二分查找(Binary Search),又称折半查找,是一种基于有序数据集合的高效查找算法。其核心思想是每次比较都将查找范围缩小一半,从而在 O(log n) 的时间复杂度内快速定位目标元素。该算法要求数据预先排序,并适用于支持随机访问的结构如数组,相较于线性查找,在处理大规模数据时优势显著。
算法原理与步骤
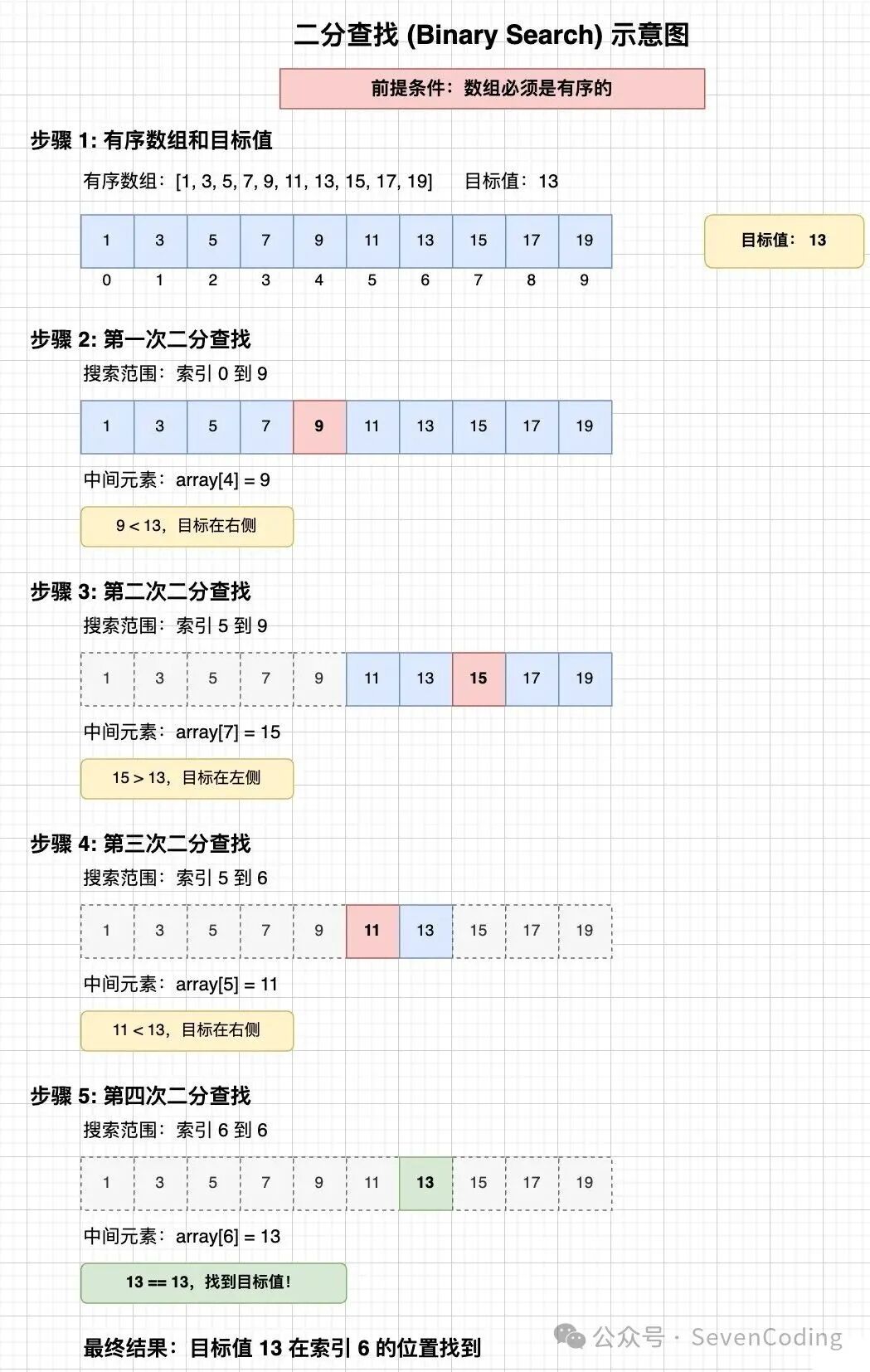
二分查找遵循一套清晰的逻辑流程:
- 初始化:确定查找范围的左边界
left 和右边界 right。
- 计算中点:取中间位置
mid。为避免整数溢出,推荐使用 mid = left + (right - left) / 2 而非 (left + right) / 2。
- 比较判断:将
arr[mid] 与目标值 target 进行比较:
- 若相等,则查找成功,返回
mid。
- 若
arr[mid] > target,说明目标值在左半部分,更新 right = mid - 1。
- 若
arr[mid] < target,说明目标值在右半部分,更新 left = mid + 1。
- 循环迭代:重复步骤2-3,直至
left > right(查找失败)或找到目标值。
核心特性:
- 前提条件:数据必须有序。
- 时间复杂度:O(log n),处理大规模数据效率极高。
- 空间复杂度:迭代实现为 O(1),递归实现为 O(log n)。
- 访问要求:依赖数据结构支持 O(1) 时间复杂度的随机访问(如数组)。
基础代码实现
以下是在 Java 中实现二分查找的两种方式:迭代与递归。
public class BinarySearch {
// 迭代实现
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
// 避免整数溢出
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// 找到目标值
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
// 在左半部分继续查找
else if (arr[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
}
// 在右半部分继续查找
else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
// 未找到目标值
return -1;
}
// 递归实现
public static int binarySearchRecursive(int[] arr, int target, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) {
return -1;
}
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] > target) {
return binarySearchRecursive(arr, target, left, mid - 1);
} else {
return binarySearchRecursive(arr, target, mid + 1, right);
}
}
// 测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2, 3, 4, 10, 40, 50, 70, 80};
int target = 10;
// 迭代方法
int result = binarySearch(arr, target);
if (result == -1) {
System.out.println("元素 " + target + " 不存在于数组中");
} else {
System.out.println("元素 " + target + " 在数组中的索引为 " + result);
}
// 递归方法
result = binarySearchRecursive(arr, target, 0, arr.length - 1);
if (result == -1) {
System.out.println("元素 " + target + " 不存在于数组中");
} else {
System.out.println("元素 " + target + " 在数组中的索引为 " + result);
}
}
}
优缺点分析
优点:
- 极高的查找效率(O(log n))。
- 在大规模数据集上表现卓越。
- 实现逻辑清晰简单。
- 迭代版本无需额外空间。
缺点:
- 强制要求数据有序,维护有序性可能带来额外开销。
- 仅适用于数组等支持随机访问的结构。
- 对于小规模数据,优势不明显甚至可能慢于线性查找。
典型应用场景
二分查找的思想广泛应用于计算机科学的各个领域,是算法与数据结构学习的基石之一。
- 数据库索引:如 B+ 树等索引结构的查找过程基于二分思想。
- 边界查找:寻找第一个/最后一个等于(或大于/小于)目标值的位置。
- 数值计算:用于求解平方根等数学问题(二分法)。
- 特殊数组查找:在旋转排序数组中查找元素或最小值。
哈希查找(Hash Search),又称散列查找,采用完全不同的设计哲学。它通过哈希函数将数据元素的关键字直接映射到存储地址(数组下标),理想情况下可实现 O(1) 时间复杂度的查找,其核心是以空间换取时间。
算法原理与步骤
哈希查找的核心在于构建和管理哈希表:
- 哈希函数设计:将关键字转换为数组索引。
- 建表与插入:根据哈希值将元素存入哈希表对应位置。
- 冲突解决:处理不同关键字映射到同一地址的“哈希冲突”(常用链地址法或开放寻址法)。
- 执行查找:用相同哈希函数计算目标关键字地址,并在该位置(及冲突链)中查找。
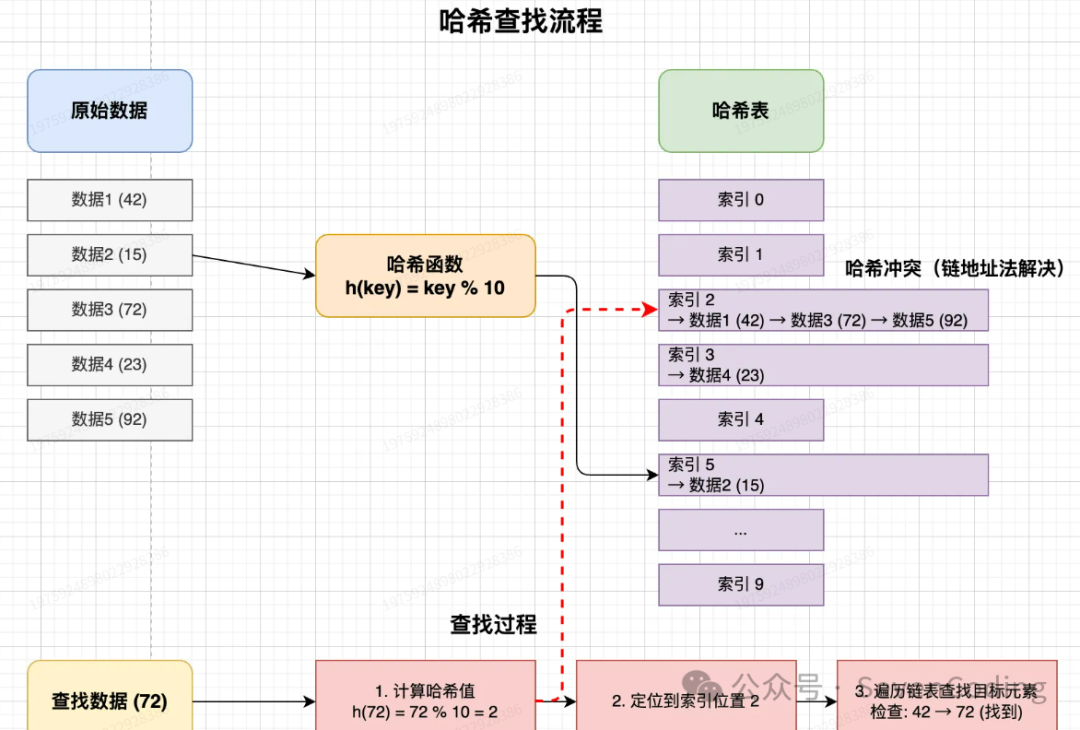
核心概念:
- 哈希函数:决定数据分布均匀性的关键。
- 哈希冲突:不可避免,处理方式直接影响性能。
- 负载因子:表中已存元素数与总容量的比值,触发扩容的阈值。
- 动态扩容:当负载因子过高时,需重建哈希表以维持性能。
基础代码实现(链地址法)
以下是一个使用链地址法解决冲突的简单哈希表实现。
public class HashSearch {
// 哈希表节点类
static class Node {
String key;
int value;
Node next;
public Node(String key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
// 哈希表类
static class HashTable {
private Node[] buckets;
private int capacity;
private int size;
private final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // 负载因子阈值
public HashTable(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.buckets = new Node[capacity];
this.size = 0;
}
// 哈希函数
private int hash(String key) {
int hash = 0;
for (char c : key.toCharArray()) {
hash = (hash * 31 + c) % capacity;
}
return Math.abs(hash);
}
// 插入键值对
public void put(String key, int value) {
if ((float)size / capacity >= LOAD_FACTOR) {
resize(2 * capacity);
}
int index = hash(key);
Node newNode = new Node(key, value);
// 如果桶为空,直接插入
if (buckets[index] == null) {
buckets[index] = newNode;
size++;
return;
}
// 处理哈希冲突,使用链地址法
Node current = buckets[index];
// 检查是否已存在相同的键
while (current != null) {
if (current.key.equals(key)) {
current.value = value; // 更新值
return;
}
if (current.next == null) {
break;
}
current = current.next;
}
// 在链表末尾添加新节点
current.next = newNode;
size++;
}
// 查找键对应的值
public Integer get(String key) {
int index = hash(key);
Node current = buckets[index];
// 遍历链表查找匹配的键
while (current != null) {
if (current.key.equals(key)) {
return current.value;
}
current = current.next;
}
// 未找到
return null;
}
// 删除键值对
public boolean remove(String key) {
int index = hash(key);
Node current = buckets[index];
Node prev = null;
// 查找目标节点
while (current != null) {
if (current.key.equals(key)) {
break;
}
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
// 未找到目标节点
if (current == null) {
return false;
}
// 删除节点
if (prev == null) {
buckets[index] = current.next;
} else {
prev.next = current.next;
}
size--;
return true;
}
// 扩容并重新哈希
private void resize(int newCapacity) {
Node[] oldBuckets = buckets;
// 创建新的哈希表
buckets = new Node[newCapacity];
capacity = newCapacity;
size = 0;
// 重新哈希所有元素
for (Node bucket : oldBuckets) {
Node current = bucket;
while (current != null) {
put(current.key, current.value);
current = current.next;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashTable hashTable = new HashTable(10);
// 插入数据
hashTable.put("apple", 5);
hashTable.put("banana", 10);
hashTable.put("orange", 15);
hashTable.put("grape", 20);
// 查找数据
System.out.println("apple: " + hashTable.get("apple"));
System.out.println("banana: " + hashTable.get("banana"));
System.out.println("orange: " + hashTable.get("orange"));
System.out.println("grape: " + hashTable.get("grape"));
System.out.println("watermelon: " + hashTable.get("watermelon"));
// 删除数据
hashTable.remove("orange");
System.out.println("After removing orange: " + hashTable.get("orange"));
}
}
优缺点分析
优点:
- 平均情况下,查找、插入、删除的时间复杂度均为 O(1)。
- 不要求数据有序,使用灵活。
- 非常适合等值查询和动态数据集。
缺点:
- 存在哈希冲突,最坏情况下性能退化为 O(n)。
- 需要额外空间存储哈希表。
- 不支持高效的范围查询或顺序遍历。
- 性能受负载因子影响,需要动态扩容。
扩展与应用场景
哈希查找是构建高效键值存储的基石,其思想在数据库与中间件的索引实现中至关重要。
- 缓存系统:如 LRU Cache 的核心组件。
- 字典/映射结构:编程语言中
HashMap, dict 的基础。
- 去重操作:快速判断元素是否存在。
- 一致性哈希:用于分布式系统中,减少数据重新分布。
- 布隆过滤器:一种基于哈希的概率型数据结构,用于高效判断“可能存在”或“一定不存在”。
算法对比与总结
| 特性 |
二分查找 (Binary Search) |
哈希查找 (Hash Search) |
| 前提条件 |
数据必须有序 |
数据无需有序 |
| 时间复杂度 |
O(log n) |
平均 O(1),最坏 O(n) |
| 空间复杂度 |
O(1) (迭代) |
O(n),需要额外哈希表空间 |
| 数据结构 |
数组等支持随机访问的结构 |
哈希表 |
| 适合操作 |
静态数据集的查找 |
动态数据集的查找、插入、删除 |
| 额外功能 |
支持范围查询、找上下界 |
主要支持等值查询 |
选择建议:
- 当数据静态有序且需要高频查找时,二分查找是经典选择。
- 当需要快速的等值查询、插入和删除,且不关心数据顺序时,哈希查找通常是更优解。
- 在实际系统如数据库中,两者常结合使用,例如在索引的局部使用二分查找。