你是否遇到过SpringBoot配置文件加载失败却查不到原因?是否好奇application.yml里的配置怎么“跑”到Environment里?本文将从PropertySourceLoader的源码出发,彻底讲透SpringBoot配置解析的底层逻辑。
一、PropertySourceLoader:配置加载的“翻译官”
在SpringBoot中,无论是.properties还是.yaml配置文件,最终都需要转换为PropertySource(Spring环境的配置单元)才能被应用读取。而完成“配置文件 → PropertySource”这一转换的核心组件,就是 PropertySourceLoader。
它是一个SPI(Service Provider Interface)接口,定义了配置加载的标准流程:
// SpringBoot核心配置加载接口
public interface PropertySourceLoader {
// 支持的配置文件扩展名(如properties、yml)
String[] getFileExtensions();
// 核心方法:将资源转为PropertySource列表
List<PropertySource<?>> load(String name, Resource resource) throws IOException;
}
所有具体的配置加载器(例如PropertiesPropertySourceLoader、YamlPropertySourceLoader)都必须实现这个接口。SpringBoot在启动时,会通过SPI机制自动发现并加载这些实现类,这是理解其扩展性的关键。
二、源码追踪:配置加载的全流程
SpringBoot启动时,ConfigFileApplicationListener(一个EnvironmentPostProcessor)会触发配置加载。让我们从它的postProcessEnvironment方法开始,逐步拆解整个核心流程。
1. 触发配置加载:EnvironmentPostProcessor的调用
当SpringApplication准备好Environment(环境上下文)之后,会调用所有EnvironmentPostProcessor的postProcessEnvironment方法。ConfigFileApplicationListener作为核心实现类,会遍历所有PropertySourceLoader,并调用它们的load方法。
// ConfigFileApplicationListener的核心逻辑(简化)
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
// 1. 定位配置文件(如application.properties)
Resource[] resources = getConfigResources(environment);
// 2. 遍历PropertySourceLoader实现类
for (PropertySourceLoader loader : SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(PropertySourceLoader.class, getClass().getClassLoader())) {
// 3. 调用load方法加载配置
List<PropertySource<?>> propertySources = loader.load(“applicationConfig”, resource);
// 4. 将PropertySource添加到Environment
addPropertySources(environment, propertySources);
}
}
2. 核心逻辑:PropertySourceLoader的load方法
以PropertiesPropertySourceLoader为例,它的load方法负责将.properties文件转换为PropertySource:
// Properties配置加载的核心实现(简化)
public class PropertiesPropertySourceLoader implements PropertySourceLoader {
@Override
public String[] getFileExtensions() {
return new String[]{"properties", "xml"}; // 支持properties和xml格式
}
@Override
public List<PropertySource<?>> load(String name, Resource resource) throws IOException {
// 关键步骤1:读取配置文件的输入流
try (InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream()) {
// 关键步骤2:解析输入流为Properties对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(inputStream); // 底层是Java标准的Properties解析
// 关键步骤3:封装为PropertySource
return Collections.singletonList(new PropertiesPropertySource(name, properties));
}
}
}
而YamlPropertySourceLoader的逻辑类似,但它会使用Yaml类(基于SnakeYAML)将输入流解析为Map结构,从而支持嵌套配置:
// Yaml配置加载的核心实现(简化)
public class YamlPropertySourceLoader implements PropertySourceLoader {
@Override
public String[] getFileExtensions() {
return new String[]{"yml", "yaml"};
}
@Override
public List<PropertySource<?>> load(String name, Resource resource) throws IOException {
try (InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream()) {
// 用SnakeYAML解析流为Map(支持嵌套)
Yaml yaml = new Yaml();
Map<String, Object> yamlMap = yaml.loadAs(inputStream, Map.class);
// 转为MapPropertySource(支持嵌套配置)
return Collections.singletonList(new MapPropertySource(name, yamlMap));
}
}
}
3. 流程可视化:UML时序图
为了更清晰地展示整个流程,下图描述了配置加载的核心时序:
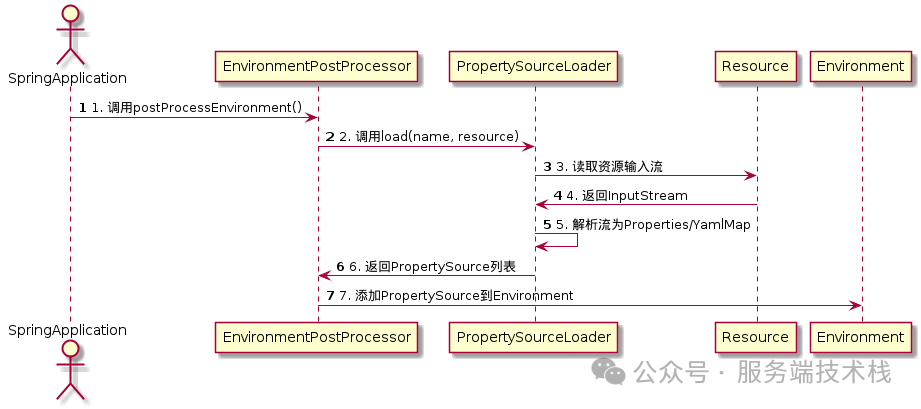
在时序图中,PropertySourceLoader扮演着“中间翻译官”的角色:它接收Resource(配置文件资源),将其解析为PropertySource,最终由框架注入到Environment中。理解Spring Boot 的这一机制,是进行高级定制和问题排查的基础。
三、实战验证:自定义PropertySourceLoader
如果我们想支持一种自定义格式的配置文件(例如JSON),只需要实现PropertySourceLoader接口即可。这是一个很好的开源实战练习,能加深对SPI扩展机制的理解。
// 自定义JSON配置加载器
public class JsonPropertySourceLoader implements PropertySourceLoader {
@Override
public String[] getFileExtensions() {
return new String[]{"json"}; // 支持.json文件
}
@Override
public List<PropertySource<?>> load(String name, Resource resource) throws IOException {
try (InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream()) {
// 用Jackson解析JSON为Map
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
Map<String, Object> jsonMap = mapper.readValue(inputStream, Map.class);
// 转为PropertySource
return Collections.singletonList(new MapPropertySource(name, jsonMap));
}
}
}
接着,在 META-INF/spring.factories 文件中进行注册:
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\
com.example.demo.JsonPropertySourceLoader
这样,SpringBoot启动时就会自动加载并识别.json配置文件。
四、总结:配置加载的“底层逻辑”
本质上,PropertySourceLoader就是SpringBoot配置加载体系的“翻译官”。它负责将你编写的各种格式(properties、yaml等)的配置文件,翻译成Spring框架能够理解的PropertySource对象,再注入到Environment中。无论格式如何变化,其核心逻辑都是固定的三步:读取资源 → 解析内容 → 封装为PropertySource。
实际开发中遇到的配置加载问题,大多都出在这个“翻译”环节。例如YAML文件的缩进错误(导致YamlPropertySourceLoader解析失败)、Properties文件的编码问题(导致PropertiesPropertySourceLoader读取乱码)。搞懂了PropertySourceLoader的工作原理,再遇到配置不生效的问题时,你就可以直指核心,定位是否是“翻译官”本身或它处理的“原材料”(配置文件)出了问题,而不是盲目排查。
希望这篇源码解析能帮助你更好地理解和驾驭SpringBoot的配置系统。如果你想深入探讨更多Spring生态的技术细节,欢迎访问云栈社区与其他开发者交流。