncate_inode_partial_folio(folio, lstart, lend))
end = folio->index;
folio_unlock(folio);
folio_put(folio);
}
whole_folios:
// 第三阶段:处理完整的 folio
index = start;
while (index < end) {
cond_resched();
// 查找范围内的 folio
if (!find_get_entries(mapping, &index, end - 1, &fbatch,
indices)) {
/* If all gone or hole-punch or unfalloc, we're done */
if (index == start || end != -1)
break;
/* But if truncating, restart to make sure all gone */
index = start;
continue;
}
for (i = 0; i < folio_batch_count(&fbatch); i++) {
folio = fbatch.folios[i];
// 处理交换条目
if (xa_is_value(folio)) {
long swaps_freed;
if (unfalloc)
continue;
swaps_freed = shmem_free_swap(mapping, indices[i], folio);
if (!swaps_freed) {
/* Swap was replaced by page: retry */
index = indices[i];
break;
}
nr_swaps_freed += swaps_freed;
continue;
}
folio_lock(folio);
if (!unfalloc || !folio_test_uptodate(folio)) {
if (folio_mapping(folio) != mapping) {
/* Page was replaced by swap: retry */
folio_unlock(folio);
index = indices[i];
break;
}
VM_BUG_ON_FOLIO(folio_test_writeback(folio),
folio);
// 根据 folio 大小选择不同的截断方式
if (!folio_test_large(folio)) {
// 普通页:直接截断
truncate_inode_folio(mapping, folio);
} else if (truncate_inode_partial_folio(folio, lstart, lend)) {
// 大页:部分截断,可能需要分割
/*
* If we split a page, reset the loop so
* that we pick up the new sub pages.
*/
if (!folio_test_large(folio)) {
folio_unlock(folio);
index = start; // 重置索引,重新处理
break;
}
}
}
folio_unlock(folio);
}
folio_batch_remove_exceptionals(&fbatch);
folio_batch_release(&fbatch);
}
// 重新计算 inode 的统计信息(释放的交换空间)
shmem_recalc_inode(inode, 0, -nr_swaps_freed);
}
访问空洞地址
我们主要研究 shmem 的情况,就用题目中的 copy_from_user 举例。
- 文件系统(如 ext4)通过检查元数据,发现该区域没有分配物理块
- 不会发起真正的磁盘 I/O 去读取数据
- 直接返回全零(0x00)给调用者
流程图
打洞期间
用户空间: copy_from_user(dst, src, size)
↓
内核空间: copy_from_user() [include/linux/uaccess.h:205]
↓
_copy_from_user() / _inline_copy_from_user()
↓
raw_copy_from_user() [arch/x86/include/asm/uaccess_64.h:139]
↓
copy_user_generic() [汇编实现,使用 rep movsb]
↓
[CPU 触发 #PF 异常,因为访问了未映射的页面]
↓
中断处理: exc_page_fault() [arch/x86/mm/fault.c:1493]
↓
handle_page_fault() [arch/x86/mm/fault.c:1469]
↓
do_user_addr_fault() [arch/x86/mm/fault.c:1211]
↓
handle_mm_fault() [mm/memory.c:6046]
↓
__handle_mm_fault() [mm/memory.c:5820]
↓
handle_pte_fault() [mm/memory.c:5736]
↓
do_pte_missing() [mm/memory.c:3959]
↓
do_fault() [mm/memory.c:5405]
↓
do_read_fault() [mm/memory.c:5281] (因为是读操作)
↓
__do_fault() [mm/memory.c:4854]
↓
vma->vm_ops->fault() [对于 shmem 文件,指向 shmem_fault]
↓
shmem_fault() [mm/shmem.c:2515]
↓
shmem_falloc_wait() [mm/shmem.c:2474] ← 关键:检查是否正在打洞
↓
schedule() ← 线程被阻塞,等待打洞完成
打洞后
shmem_falloc_wait() 返回 VM_FAULT_RETRY
↓
向上传播到 do_user_addr_fault()
↓
检测到 fault & VM_FAULT_RETRY
↓
设置 flags |= FAULT_FLAG_TRIED
↓
goto retry - 跳回 retry 标签
↓
重新获取 VMA 锁 (lock_mm_and_find_vma)
↓
重新调用 handle_mm_fault()
↓
再次进入 shmem_fault()
↓
这次 inode->i_private 已经为空(打洞完成)
↓
正常调用 shmem_get_folio_gfp() 分配页面
↓
完成页面映射,返回成功
copy_from_user → raw_copy_from_user
- 检查复制大小,调用底层复制函数
- 在 x86_64 上通常走
_inline_copy_from_user(),最终调用 raw_copy_from_user()
static __always_inline __must_check unsigned long
copy_from_user(void *to, const void __user *from, unsigned long n)
{
if (!check_copy_size(to, n, false))
return n;
#ifdef INLINE_COPY_FROM_USER
return _inline_copy_from_user(to, from, n);
#else
return _copy_from_user(to, from, n);
#endif
}
raw_copy_from_user()
x86_64 实现
- 调用
copy_user_generic()(汇编实现,使用 rep movsb)
- 访问用户空间地址时,若页面未映射或不可访问,CPU 触发
#PF 异常
static __always_inline __must_check unsigned long
raw_copy_from_user(void *dst, const void __user *src, unsigned long size)
{
return copy_user_generic(dst, (__force void *)src, size);
}
exc_page_fault()
- 从
CR2 读取触发异常的地址
- 调用
handle_page_fault() 处理
DEFINE_IDTENTRY_RAW_ERRORCODE(exc_page_fault)
{
irqentry_state_t state;
unsigned long address;
address = cpu_feature_enabled(X86_FEATURE_FRED) ? fred_event_data(regs) : read_cr2();
prefetchw(¤t->mm->mmap_lock);
/*
* KVM uses #PF vector to deliver 'page not present' events to guests
* (asynchronous page fault mechanism). The event happens when a
* userspace task is trying to access some valid (from guest's point of
* view) memory which is not currently mapped by the host (e.g. the
* memory is swapped out). Note, the corresponding "page ready" event
* which is injected when the memory becomes available, is delivered via
* an interrupt mechanism and not a #PF exception
* (see arch/x86/kernel/kvm.c: sysvec_kvm_asyncpf_interrupt()).
*
* We are relying on the interrupted context being sane (valid RSP,
* relevant locks not held, etc.), which is fine as long as the
* interrupted context had IF=1. We are also relying on the KVM
* async pf type field and CR2 being read consistently instead of
* getting values from real and async page faults mixed up.
*
* Fingers crossed.
*
* The async #PF handling code takes care of idtentry handling
* itself.
*/
if (kvm_handle_async_pf(regs, (u32)address))
return;
/*
* Entry handling for valid #PF from kernel mode is slightly
* different: RCU is already watching and ct_irq_enter() must not
* be invoked because a kernel fault on a user space address might
* sleep.
*
* In case the fault hit a RCU idle region the conditional entry
* code reenabled RCU to avoid subsequent wreckage which helps
* debuggability.
*
* The async #PF handling code takes care of idtentry handling
* itself.
*/
state = irqentry_enter(regs);
instrumentation_begin();
handle_page_fault(regs, error_code, address);
instrumentation_end();
irqentry_exit(regs, state);
}
do_user_addr_fault()
如果返回 VM_FAULT_RETRY 标签就会重新尝试访问。重新调用
- 设置
FAULT_FLAG_USER 和 FAULT_FLAG_WRITE 等标志
- 查找并锁定 VMA
- 调用
handle_mm_fault() 处理
static inline
void do_user_addr_fault(struct pt_regs *regs,
unsigned long error_code,
unsigned long address)
{
struct vm_area_struct *vma;
struct task_struct *tsk;
struct mm_struct *mm;
vm_fault_t fault;
unsigned int flags = FAULT_FLAG_DEFAULT;
tsk = current;
mm = tsk->mm;
if (unlikely((error_code & (X86_PF_USER | X86_PF_INSTR)) == X86_PF_INSTR)) {
/*
* Whoops, this is kernel mode code trying to execute from
* user memory. Unless this is AMD erratum #93, which
* corrupts RIP such that it looks like a user address,
* this is unrecoverable. Don't even try to look up the
* VMA or look for extable entries.
*/
if (is_errata93(regs, address))
return;
page_fault_oops(regs, error_code, address);
return;
}
/* kprobes don't want to hook the spurious faults: */
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(kprobe_page_fault(regs, X86_TRAP_PF)))
return;
/*
* Reserved bits are never expected to be set on
* entries in the user portion of the page tables.
*/
if (unlikely(error_code & X86_PF_RSVD))
pgtable_bad(regs, error_code, address);
/*
* If SMAP is on, check for invalid kernel (supervisor) access to user
* pages in the user address space. The odd case here is WRUSS,
* which, according to the preliminary documentation, does not respect
* SMAP and will have the USER bit set so, in all cases, SMAP
* enforcement appears to be consistent with the USER bit.
*/
if (unlikely(cpu_feature_enabled(X86_FEATURE_SMAP) &&
!(error_code & X86_PF_USER) &&
!(regs->flags & X86_EFLAGS_AC))) {
/*
* No extable entry here. This was a kernel access to an
* invalid pointer. get_kernel_nofault() will not get here.
*/
page_fault_oops(regs, error_code, address);
return;
}
/*
* If we're in an interrupt, have no user context or are running
* in a region with pagefaults disabled then we must not take the fault
*/
if (unlikely(faulthandler_disabled() || !mm)) {
bad_area_nosemaphore(regs, error_code, address);
return;
}
/* Legacy check - remove this after verifying that it doesn't trigger */
if (WARN_ON_ONCE(!(regs->flags & X86_EFLAGS_IF))) {
bad_area_nosemaphore(regs, error_code, address);
return;
}
local_irq_enable();
perf_sw_event(PERF_COUNT_SW_PAGE_FAULTS, 1, regs, address);
/*
* Read-only permissions can not be expressed in shadow stack PTEs.
* Treat all shadow stack accesses as WRITE faults. This ensures
* that the MM will prepare everything (e.g., break COW) such that
* maybe_mkwrite() can create a proper shadow stack PTE.
*/
if (error_code & X86_PF_SHSTK)
flags |= FAULT_FLAG_WRITE;
if (error_code & X86_PF_WRITE)
flags |= FAULT_FLAG_WRITE;
if (error_code & X86_PF_INSTR)
flags |= FAULT_FLAG_INSTRUCTION;
/*
* We set FAULT_FLAG_USER based on the register state, not
* based on X86_PF_USER. User space accesses that cause
* system page faults are still user accesses.
*/
if (user_mode(regs))
flags |= FAULT_FLAG_USER;
#ifdef CONFIG_X86_64
/*
* Faults in the vsyscall page might need emulation. The
* vsyscall page is at a high address (>PAGE_OFFSET), but is
* considered to be part of the user address space.
*
* The vsyscall page does not have a "real" VMA, so do this
* emulation before we go searching for VMAs.
*
* PKRU never rejects instruction fetches, so we don't need
* to consider the PF_PK bit.
*/
if (is_vsyscall_vaddr(address)) {
if (emulate_vsyscall(error_code, regs, address))
return;
}
#endif
if (!(flags & FAULT_FLAG_USER))
goto lock_mmap;
vma = lock_vma_under_rcu(mm, address);
if (!vma)
goto lock_mmap;
if (unlikely(access_error(error_code, vma))) {
bad_area_access_error(regs, error_code, address, NULL, vma);
count_vm_vma_lock_event(VMA_LOCK_SUCCESS);
return;
}
fault = handle_mm_fault(vma, address, flags | FAULT_FLAG_VMA_LOCK, regs);
if (!(fault & (VM_FAULT_RETRY | VM_FAULT_COMPLETED)))
vma_end_read(vma);
if (!(fault & VM_FAULT_RETRY)) {
count_vm_vma_lock_event(VMA_LOCK_SUCCESS);
goto done;
}
count_vm_vma_lock_event(VMA_LOCK_RETRY);
if (fault & VM_FAULT_MAJOR)
flags |= FAULT_FLAG_TRIED;
/* Quick path to respond to signals */
if (fault_signal_pending(fault, regs)) {
if (!user_mode(regs))
kernelmode_fixup_or_oops(regs, error_code, address,
SIGBUS, BUS_ADRERR,
ARCH_DEFAULT_PKEY);
return;
}
lock_mmap:
retry:
vma = lock_mm_and_find_vma(mm, address, regs);
if (unlikely(!vma)) {
bad_area_nosemaphore(regs, error_code, address);
return;
}
/*
* Ok, we have a good vm_area for this memory access, so
* we can handle it..
*/
if (unlikely(access_error(error_code, vma))) {
bad_area_access_error(regs, error_code, address, mm, vma);
return;
}
/*
* If for any reason at all we couldn't handle the fault,
* make sure we exit gracefully rather than endlessly redo
* the fault. Since we never set FAULT_FLAG_RETRY_NOWAIT, if
* we get VM_FAULT_RETRY back, the mmap_lock has been unlocked.
*
* Note that handle_userfault() may also release and reacquire mmap_lock
* (and not return with VM_FAULT_RETRY), when returning to userland to
* repeat the page fault later with a VM_FAULT_NOPAGE retval
* (potentially after handling any pending signal during the return to
* userland). The return to userland is identified whenever
* FAULT_FLAG_USER|FAULT_FLAG_KILLABLE are both set in flags.
*/
fault = handle_mm_fault(vma, address, flags, regs);
if (fault_signal_pending(fault, regs)) {
/*
* Quick path to respond to signals. The core mm code
* has unlocked the mm for us if we get here.
*/
if (!user_mode(regs))
kernelmode_fixup_or_oops(regs, error_code, address,
SIGBUS, BUS_ADRERR,
ARCH_DEFAULT_PKEY);
return;
}
/* The fault is fully completed (including releasing mmap lock) */
if (fault & VM_FAULT_COMPLETED)
return;
/*
* If we need to retry the mmap_lock has already been released,
* and if there is a fatal signal pending there is no guarantee
* that we made any progress. Handle this case first.
*/
if (unlikely(fault & VM_FAULT_RETRY)) {
flags |= FAULT_FLAG_TRIED;
goto retry;
}
mmap_read_unlock(mm);
done:
if (likely(!(fault & VM_FAULT_ERROR)))
return;
if (fatal_signal_pending(current) && !user_mode(regs)) {
kernelmode_fixup_or_oops(regs, error_code, address,
0, 0, ARCH_DEFAULT_PKEY);
return;
}
if (fault & VM_FAULT_OOM) {
/* Kernel mode? Handle exceptions or die: */
if (!user_mode(regs)) {
kernelmode_fixup_or_oops(regs, error_code, address,
SIGSEGV, SEGV_MAPERR,
ARCH_DEFAULT_PKEY);
return;
}
/*
* We ran out of memory, call the OOM killer, and return the
* userspace (which will retry the fault, or kill us if we got
* oom-killed):
*/
pagefault_out_of_memory();
} else {
if (fault & (VM_FAULT_SIGBUS|VM_FAULT_HWPOISON|
VM_FAULT_HWPOISON_LARGE))
do_sigbus(regs, error_code, address, fault);
else if (fault & VM_FAULT_SIGSEGV)
bad_area_nosemaphore(regs, error_code, address);
else
BUG();
}
}
NOKPROBE_SYMBOL(do_user_addr_fault);
handle_mm_fault(页错误处理入口)
CPU 硬件检测
↓ (触发 #PF 异常)
软件层页表遍历 (__handle_mm_fault)
├─ PGD → P4D → PUD → PMD → PTE
├─ 检查大页 (PUD/PMD 级别)
└─ 都不是大页 → handle_pte_fault()
↓
handle_pte_fault() 检查 PTE
├─ pte_none() → do_pte_missing() → do_fault() → shmem_fault()
├─ !pte_present() → do_swap_page() (页面在 swap)
└─ pte_present() → 处理权限问题或更新访问标志
- 处理内存控制组(memcg)和 LRU
- 调用
__handle_mm_fault() 进行实际处理
/**
* handle_mm_fault - 页错误处理的主入口函数
* @vma: 发生页错误的虚拟内存区域
* @address: 触发页错误的地址
* @flags: 页错误标志(FAULT_FLAG_USER, FAULT_FLAG_WRITE 等)
* @regs: 寄存器状态(可选,用于统计)
*
* 功能说明:
* 这是内存管理子系统处理页错误的主要入口点。
* 在 do_user_addr_fault() 中找到 VMA 后,会调用此函数。
*
* 处理流程:
* 1. 验证 VMA 访问权限
* 2. 处理内存控制组(memcg)和 LRU 相关逻辑
* 3. 区分大页(hugetlb)和普通页,分别处理
* 4. 对于普通页,调用 __handle_mm_fault() 进行页表遍历和 PTE 处理
*
* 返回值:
* VM_FAULT_* 系列返回值,表示页错误处理结果
*
* 注意:
* 函数返回后,vma 可能已经被释放(如果 mmap_lock 被释放),
* 因此不能再访问 vma 指针。
*/
vm_fault_t handle_mm_fault(struct vm_area_struct *vma, unsigned long address,
unsigned int flags, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
/* If the fault handler drops the mmap_lock, vma may be freed */
struct mm_struct *mm = vma->vm_mm;
vm_fault_t ret;
bool is_droppable;
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
ret = sanitize_fault_flags(vma, &flags);
if (ret)
goto out;
if (!arch_vma_access_permitted(vma, flags & FAULT_FLAG_WRITE,
flags & FAULT_FLAG_INSTRUCTION,
flags & FAULT_FLAG_REMOTE)) {
ret = VM_FAULT_SIGSEGV;
goto out;
}
is_droppable = !!(vma->vm_flags & VM_DROPPABLE);
/*
* Enable the memcg OOM handling for faults triggered in user
* space. Kernel faults are handled more gracefully.
*/
if (flags & FAULT_FLAG_USER)
mem_cgroup_enter_user_fault();
lru_gen_enter_fault(vma);
if (unlikely(is_vm_hugetlb_page(vma)))
ret = hugetlb_fault(vma->vm_mm, vma, address, flags);
else
ret = __handle_mm_fault(vma, address, flags);
/* Warning: It is no longer safe to dereference vma-> after this point,
* because mmap_lock might have been dropped by __handle_mm_fault(), so
* vma might be destroyed from underneath us.
*/
lru_gen_exit_fault();
/* If the mapping is droppable, then errors due to OOM aren't fatal. */
if (is_droppable)
ret &= ~VM_FAULT_OOM;
if (flags & FAULT_FLAG_USER) {
mem_cgroup_exit_user_fault();
/* The task may have entered a memcg OOM situation but
* if the allocation error was handled gracefully (no
* VM_FAULT_OOM), there is no need to kill anything.
* Just clean up the OOM state peacefully.
*/
if (task_in_memcg_oom(current) && !(ret & VM_FAULT_OOM))
mem_cgroup_oom_synchronize(false);
}
out:
mm_account_fault(mm, regs, address, flags, ret);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(handle_mm_fault);
__handle_mm_fault
/**
* __handle_mm_fault - 页表遍历和页错误处理的核心函数
* @vma: 发生页错误的虚拟内存区域
* @address: 触发页错误的地址
* @flags: 页错误标志
*
* 功能说明:
* 这是页错误处理的核心函数,负责遍历页表结构并处理不同级别的页错误。
* 对于 punch hole 场景,最终会遍历到 PTE 级别,发现 PTE 为空后调用
* handle_pte_fault() 处理。
*
* 页表遍历流程(x86_64 五级页表):
* PGD (Page Global Directory)
* ↓
* P4D (Page 4th Directory)
* ↓
* PUD (Page Upper Directory) - 检查是否为大页(1GB)
* ↓
* PMD (Page Middle Directory) - 检查是否为大页(2MB)
* ↓
* PTE (Page Table Entry) - 普通页(4KB)
*
* 处理逻辑:
* 1. 逐级分配页表项(如果不存在)
* 2. 检查每一级是否为大页(THP),如果是则特殊处理
* 3. 如果都不是大页,继续到下一级
* 4. 最终到达 PTE 级别,调用 handle_pte_fault() 处理
*
* 对于 punch hole 场景:
* - PTE 为空(pte_none),表示页面未映射
* - handle_pte_fault() 会检测到并调用 do_pte_missing()
* - 最终调用文件系统的 fault 处理函数(如 shmem_fault)
*/
static vm_fault_t __handle_mm_fault(struct vm_area_struct *vma,
unsigned long address, unsigned int flags)
{
struct vm_fault vmf = {
.vma = vma,
.address = address & PAGE_MASK,
.real_address = address,
.flags = flags,
.pgoff = linear_page_index(vma, address),
.gfp_mask = __get_fault_gfp_mask(vma),
};
struct mm_struct *mm = vma->vm_mm;
unsigned long vm_flags = vma->vm_flags;
pgd_t *pgd;
p4d_t *p4d;
vm_fault_t ret;
/* 步骤1: 遍历 PGD 和 P4D */
pgd = pgd_offset(mm, address);
p4d = p4d_alloc(mm, pgd, address);
if (!p4d)
return VM_FAULT_OOM;
/* 步骤2: 遍历 PUD,检查是否为大页(1GB) */
vmf.pud = pud_alloc(mm, p4d, address);
if (!vmf.pud)
return VM_FAULT_OOM;
retry_pud:
if (pud_none(*vmf.pud) &&
thp_vma_allowable_order(vma, vm_flags,
TVA_IN_PF | TVA_ENFORCE_SYSFS, PUD_ORDER)) {
ret = create_huge_pud(&vmf);
if (!(ret & VM_FAULT_FALLBACK))
return ret;
} else {
pud_t orig_pud = *vmf.pud;
barrier();
if (pud_trans_huge(orig_pud) || pud_devmap(orig_pud)) {
/*
* TODO once we support anonymous PUDs: NUMA case and
* FAULT_FLAG_UNSHARE handling.
*/
if ((flags & FAULT_FLAG_WRITE) &&
!pud_write(orig_pud)) {
ret = wp_huge_pud(&vmf, orig_pud);
if (!(ret & VM_FAULT_FALLBACK))
return ret;
} else {
huge_pud_set_accessed(&vmf, orig_pud);
return 0;
}
}
}
/* 步骤3: 遍历 PMD,检查是否为大页(2MB) */
vmf.pmd = pmd_alloc(mm, vmf.pud, address);
if (!vmf.pmd)
return VM_FAULT_OOM;
/* Huge pud page fault raced with pmd_alloc? */
if (pud_trans_unstable(vmf.pud))
goto retry_pud;
if (pmd_none(*vmf.pmd) &&
thp_vma_allowable_order(vma, vm_flags,
TVA_IN_PF | TVA_ENFORCE_SYSFS, PMD_ORDER)) {
ret = create_huge_pmd(&vmf);
if (!(ret & VM_FAULT_FALLBACK))
return ret;
} else {
vmf.orig_pmd = pmdp_get_lockless(vmf.pmd);
if (unlikely(is_swap_pmd(vmf.orig_pmd))) {
VM_BUG_ON(thp_migration_supported() &&
!is_pmd_migration_entry(vmf.orig_pmd));
if (is_pmd_migration_entry(vmf.orig_pmd))
pmd_migration_entry_wait(mm, vmf.pmd);
return 0;
}
if (pmd_trans_huge(vmf.orig_pmd) || pmd_devmap(vmf.orig_pmd)) {
if (pmd_protnone(vmf.orig_pmd) &&
vma_is_accessible(vma))
return do_huge_pmd_numa_page(&vmf);
if ((flags & (FAULT_FLAG_WRITE | FAULT_FLAG_UNSHARE)) &&
!pmd_write(vmf.orig_pmd)) {
ret = wp_huge_pmd(&vmf);
if (!(ret & VM_FAULT_FALLBACK))
return ret;
} else {
huge_pmd_set_accessed(&vmf);
return 0;
}
}
}
/* 步骤4: 都不是大页,处理普通页(4KB),检查 PTE */
return handle_pte_fault(&vmf);
}
handle_pte_fault
- 获取 pte 检查是否为空(
pte_none),如果为空则调用 do_pte_missing()
/**
* handle_pte_fault - 处理 PTE(页表项)级别的页错误
* @vmf: 页错误描述结构体
*
* 功能说明:
* 这是页表遍历的最后一级,负责检查和处理 PTE 的状态。
* 对于 punch hole 场景,PTE 为空(pte_none),表示页面未映射。
*
* PTE 状态检查和处理:
* 1. pte_none() - PTE 为空(页面未映射)
* → 调用 do_pte_missing() → do_fault() → shmem_fault()
* → 这是 punch hole 场景的路径!
*
* 2. !pte_present() - PTE 存在但不是 present(页面在 swap)
* → 调用 do_swap_page() 从 swap 换入页面
*
* 3. pte_protnone() - PTE 存在但权限不足(NUMA 页面)
* → 调用 do_numa_page() 处理 NUMA 迁移
*
* 4. pte_present() - PTE 存在且有效
* → 检查写权限,处理写时复制(COW)或更新访问标志
*
* 对于 punch hole 攻击:
* 当访问被 fallocate PUNCH_HOLE 打洞的地址时:
* - PTE 为空(pte_none),vmf->pte 被设置为 NULL
* - 调用 do_pte_missing() 处理缺失的页面
* - 最终会调用文件系统的 fault 处理函数
*/
static vm_fault_t handle_pte_fault(struct vm_fault *vmf)
{
pte_t entry;
if (unlikely(pmd_none(*vmf->pmd))) {
/* Leave __pte_alloc() until later: because vm_ops->fault may
* want to allocate huge page, and if we expose page table
* for an instant, it will be difficult to retract from
* concurrent faults and from rmap lookups.
*/
vmf->pte = NULL;
vmf->flags &= ~FAULT_FLAG_ORIG_PTE_VALID;
} else {
/* A regular pmd is established and it can't morph into a huge
* pmd by anon khugepaged, since that takes mmap_lock in write
* mode; but shmem or file collapse to THP could still morph
* it into a huge pmd: just retry later if so.
*/
/* 获取 PTE 指针 */
vmf->pte = pte_offset_map_nolock(vmf->vma->vm_mm, vmf->pmd,
vmf->address, &vmf->ptl);
if (unlikely(!vmf->pte))
return 0;
/* 读取 PTE 的值(无锁读取) */
vmf->orig_pte = ptep_get_lockless(vmf->pte);
vmf->flags |= FAULT_FLAG_ORIG_PTE_VALID;
/* 关键检查:如果 PTE 为空(页面未映射,例如被 punch hole) */
if (pte_none(vmf->orig_pte)) {
pte_unmap(vmf->pte);
vmf->pte = NULL; /* 标记 PTE 不存在 */
}
}
/* 情况1: PTE 为空(页面未映射)- punch hole 场景走这里 */
if (!vmf->pte)
return do_pte_missing(vmf);
/* 情况2: PTE 存在但不是 present(页面在 swap 中) */
if (!pte_present(vmf->orig_pte))
return do_swap_page(vmf);
/* 情况3: PTE 存在但权限不足(NUMA 页面) */
if (pte_protnone(vmf->orig_pte) && vma_is_accessible(vmf->vma))
return do_numa_page(vmf);
spin_lock(vmf->ptl);
entry = vmf->orig_pte;
if (unlikely(!pte_same(ptep_get(vmf->pte), entry))) {
update_mmu_tlb(vmf->vma, vmf->address, vmf->pte);
goto unlock;
}
if (vmf->flags & (FAULT_FLAG_WRITE | FAULT_FLAG_UNSHARE)) {
if (!pte_write(entry))
return do_wp_page(vmf);
else if (likely(vmf->flags & FAULT_FLAG_WRITE))
entry = pte_mkdirty(entry);
}
entry = pte_mkyoung(entry);
if (ptep_set_access_flags(vmf->vma, vmf->address, vmf->pte, entry,
vmf->flags & FAULT_FLAG_WRITE)) {
update_mmu_cache_range(vmf, vmf->vma, vmf->address, vmf->pte,
1);
} else {
/* Skip spurious TLB flush for retried page fault */
if (vmf->flags & FAULT_FLAG_TRIED)
goto unlock;
/* This is needed only for protection faults but the arch code
* is not yet telling us if this is a protection fault or not.
* This still avoids useless tlb flushes for .text page faults
* with threads.
*/
if (vmf->flags & FAULT_FLAG_WRITE)
flush_tlb_fix_spurious_fault(vmf->vma, vmf->address,
vmf->pte);
}
unlock:
pte_unmap_unlock(vmf->pte, vmf->ptl);
return 0;
}
do_pte_missing
- 若为 swap,调用
do_swap_page()
- 对于
shmem 文件映射,通常走 do_pte_missing[do_pte_missing() → do_fault()]
/**
* do_pte_missing - 处理 PTE 为空(页面未映射)的情况
* @vmf: 页错误描述结构体
*
* 功能说明:
* 当 handle_pte_fault() 检测到 PTE 为空时调用此函数。
* 这是 punch hole 攻击场景的关键路径。
*
* 处理逻辑:
* - 匿名 VMA(匿名内存映射):调用 do_anonymous_page() 分配新页面
* - 文件映射 VMA(如 shmem 文件):调用 do_fault() 处理文件页错误
*
* 对于 punch hole 场景:
* - shmem 文件映射走 do_fault() 路径
* - 最终会调用 shmem_fault(),检测到正在打洞时会阻塞等待
*/
static vm_fault_t do_pte_missing(struct vm_fault *vmf)
{
if (vma_is_anonymous(vmf->vma))
return do_anonymous_page(vmf);
else
return do_fault(vmf);
}
do_fault
- 读操作走
do_read_fault,写操作根据是否共享选择 do_cow_fault 或 do_shared_fault
- 当然我们这里是走
copy_from_user 是读操作,走 do_read_fault(do_read_fault → _do_fault)
/**
* do_fault - 处理文件映射的页错误
* @vmf: 页错误描述结构体
*
* 功能说明:
* 当 do_pte_missing() 检测到是文件映射(非匿名)时调用此函数。
* 根据访问类型(读/写)和 VMA 属性(共享/私有)选择不同的处理路径。
*
* 处理路径:
* 1. 没有 fault 处理函数:返回错误
* 2. 读操作(copy_from_user 是读):
* → do_read_fault() → __do_fault() → vma->vm_ops->fault()
* → 对于 shmem: shmem_fault()
* 3. 写操作 + 私有映射(COW):
* → do_cow_fault() 写时复制
* 4. 写操作 + 共享映射:
* → do_shared_fault() 共享写入
*
* 对于 punch hole 场景:
* - copy_from_user 是读操作,走 do_read_fault() 路径
* - 最终调用 shmem_fault(),检测到正在打洞时会阻塞
*/
static vm_fault_t do_fault(struct vm_fault *vmf)
{
struct vm_area_struct *vma = vmf->vma;
struct mm_struct *vm_mm = vma->vm_mm;
vm_fault_t ret;
/*
* The VMA was not fully populated on mmap() or missing VM_DONTEXPAND
*/
if (!vma->vm_ops->fault) {
vmf->pte = pte_offset_map_lock(vmf->vma->vm_mm, vmf->pmd,
vmf->address, &vmf->ptl);
if (unlikely(!vmf->pte))
ret = VM_FAULT_SIGBUS;
else {
/*
* Make sure this is not a temporary clearing of pte
* by holding ptl and checking again. A R/M/W update
* of pte involves: take ptl, clearing the pte so that
* we don't have concurrent modification by hardware
* followed by an update.
*/
if (unlikely(pte_none(ptep_get(vmf->pte))))
ret = VM_FAULT_SIGBUS;
else
ret = VM_FAULT_NOPAGE;
pte_unmap_unlock(vmf->pte, vmf->ptl);
}
} else if (!(vmf->flags & FAULT_FLAG_WRITE))
/* 读操作:copy_from_user 走这里 */
ret = do_read_fault(vmf);
else if (!(vma->vm_flags & VM_SHARED))
/* 写操作 + 私有映射:写时复制 */
ret = do_cow_fault(vmf);
else
/* 写操作 + 共享映射:共享写入 */
ret = do_shared_fault(vmf);
/* preallocated pagetable is unused: free it */
if (vmf->prealloc_pte) {
pte_free(vm_mm, vmf->prealloc_pte);
vmf->prealloc_pte = NULL;
}
return ret;
}
__do_fault → vma->vm_ops->fault
然后如果我们是 shmem_fault 调用的则指向 shmem_fault
static vm_fault_t __do_fault(struct vm_fault *vmf)
{
struct vm_area_struct *vma = vmf->vma;
struct folio *folio;
vm_fault_t ret;
/*
* Preallocate pte before we take page_lock because this might lead to
* deadlocks for memcg reclaim which waits for pages under writeback:
* lock_page(A)
* SetPageWriteback(A)
* unlock_page(A)
* lock_page(B)
* lock_page(B)
* pte_alloc_one
* shrink_folio_list
* wait_on_page_writeback(A)
* SetPageWriteback(B)
* unlock_page(B)
* # flush A, B to clear the writeback
*/
if (pmd_none(*vmf->pmd) && !vmf->prealloc_pte) {
vmf->prealloc_pte = pte_alloc_one(vma->vm_mm);
if (!vmf->prealloc_pte)
return VM_FAULT_OOM;
}
ret = vma->vm_ops->fault(vmf);
if (unlikely(ret & (VM_FAULT_ERROR | VM_FAULT_NOPAGE | VM_FAULT_RETRY |
VM_FAULT_DONE_COW)))
return ret;
folio = page_folio(vmf->page);
if (unlikely(PageHWPoison(vmf->page))) {
vm_fault_t poisonret = VM_FAULT_HWPOISON;
if (ret & VM_FAULT_LOCKED) {
if (page_mapped(vmf->page))
unmap_mapping_folio(folio);
/* Retry if a clean folio was removed from the cache. */
if (mapping_evict_folio(folio->mapping, folio))
poisonret = VM_FAULT_NOPAGE;
folio_unlock(folio);
}
folio_put(folio);
vmf->page = NULL;
return poisonret;
}
if (unlikely(!(ret & VM_FAULT_LOCKED)))
folio_lock(folio);
else
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(!folio_test_locked(folio), vmf->page);
return ret;
}
shmem_fault(检查是否正在打洞)
inode->i_private 非空表示正在打洞 - 调用
shmem_falloc_wait() 等待打洞完成
/**
* shmem_falloc_wait - 等待 fallocate PUNCH_HOLE 操作完成
* @vmf: 页错误描述结构体
* @inode: shmem 文件的 inode
*
* 功能说明:
* 这是 punch hole 攻击的核心函数!
* 当 shmem_fault() 检测到正在打洞时调用此函数。
*
* 处理流程:
* 1. 检查当前页号是否在打洞范围内
* 2. 准备等待队列,设置线程状态为 TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE
* 3. 调用 schedule() 让出 CPU,线程被阻塞
* 4. 等待打洞线程完成并调用 wake_up_all() 唤醒
* 5. 清理等待状态,返回 VM_FAULT_RETRY 重试
*
* 攻击利用:
* 在 schedule() 阻塞期间:
* - copy_from_user 所在的线程被阻塞
* - 攻击者可以利用这个时间窗口进行堆操作
* - 例如:在 free 后、置空前进行 UAF 或 Double Free
*
* 时间窗口:
* - 从 schedule() 调用开始,到打洞完成并 wake_up_all() 为止
* - 这个时间窗口足够长,可以进行多次堆操作
*/
static vm_fault_t shmem_falloc_wait(struct vm_fault *vmf, struct inode *inode)
{
struct shmem_falloc *shmem_falloc;
struct file *fpin = NULL;
vm_fault_t ret = 0;
spin_lock(&inode->i_lock);
shmem_falloc = inode->i_private;
/* 检查:当前页号是否在打洞范围内 */
if (shmem_falloc && shmem_falloc->waitq &&
vmf->pgoff >= shmem_falloc->start &&
vmf->pgoff < shmem_falloc->next) {
wait_queue_head_t *shmem_falloc_waitq;
DEFINE_WAIT_FUNC(shmem_fault_wait, synchronous_wake_function);
ret = VM_FAULT_NOPAGE;
fpin = maybe_unlock_mmap_for_io(vmf, NULL);
shmem_falloc_waitq = shmem_falloc->waitq;
/* 步骤1: 准备等待,设置线程状态为不可中断睡眠 */
prepare_to_wait(shmem_falloc_waitq, &shmem_fault_wait,
TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE);
spin_unlock(&inode->i_lock);
/* 步骤2: 关键阻塞点 - 让出 CPU,线程被阻塞 */
/* 攻击者可以利用这个时间窗口进行堆操作! */
schedule();
/*
* shmem_falloc_waitq points into the shmem_fallocate()
* stack of the hole-punching task: shmem_falloc_waitq
* is usually invalid by the time we reach here, but
* finish_wait() does not dereference it in that case;
* though i_lock needed lest racing with wake_up_all().
*/
/* 步骤3: 打洞完成,被唤醒,清理等待状态 */
spin_lock(&inode->i_lock);
finish_wait(shmem_falloc_waitq, &shmem_fault_wait);
}
spin_unlock(&inode->i_lock);
if (fpin) {
fput(fpin);
/* 返回 RETRY,让调用者重试页错误处理 */
ret = VM_FAULT_RETRY;
}
return ret;
}
shmem_falloc_wait(核心)
然后这里会返回 VM_FAULT_RETRY 标签
- 检查当前页号是否在打洞范围内
prepare_to_wait() + schedule() 使线程进入不可中断睡眠 - 等待期间,内核线程被阻塞,为攻击者提供时间窗口
- 打洞完成后,
wake_up_all() 唤醒等待线程
static vm_fault_t shmem_falloc_wait(struct vm_fault *vmf, struct inode *inode)
{
struct shmem_falloc *shmem_falloc;
struct file *fpin = NULL;
vm_fault_t ret = 0;
spin_lock(&inode->i_lock);
shmem_falloc = inode->i_private;
// 关键检查: 确认正在打洞,且当前页在打洞范围内
if (shmem_falloc &&
shmem_falloc->waitq &&
vmf->pgoff >= shmem_falloc->start &&
vmf->pgoff < shmem_falloc->next) {
wait_queue_head_t *shmem_falloc_waitq;
DEFINE_WAIT_FUNC(shmem_fault_wait, synchronous_wake_function);
ret = VM_FAULT_NOPAGE;
fpin = maybe_unlock_mmap_for_io(vmf, NULL);
shmem_falloc_waitq = shmem_falloc->waitq;
// 关键步骤1: 准备等待
prepare_to_wait(shmem_falloc_waitq, &shmem_fault_wait,
TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE);
spin_unlock(&inode->i_lock);
// 关键步骤2: 调用 schedule() 让出 CPU,线程被阻塞
// 这里就是"慢页面错误"的关键!
// 线程会一直等待,直到打洞完成并调用 wake_up_all()
schedule();
/*
* shmem_falloc_waitq points into the shmem_fallocate()
* stack of the hole-punching task: shmem_falloc_waitq
* is usually invalid by the time we reach here, but
* finish_wait() does not dereference it in that case;
* though i_lock needed lest racing with wake_up_all().
*/
// 防止在打洞期间将页面错误处理到洞中,避免打洞无法完成
// 使用等待队列而非互斥锁,因为不能在 fault 处理中持有 i_rwsem
spin_lock(&inode->i_lock);
finish_wait(shmem_falloc_waitq, &shmem_fault_wait);
}
spin_unlock(&inode->i_lock);
if (fpin) {
fput(fpin);
ret = VM_FAULT_RETRY; // 返回 RETRY,让调用者重试
}
return ret;
}
重试
可能有点啰嗦,但是我们需要注意的是当 shmem_falloc_wait 调用后会返回 VM_FAULT_RETRY 给 do_user_addr_fault(),然后重新调用一次 handle_mm_fault。那么我们就可以利用这一点,一直尝试打洞,这样就可以提高利用的成功率。可以发现还是能拖延很多次调用时间的,成功率较大。那么我们利用这个条件竞争就可以比较轻松打出 double-free 或者 UAF。
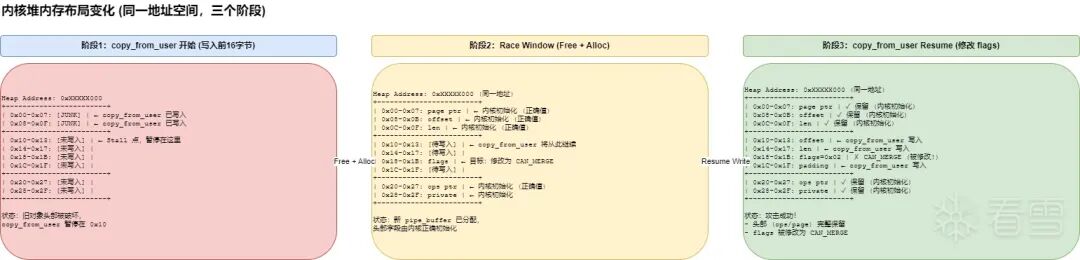
小 trick:任意 offset 读写
然后也是听 Tplus 大佬那里学到了一个关于 punch hole 实现任意 offset 读写的小 trick。感觉特别强,在这里做分享。
前面讲到了 punch hole,我们拥有了延迟 copy_from_user 的能力,那么进一步扩展这个能力我们可以得到什么?
先回到题目中:
case 322376505:
v8 = allocated_objects[v9.index];
if ( !v8 )
return -1;
if ( v9.length > 0x7FFFFFFFuLL )
BUG();
return -(copy_from_user(v8, v9.buf, v9.length) != 0);
- 我们可以看见这里有个写入操作,正常情况下我们理解都是只能从
obj 的头开始写入的。
原理
当然这个题目本身是可以完成 Double-Free 这种更好用的原语,但是如果我们非得用 UAF 的情况下挑战自己有没有什么比较好的办法实现提权捏?那么这里就是关键,我们可以将我们的 buf 刚好卡在两个 Page 的中间,让第一个 Page 是正常的 page,第二个 page 是处于 hole 中的。
本质是利用 copy_from_user 的非原子性,通过 FALLOC_FL_PUNCH_HOLE 制造时间窗口,在 Stall 期间释放旧对象并分配新对象,最终实现“保护头部、修改尾部”的攻击效果。
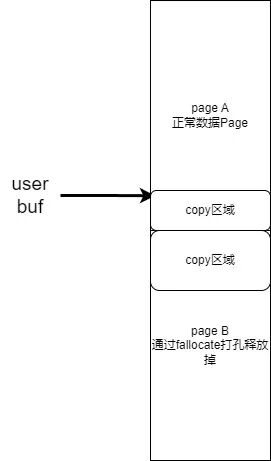
那么有什么作用?首先就是 v8 先是我们正常的 obj,然后触发 copy_from_user 正常进行读操作,随后访问到第二个 Page 的时候,由于是 hole 所以会触发缺页中断并且等待打洞完成。(如图)
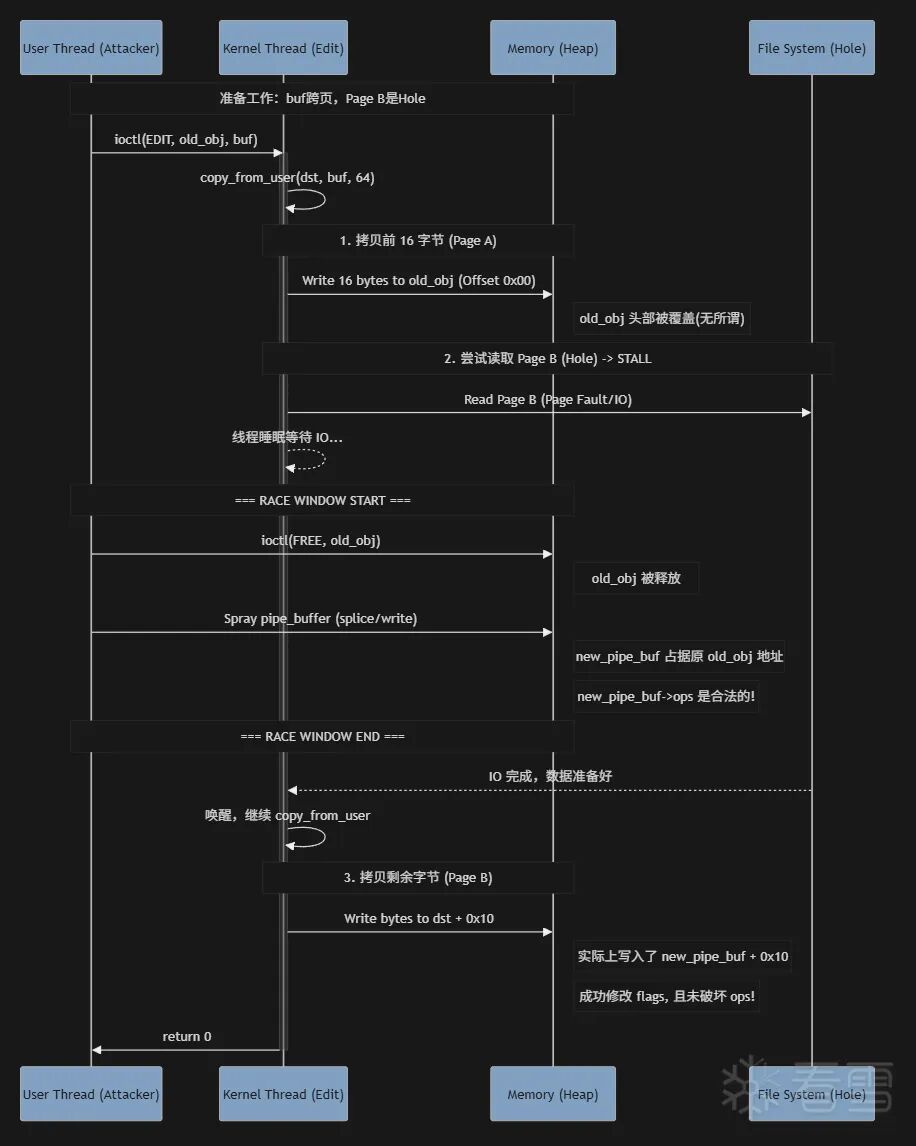
那么这个时候我们快速释放掉这个 Obj,并且堆喷上我们的目标结构体,那么此时 obj 已经变成我们的目标 obj 了,但是 copy_from_user 的 offset 不会改变。所以就会直接改写对应 offset 的内存。
时序图

参考文章